HashSet으로 정렬
Set 클래스로 중복을 체크 후 List로 변환하여 정렬한다
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<>();
while (hs.size() < 6) {
Integer ir = (int) (Math.random() * 45) + 1;
//중복값을 허용하지 않음
hs.add(ir);
}
//HashSet -> Set -> Collection
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(hs);
//정렬
Collections.sort(list);
//확장 for문을 이용한 추쳙
for(int num : list) {
System.out.println(num+"\t");
}
}출력 결과
7 8 12 26 27 36 HashMap
키(key)와 값(value)으로 구성된 엔트리 객체를 저장하는 자료구조
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashMapMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] msg = {"Berlin","Paris","Seoul","New York","London"};
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
//반복문을 이용해서 key, value 저장
for(int i=0; i<msg.length; i++) {
map.put(i, msg[i]);
}
//HashMap에 저장된 key와 value 목록
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
/*
Set<Integer> s = map.keySet();
Iterator<Integer> keys =s.iterator();
*/
Iterator<Integer> keys = map.keySet().iterator();
while(keys.hasNext()) {
Integer key =keys.next();
System.out.println(key+", "+map.get(key));
}
}
}
출력 결과
{0=Berlin, 1=Paris, 2=Seoul, 3=New York, 4=London}
----------------------------------
0, Berlin
1, Paris
2, Seoul
3, New York
4, LondonHashtable
hashmap처럼 키,값으로 구성된 객체를 저장하고 null값을 넣고 실행시 예외가 발생된다
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Enumeration;
public class HashtableMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<String,String> h = new Hashtable<String,String>();
h.put("name", "홍길동");
h.put("age", "27");
h.put("tel", "010-1234-5678");
h.put("hobby", "음악감상");
h.put("job", "경찰");
//key가 중복되면 마지막에 입력한 값으로 value가 대체됨
h.put("name", "홍길순");
//value에 null 불인정, 실행시 예외 발생
//h.put("address", null);
//key에 null 불인정, 실행시 예외 발생
//h.put(null, "서울고등학교");
//Hashtable에 저장된 key,value 목록
System.out.println(h);
String name = h.get("name");
System.out.println("이름은 " + name);
System.out.println("----------------");
//Hashtable에 저장된 key,value 출력
Enumeration<String> en = h.keys();
while(en.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = en.nextElement();//key 반환
//key value
System.out.println(key + " : " + h.get(key));
}
}
}출력 결과
{age=27, tel=010-1234-5678, name=홍길순, hobby=음악감상, job=경찰}
이름은 홍길순
----------------
age : 27
tel : 010-1234-5678
name : 홍길순
hobby : 음악감상
job : 경찰File 클래스
- 시스템에 있는 파일이나 디렉토리를 추상화한 클래스
- 파일의 크기, 생성, 삭제, 변경 및 마지막 수정날짜 등 다양한 정보를 알 수 있다
file 경로 출력
import java.io.File;
public class FileMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\";
File f = new File(path);
//exists() : 파일 또는 디렉토리의 존재 여부 체크
//isDirectory() : 디렉토리이면 true
if(!f.exists() || !f.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("유효하지 않는 디렉토리입니다.");
System.exit(0);//프로그램 종료
}
//listFiles() : 지정한 경로의 하위 경로와 파일 정보를 File[]로 반환
File[] files = f.listFiles();
for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++) {
File f2 = files[i];
if(f2.isDirectory()) {//디렉토리
System.out.println("[" + f2.getName() + "]");
}else {//파일
System.out.print(f2.getName());
System.out.printf("(%,dbytes)%n",f2.length());
}
}
}
}출력 결과
[!!!#1(0902800)]
[$Recycle.Bin]
[$SysReset]
[$WinREAgent]
agentlog.txt(87bytes)
[Documents and Settings]
DumpStack.log.tmp(8,192bytes)
hiberfil.sys(3,400,118,272bytes)
[Intel]
[javaWork]
[OneDriveTemp]
pagefile.sys(13,926,182,912bytes)
[PerfLogs]
[Program Files]
[Program Files (x86)]
[ProgramData]
[RansomDefenderBackup]
[ransomzerootfb]
[recovery]
[Riot Games]
swapfile.sys(285,212,672bytes)
[System Volume Information]
[temp]
[Users]
[Windows]file을 이용하여 텍스트 생성
file 클래스를 이용하여 txt파일을 생성하기
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//절대경로 지정
//String path = "C:\\javaWork\\sample.txt";
//상대경로 지정
String path = "sample.txt";
//경로를 지정해서 File 객체 생성
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("===파일 생성===");
try {
/*
* 제공된 경로를 기반으로 파일 생성. 파일이 생성되면 true 반환,
* 생성되지 않으면 false 반환.
