📙연습 문제
- 1에서 10까지의 합
package chapter03;
//1에서 10까지의 합
public class ForSample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
sum = sum + i;
System.out.print(i); // 여기까지 하면 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10이 출력
if (i <= 9) {
System.out.print("+");
} else
System.out.print("="); // if문 안쓰면 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10+55가 출력되므로 if문 사용
}
System.out.print(sum); // 1에서 10까지의 합인 55가 출력
}
}- 문자에서 특정 문자의 갯수를 출력
package chapter03;
// 문장에서 특정 문자의 갯수를 출력
public class ContinueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="no new is good news";
int n =0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
// 문장 길이 만큼으로 제한 둘거임
//.charAt(index) : 인덱스가 들어가는 데 해당하는 문자열
// 인덱스는 0부터 시작함. 여기서 n은 0임.
//s.charAt(i)와 같이 하면 s의 문장 처음부터 끝까지를 뜻함.
if (s.charAt(i)=='n') {
n++;
}
}
System.out.println("문장에서 발견된 n의 갯수"+n);
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
package chapter03;
// 문장에서 특정 문자의 갯수를 출력
public class ContinueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "no new is good news";
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 문장 길이 만큼으로 제한 둘거임
// .charAt(index) : 인덱스가 들어가는 데 해당하는 문자열
// 인덱스는 0부터 시작함. 여기서 n은 0임.
// s.charAt(i)와 같이 하면 s의 문장 처음부터 끝까지를 뜻함.
if (s.charAt(i) != 'n') {
continue;
}
n++;
//if (s.charAt(i) == 'n') {
// n++;
//}
}
System.out.println("문장에서 발견된 n의 갯수" + n);
}
}
보통 아래의 방식으로 많이 함. 두 방식 동일함. - 1에서 10까지의 정수 출력 중 3,6,9 는 박수 소리가 나게 하기
package chapter03;
//1부터 10까지의 정수 출력 중 3,6,9에는 박수소리 나게 하기.
public class ContinueSamYukGu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println("짝");
} else {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------
(처음에 했을때 아래와 같이 했는데 결과는
123짝456짝789짝10
순으로 나옴. 그래서 위처럼 바꿈
package chapter03;
public class ContinueSamYukGu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
if (i % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println("짝");
}
}
}
}- 정수 5개 입력, 그것들의 합
package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ContinueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("정수 5개를 입력하시오.");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//강사님 방법
int sum =0;
for (int i = 0; i <5; i++) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
if (n<=0) {
continue;
}else {
sum+=n;
}
}
System.out.println("양수의 합은"+sum);
scanner.close();
```
5. exit를 입력하면 강제 종료되는 프로그램
```java
package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BreakExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("exit을 입력하면 종료합니다.");
while(true) { //참이 될때까지 무한 반복
System.out.println(">>");
String n = scanner.next();
if (n.equals("exit")) {
System.out.println("종료합니다.");
break;
}else {// 굳이 이거 할 필요 없음. 앞에 while은 true로 해놓았으니깐!!!!!!!
continue;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}
--------------
package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BreakExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("exit을 입력하면 종료합니다.");
while(true) { //참이 될때까지 무한 반복
System.out.println(">>");
String n = scanner.next();
if (n.equals("exit")) {
System.out.println("종료합니다.");
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}- DoWhile을 이용해서 0 부터 99까지의 짝수들의 합 계산
package chapter03;
//DoWhile을 이용해서 0부터 99 까지의 짝수들의 합 계산하기
public class DoWhileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=0;
int sum =0;
do {
sum = sum +i;
i+=2;
}while(i<=99);
System.out.println(sum);
/* 강사님 방법
do {
if (i>99){
break;
}
sum +=1;
i +=2;
} while (true);
System.out.println(sum);
*/
}
}- 부정행위 여부, 출석률, 총점 입력하면 학점 부여하는 프로그램
package chapter03;
//부정행위 여부. 출석률, 총점을 입력하고 학점 부여
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CalculateGrade {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String grade;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("부정행위 여부(true 혹은 false)");
boolean cheating = scanner.nextBoolean();
System.out.println("출석률(0~100사이의 정수값)");
int attendrate = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("총점(0~100사이의 정수값)");
int totalscore = scanner.nextInt();
if (cheating ==true) {
grade = "F";
}else {
if (attendrate<80) {
grade = "F";
}else {
if (totalscore>=90) {
grade = "A";
}else if(totalscore>=80) {
grade = "B";
}else if(totalscore>=70) {
grade = "C";
}else if(totalscore>=60) {
grade = "D";
}else {
grade = "F";
}
}
System.out.println("부정행위 여부 ="+cheating);
System.out.println("출석률 = "+attendrate);
System.out.println("총점 = "+totalscore);
System.out.println("학점 = "+grade);
}
scanner.close();
}
}
// String grade말고 char 사용해보기.(마친가지로 그러면 grade = "F";을 grade = 'F'; 로 수정
--------------------------------
package chapter03;
//강사님 방법
