참조타입의 자료형 중 배열(Array)에 대해 정리하면서 자바스크립트의 데이터 타입에 대한 정리를 끝마치려고 한다.
Array
하나의 변수 안에 다양한 목록의 데이터를 저장시키고자 할 때 쓰이는 자바스크립트 내장 객체이다.
배열 선언(Declaration)
<script> const alphabet = ["a", "b", "c", "d"] // 리터럴 표기법 const alphabet = new Array["a", "b", "c", "d"] // 내장 객체 Array를 활용한 표기법 </script>
인덱스(index)
배열 안의 요소는 Array[index]를 활용하여 그 값을 얻어낼 수 있다. 인덱스는 1이 아닌 0부터 시작한다는 점을 유의해야 한다.
<script>
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana'];
console.log(fruits); // ['apple', 'banana'] 출력
console.log(fruits[0]); // apple 출력
console.log(fruits[1]); // banana 출력
console.log(fruits.length); // 2 출력
console.log(fruits[fruits.length -1]); // banana 출력
</script>반대로 요소를 가지고 인덱스를 찾아낼 수도 있다.
<script>
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana'];
console.log(fruits.indexOf('apple')); // 0 출력
console.log(fruits.indexOf('banana')); // 1 출력
</script>만약 배열 내에 없는 요소의 인덱스 값을 찾거나, 동일한 요소가 2개인 경우의 인덱스는 아래와 같이 얻어낼 수 있다.
<script>
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'apple'];
console.log(fruits.indexOf('coconut')); // -1 출력
console.log(fruits.indexOf('apple')); // 0 출력
console.log(fruits.lastIndexOf('apple')); // 2 출력
</script>배열 반복문(Looping over an array)
배열 안에 있는 요소들를 하나하나 확인하기 위해서는 반복문(for문)을 사용하여 배열 안에 있는 요소를 처음부터 끝까지 반복하면 된다. 여기서 처음부터 끝이란 인덱스 처음 값인 0에서 배열 인덱스 가장 마지막 값 -1 (length-1)까지 이다.
<script>
const fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
for(let i=0; i<fruits.length; i++) {
console.log(fruits[i]);
} // apple, banana 출력
</script>또한 간단하게 for・・・of로도 요소 확인이 가능하다.
<script>
for(let fruit of fruits) {
console.log(fruit);
}
</script>배열 내장 함수(Array API)
배열 객체에는 요소를 추가, 삭제, 변경하거나 특정 방식으로 추출하는 등 다양하게 배열을 활용할 수 있는 내장 함수가 있다.
:: push, pop, unshift, shift, splice
<script>
const fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
fruits.push("orange");
// 배열 가장 뒤에 데이터 추가
// const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
fruits.pop();
// 배열 가장 뒤 데이터를 삭제하여 삭제된 데이터 반환
// console.log(fruits.pop()); => orange 출력
// const fruits = ["apple", "banana"]
fruits.unshift("lemon", "peach");
// 배열 가장 앞에 데이터 추가
// const fruits = ["lemon", "peach", "apple", "banana"]
fruits.shift();
// 배열 가장 앞 데이터를 삭제하여 삭제된 데이터 반환
// console.log(fruits.shift()); => lemon 출력
// const fruits = ["peach", "apple", "banana"]
fruits.splice(2);
// 인덱스가 2인 데이터부터 데이터 전부 지움
// const fruits = ["peach", "apple"]
fruits.splice(0, 1, "strawbarry", "coconut")
// 인덱스 0부터 1개의 데이터를 삭제하고 그 위치에 "strawbarry", "coconut" 추가
// const fruits = ["strawbarry", "coconut", "apple"]
</script>:: concat
둘 이상의 배열을 연결하는 함수이다.
<script>
const fruits = ["apple", "banana"];
const person = ["Harry", "Tom", "Emma"];
const newArr = fruits.concat(person); // fruits배열에 person배열 연결
console.log(newArr); // ["apple", "banana", "Harry", "Tom", "Emma"] 출력
</script>:: join
배열에서 데이터를 추출하여 하나의 문자열(string)으로 나타낸다.
<script>
const person = ["Harry", "Tom", "Emma"];
console.log(person.join()); // Harry,Tom,Emma 출력
console.log(person.join('*')); // Harry*Tom*Emma 출력
</script>:: split
문자열 데이터로 배열을 만든다.
<script>
const person = 'Harry, Tom, Emma";
console.log(person.split(',')); // ["Harry", "Tom", "Emma"] 출력
console.log(person.split(',' 2));
// size를 2로 지정하여 맨 앞에서 부터 2개의 문자열만 배열로 가져온다.
// ["Harry", "Tom"] 출력
</script>:: reverse
배열 데이터의 순서를 반대로 바꾼다.