* 경로가 잘못되면 IOException 발생
*/
System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("===파일정보===");
System.out.println("절대경로:" + f1.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("상대경로:" + f1.getPath());
System.out.println("디렉토리명:" + f1.getParent());
System.out.println("파일명:" + f1.getName());
}
}프로그램 실행 결과
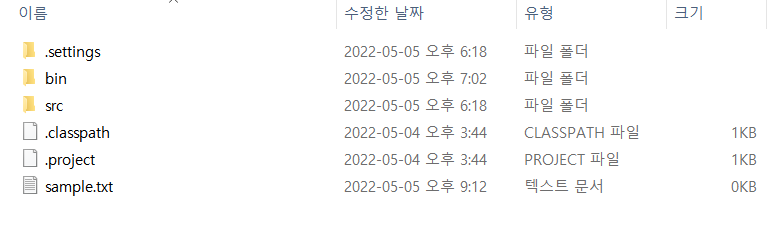
지정한 경로애 sample.txt가 생성되었다
파일명 바꾸기
import java.io.File;
public class FileMain03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상대경로 지정
//원래파일명
String path = "sample.txt";
//새파일명
String new_path = "example.txt";
//원래파일명을 지정한 File 객체 생성
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("===파일명 변경===");
//새파일명을 지정한 File 객체 생성
File f2 = new File(new_path);
//renameTo() : 파일명을 변경할 수 있으면 파일명을
// 변경하고 true 반환, 변경을 못 하면
// false
System.out.println(f1.renameTo(f2));
}
}프로그램 실행 결과
sample.txt -> example.txt 로 변경된 것을 확인할 수 있다
파일 삭제
package kr.s01.file;
import java.io.File;
public class FileMain04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상대경로 지정
String path = "example.txt";
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("===파일삭제===");
//delete() : 삭제할 수 있으면 삭제하고 true 반환
// 삭제할 수 없으면 false 반환
if(f1.delete()) {
System.out.println(f1.getName() + " 파일 삭제");
}else {
System.out.println("파일을 삭제하지 못 했습니다.");
}
}
}출력 결과
===파일삭제===
example.txt 파일 삭제
파일 삭제 라는 문구가 출력 되며 파일도 삭제 된다
만약 example.txt파일이 삭제된 후 한번 더 코드를 실행하면
===파일삭제===
파일을 삭제하지 못 했습니다.이 문구가 출력이 된다
새 디렉토리 생성
import java.io.File;
public class FileMain05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//절대경로 지정
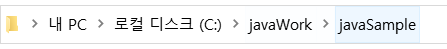
String path = "C:\\javaWork\\javaSample";
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("===디렉토리 생성===");
System.out.println(f1.mkdir());
}
}출력 결과
새로운 디렉토리가 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다
디렉토리 삭제
import java.io.File;
public class FileMain06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//절대경로 지정
String path = "C:\\javaWork\\javaSample";
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("===디렉토리 삭제===");
if(f1.delete()) {//삭제 후에 true 반환
System.out.println(f1.getName() + " 디렉토리 삭제");
}else {//삭제 불가 false 반환
System.out.println("디렉토리를 삭제할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}출력 결과
===디렉토리 삭제===
javaSample 디렉토리 삭제해당 출력과 함께 디렉토리도 삭제 됨을 확인할 수 있다