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CalculateGrade {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String grade;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("부정행위 여부(true 혹은 false)");
boolean cheating = scanner.nextBoolean();
System.out.println("출석률(0~100사이의 정수값)");
int attendrate = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("총점(0~100사이의 정수값)");
int totalscore = scanner.nextInt();
if (cheating ==true) {
grade = "F";
}else if (attendrate<80) {
grade = "F";
}else {
if (totalscore>=90) {
grade = "A";
}else if(totalscore>=80) {
grade = "B";
}else if(totalscore>=70) {
grade = "C";
}else if(totalscore>=60) {
grade = "D";
}else {
grade = "F";
}
}
System.out.println("부정행위 여부 ="+cheating);
System.out.println("출석률 = "+attendrate);
System.out.println("총점 = "+totalscore);
System.out.println("학점 = "+grade);
scanner.close();
}
}
- 양의 정수 입력시 3,5,8의 배수인지 확인
package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Mutiple {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean mutiple =false;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("양의 정수를 입력하세요: ");
int number = scanner.nextInt();
//처음에 작성했던 식
/*if (number%120 == 0) {
System.out.println("3의 배수이다.");
System.out.println("5의 배수이다.");
System.out.println("8의 배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
} else if (number % 15 == 0) {
System.out.println("3의 배수이다.");
System.out.println("5의 배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
} else if (number % 24 == 0) {
System.out.println("3의 배수이다.");
System.out.println("8의 배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
} else if (number % 40 == 0) {
System.out.println("8의 배수이다.");
System.out.println("5의 배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
} else if (number % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println("3의 배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
} else if (number % 5 == 0) {
System.out.println("5의 배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
} else if (number % 8 == 0) {
System.out.println("8의 배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
} else {
System.out.println("어느 배수도 아니다.");
mutiple = false;
}*/
if (number %3 ==0) {
mutiple = true;
System.out.println("3의배수이다.");
if (number %5 ==0) {
System.out.println("5의배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
if(number %8 ==0) {
System.out.println("5의배수이다.");
mutiple = true;
}
}
}else {
System.out.println("어느 배수도 아니다.");
mutiple = false;
}
scanner.close();
}
}
//multiple이 false일때 어느 배수도 아니다가 출력되어야 하므로 강사님 답이 옳다.(난. 쌩 무시했구.)- 주식
package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Tesla {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("매수 수량을 입력하시오>>");
int Tesla =520;
int money, num;
num = scanner.nextInt();
money = Tesla*num;
int res = money /100;
money = money %100;
if (res>0) {
System.out.println("100달러짜리"+res+"매");
}
res = money /10;
if (res>0) {
System.out.println("10달러짜리"+res+"매");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
- 지원금 지급
package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class EmergencyMoney {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("가구수를 입력하시오>>");
int num = scanner.nextInt();
int dollar = 1200;
int won;
if (num == 1) {
won = 400000;
int hun = won/dollar/100;
int ten = ((won/dollar)%100)/10;
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+hun+"매");
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+ten+"매");
}
if (num == 2) {
won = 600000;
int hun = won/dollar/100;
int ten = ((won/dollar)%100)/10;
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+hun+"매");
}
if (num == 3) {
won = 800000;
int hun = won/dollar/100;
int ten = ((won/dollar)%100)/10;
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+hun+"매");
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+ten+"매");
}
if (num>=4) {
won = 1000000;
int hun = won/dollar/100;
int ten = ((won/dollar)%100)/10;
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+hun+"매");
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+ten+"매");
}
if(num ==2) {
won = 600000;
int hun = won/dollar/100;
System.out.println("100달러짜리 "+hun+"매");
}else if (num!=2 ) {
}
scanner.close();
}
}- 입력한 값 만큼 별이 역순으로 찍힘
package chapter03;
// 입력한 값만큼 별이 역순으로 찍힘.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintAsterisk {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수를 입력하시오>>");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = n; i >0; i--) { // n만큼 반복
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {// j가 i(n)만큼 반복
System.out.print('*'); // *출력
}
System.out.println();
}
scanner.close();
}
}📙배열
: 여러 데이터를 하나로 묶은것
일련의 공간을 여러칸으로 나눈것.