<script>
const person = ["Harry", "Tom", "Emma"];
person.reverse();
console.log(person);
// ["Emma", "Tom", "Harry"] 출력
</script>:: slice
기존 배열에서 특정 데이터 값만 추출하여 새로운 배열을 만든다. splice는 기존 배열에서 특정 데이터를 삭제하고 새로운 배열을 만드는 것은 아니라는 점에서 차이가 있다.
<script>
const originArr = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"];
const newArr = originArr.slice(2, 4);
// index 2에서 index 4 전까지 추출하여 배열을 만듦
console.log(originArr); // ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"] 출력
console.log(newArr); // ["3", "4"] 출력
</script>:: find, filter, map, some, every, reduce
<script>
class Book {
constructor(title, reprinted, price) {
this.title = title;
this.reprinted = reprinted;
this.price = price;
}
}
const books = [
new Book('A', true, 45),
new Book('B', false, 80),
new Book('C', true, 90),
new Book('D', false, 66),
new Book('E', true, 88),
];
// 1. find: 특정 조건에 부합하는 첫 번째 요소를 찾아 반환한다.
const findResult = books.find((book) => book.price === 90); // 가격이 90달러인 요소를 찾아 반환
console.log(findResult); // Book {title: "C", reprinted: true, price: 90} 출력
// 2, filter: 조건에 부합하는 요소를 추출하여 새로운 배열을 만든다.
const filterResult = books.filter((book) => book.reprinted); // 재쇄된 책만 추출
console.log(filterResult); // [Book, Book, Book] 출력
// 0: Book {title: "A", reprinted: true, price: 45}
// 1: Book {title: "C", reprinted: true, price: 90}
// 2: Book {title: "E", reprinted: true, price: 88}
// 3. map: 배열 안의 요소 중 특정 필드값만 추출하여 새로운 배열을 만든다.
const mapResult = books.map((book) => book.price) // 책 가격만 추출하여 재배열
console.log(mapResult); // [45, 80, 90, 66, 88] 추출
// 4. some: 배열의 요소 중 콜백함수의 조건에 부합하는 요소가 있는지 Boolean을 반환한다.
const someResult = books.some((book) => book.price < 40); // price가 40 미만인 경우
console.log(someResult); // false 출력
// 5. every: 배열의 모든 요소 중 콜백함수의 조건에 부합하는 요소가 있는지 Boolean을 반환한다.
const everyResult = books.every((book) => book.price > 40); // 모든 price가 40 이상
console.log(everyResult); // true 출력
const notEveryResult = !books.every((book) => book.price > 40); // !로 결과값이 반대가 되게 한다.
console.log(everyResult); // false 출력
// 6. reduce: 배열의 요소 하나하나를 반복하여 누적한다.
const reduceResult = books.reduce((pre, crr) => pre + crr.price, 0);
// pre= 0부터 시작하여 책의 price를 누적
console.log(reduceResult); // 369 누적
</script> ** reduce의 누적 원리는 아래와 같이 생각할 수 있을 것 같다.
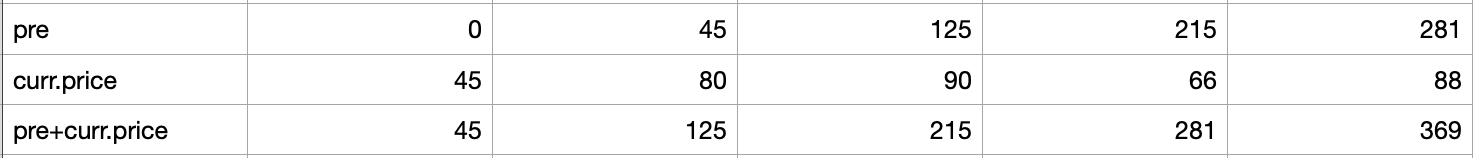
:: API 결합
내장 함수를 중복 사용하여 배열을 다양하게 변경할 수 있다.
<script>
class Book {
constructor(title, reprinted, price) {
this.title = title;
this.reprinted = reprinted;
this.price = price;
}
}
const books = [
new Book('A', true, 45),
new Book('B', false, 80),
new Book('C', true, 90),
new Book('D', false, 66),
new Book('E', true, 88),
];
// 1. 책 price만 문자열로 표현 => result 45,80,90,66,88
const combine1 = books
.map((book) => book.price) // 책 price만 추출하여 배열 만듦
.join(','); // 배열을 문자열로 변경
// 2. 책 price를 크기 순서로 재배열 => result [45, 66, 80, 88, 90]
const combine2 = books
.map((book) => book.price) // 책 price만 추출하여 배열 만듦
.sort((a, b) => a - b) // a-b가 마이너스 값인 경우에 요소로 출력 됨
</script>