int[] scores = {88, 98, 68, 72, 47};- 여기서
int[] scores→ 정수형 배열을 가리키는 변수 {88, 98, 68, 72, 47}→ 정수형 배열
📖배열의 특징
- 배열의 값은 모두 같은 타입
- 배열에 담긴 데이터는 타입 유형이 같음
- 정수형 배열에는 정숫값, 실수형 배열에는 실숫값만 담겨야함
- 배열은 인덱스로 구분
- 인덱스 : 배열 공간을 번호로 구분한것으로
0부터 시작
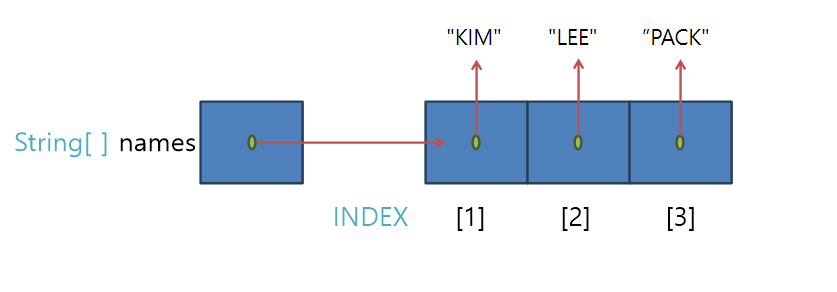
String[] names = {"KIM","LEE","PACK"};
→ "KIM" : 0번 인덱스,
"LEE" : 1번 인덱스,
"PACK" : 2번 인덱스,
- 배열의 길이는 변하지 않음
- 배열을 4칸 길이로 만들었으면 최대 4개의 데이터까지만 저장가능(인덱스는 3까지)
boolean[ ] flags ={true,false,false,true};
→ 4개의 논릿값을 담는 배열 - 배열의 길이는 length 키워드를 통해 가져올 수 있음
System.out.println(flags.length); //4
→ flags.length : flags 배열의 길이 출력
📖배열 만들기
1) 초기화를 통한 생성
:중괄호 안에 초깃값을 명시하여 만드는 방법
int[] scores = {88, 98, 68, 72, 47};2) 길이 지정을 통한 생성
: new 키워드와 배열의 타입, 길이 정보를 명시
double [ ] grades = new double[4];double [ ] grades → 실수형 배열을 가리키는 변수(레퍼런스변수 : grades
new double[4] → 길이가 4인 실수형 배열을 생성
[ 초기값 ]
정수형 배열(0)
실수형 배열(0.0)
논리형 배열(false)
문자열 배열(null)
📖레퍼런스 변수와 배열
int intArray[ ];: 참조변수 선언만 함int intArray = new int [5];: 참조변수 선언, 인덱스안에 값 부여
📖배열 초기화 및 생성
int intArray[ ] = {4, 3, 2, 1 ,0};
double doubleArray[ ] = {0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04};
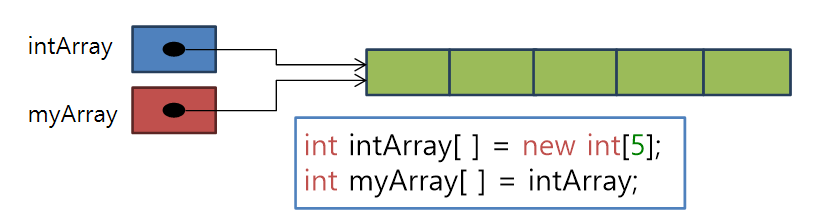
📖레퍼런스 배열공유와 치환
-
배열 공유
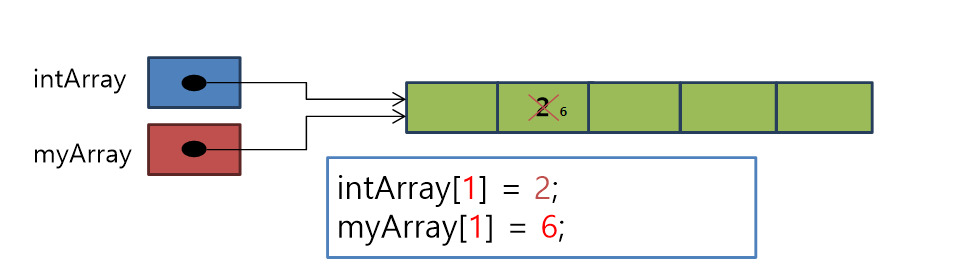
-
치환
📖배열의 크기
int intArray[];
intArray = new int[5];
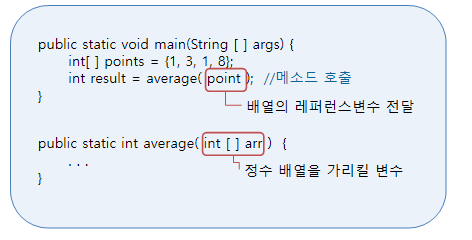
int size = intArray.lenght;📖메소드로 배열 전달하기
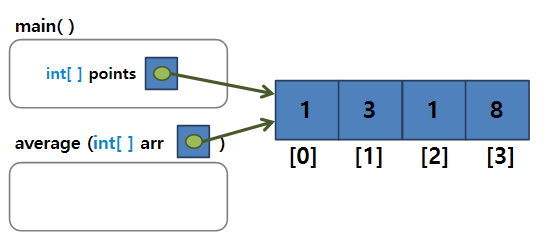
📖인덱스 범위
: 배열 사용시 인덱스 범위를 벗어나면 에러 발생(프로그램 비정상 종료)
ex) 인덱스가 음수인경우, 인덱스가 배열의 길이보다 크거나 같은 경우
📖toCharArray
: 문자열은 toCharArray을 통해 문자의 배열로 바뀔 수 있음
String str = "ABCD";
char[] charArr = str.toCharArray();
// char[] charArr = {'A','B','C','D'};와 동일→ 여기서 toCharArray는 메소드 역할
Str을 toCharArray라는 메소드를 통해서 charArr라는 배열로 치환
📙2차원 배열
: 기본 배열(일차원 배열)을 묶어 새로운 배열을 이루는 형태
int [] row1 = {1, 2, 3, 4 };
int [] row2 = {5, 6, 7, 8 };
int [][] matrix 1 = {row1, row2 };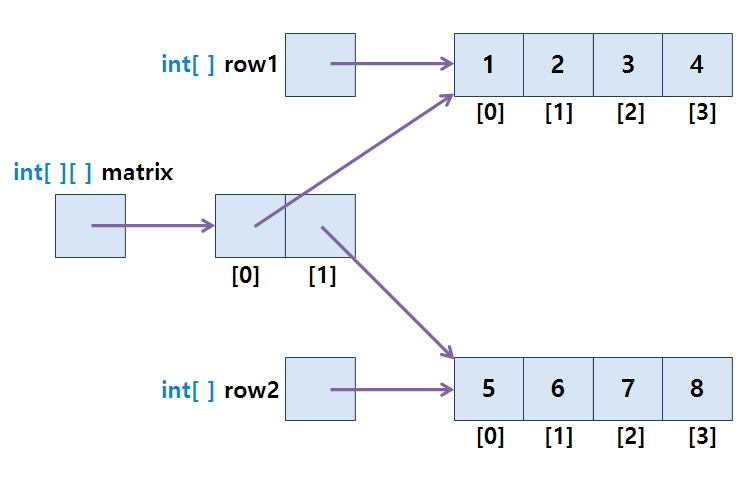
int i [][] = new int[2][5] // 2행 5열
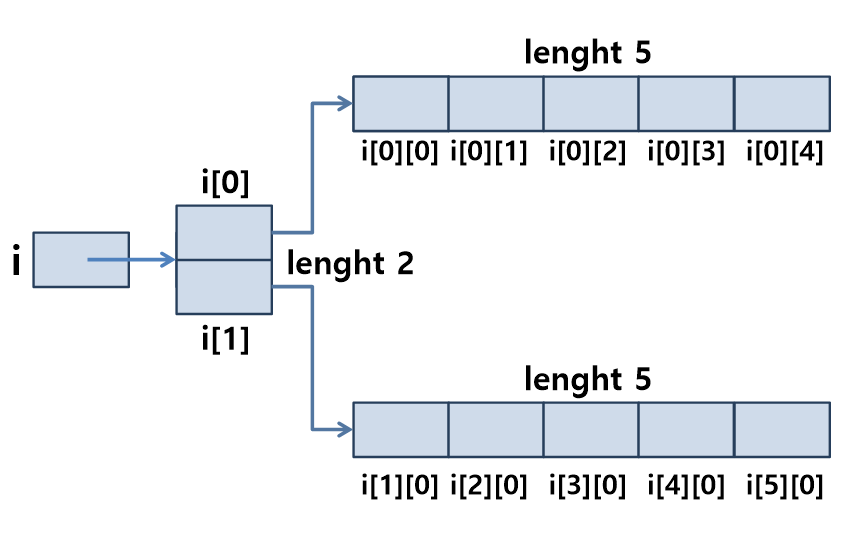
int i[][] = new int [2][5];
int size1 = i.length; //2
int size2 = i[0].length; //5
int size3 = i[1].length; //5📙3차원 배열
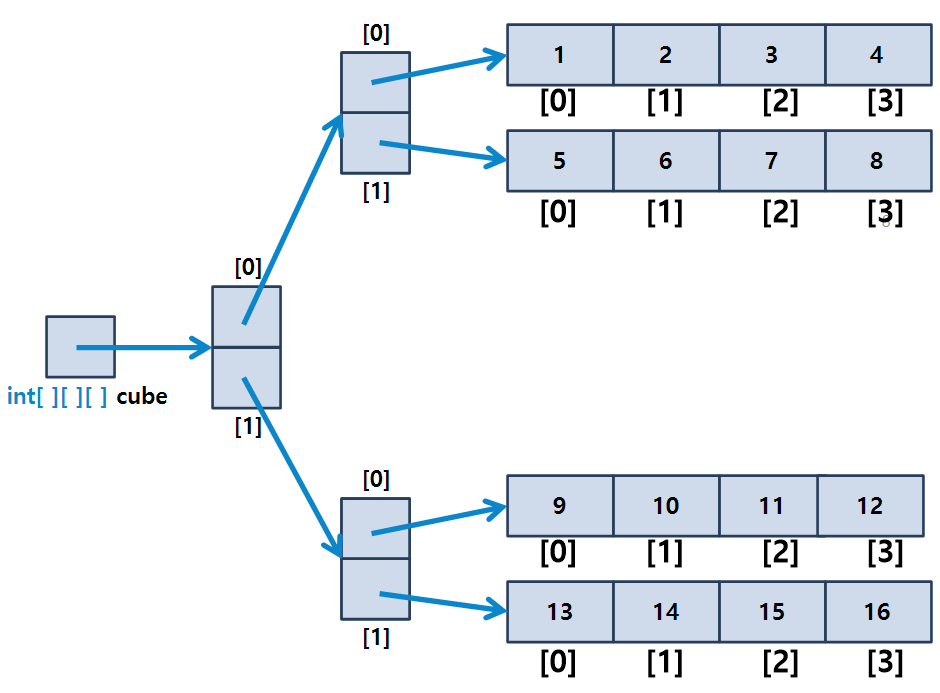
int i[][][] cube = {
{
{1, 2, 3, 4} ,
{5, 6, 7, 8}
} ,
{
{9, 10, 11, 12} ,
{13, 14, 15, 16}
}
}; 📙정방형 / 비정방형 배열
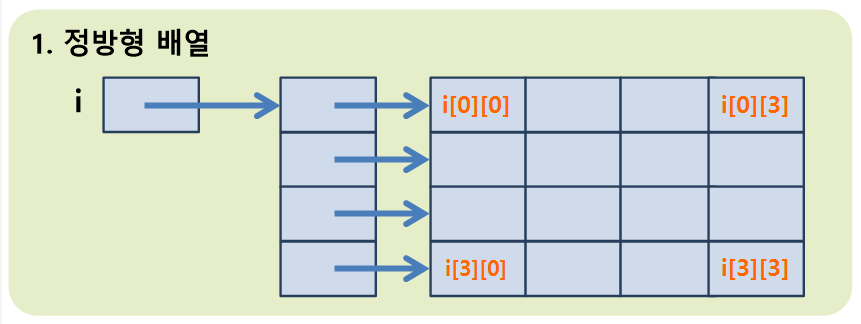
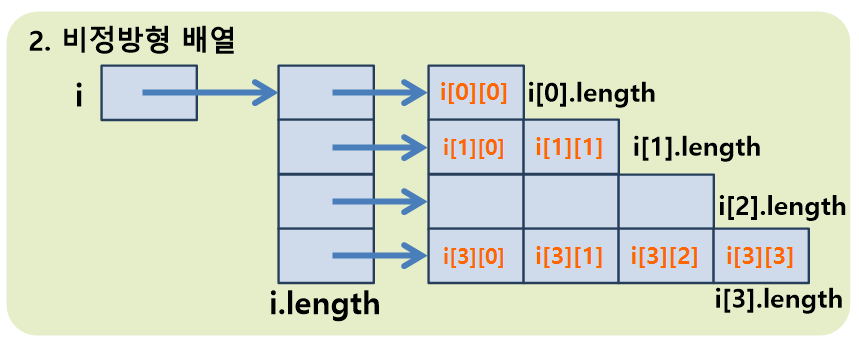
📙배열 관련 문제
package chapter03;
public class Ex3_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names= {"Sam","Kate","John","Jenny"};
System.out.println(names[0]);
System.out.println(names[1]);
System.out.println(names[2]);
System.out.println(names[3]);
}
}public class Ex3_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[]sales= new int[5];
sales[0]=52;
sales[1]=50;
sales[2]=55;
sales[3]=42;
sales[4]=38;
int sum = sales[0]+sales[1]+sales[2]+sales[3]+sales[4];
System.out.println("총판매량:"+sum);
}
}package chapter03;
// 양수 5개를 받아 최댓값이 출력되게 하기
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayAccess {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("양수 5개를 입력하세요");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int number[] = new int[5]; // 양수 5개를 받도록함
int max =0;//max의 초기값 설정
for (int i = 0; i < number.length; i++) {//인덱스만큼 반복
number[i] = scanner.nextInt();// number라는 배열안에 값을 저장
if (number[i]>max) {
max = number[i];// 초기값 max =0보다 입력된 i값이 크면 max가 됨
//이게 number의 인덱스 수만큼 반복됨. (새로운 값이 클 경우 max의 값이 바뀜)
}
}
System.out.println("가장 큰 수는 " + max+ "입니다.");
scanner.close();
}
}//배열 크기만큼 정수를 입력받고 평균을 구하는 프로그램
package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayLength {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("5개의 정수를 입력하세요>>");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int inarray[] = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < inarray.length; i++) {
inarray[i] =scanner.nextInt();
}
int sum =inarray[0]+inarray[1]+inarray[2]+inarray[3]+inarray[4];
double average = (double) sum/5;
System.out.println("평균은"+average);
scanner.close();
}
}
또는package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayLength {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intarray[] = new int[5];
int sum=0;
//System.out.print("5개의 정수를 입력하세요>>");
System.out.print(intarray.length+"개의 정수를 입력하세요>>");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < intarray.length; i++) {
intarray[i] =scanner.nextInt(); // 배열안에 숫자 저장
}
//int sum =intarray[0]+intarray[1]+intarray[2]+intarray[3]+intarray[4];
for (int i = 0; i < intarray.length; i++) {
sum+=intarray[i];
}
double average = (double) sum/5;
System.out.println("평균은"+average);
scanner.close();
}
}package chapter03;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayLength {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intarray[] = new int[5];
int sum=0;
System.out.print(intarray.length+"개의 정수를 입력하세요>>");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < intarray.length; i++) {
intarray[i] =scanner.nextInt(); // 배열안에 숫자 저장
}
for (int i = 0; i < intarray.length; i++) {
sum+=intarray[i];
}
double average = (double) sum/5;
System.out.println("평균은"+average);
scanner.close();
}
}package chapter03;
public class Ex3_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] evens = {0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18};
int[] primes = {2,3,4,5,7,11,13,17,19};
int evenSum = sum(evens);
System.out.println("짝수 배열의 합:"+evenSum);
}
public static int sum(int[]arr) {
int sum =0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum; //반환값 : 메소드의 최종 결과, 반환 될 값
}
}package chapter03;
public class Ex3_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="Progranming is fun! Right?";
char[] charArr = str.toCharArray(); // 문자열을 배열원소값으로 넣음
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < charArr.length; i++) {
if (charArr[i] == 'R'||charArr[i] == 'r') {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println("=> R(r)의 갯수 : "+count);
}
}package chapter03;
// 2차원 배열
// 학년별 1,2학기 성적 저장
// 4년간 전체평점 평균
public class Ex3_10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double score[][] = { { 3.3, 3.4 }, // 4행 2열
{ 3.5, 3.6 },
{ 3.7, 4.0 },
{ 4.1, 4.2 } };
double sum = 0;
for (int year = 0; year < score.length; year++) {
for (int term = 0; term < score[year].length; term++) {
sum += score[year][term];
}
}
int n = score.length;
int m = score[0].length;
System.out.println("4년 전체 평점 평균은"+sum/(n*m));
}
}
