
1. Class
1) Class란?
- 객체를 찍어내는 공장! Constructor function의 대체재!
TIP! 클래스를 이용할 수 없는 웹브라우저에서는? babeljs.io에서 컴파일하여 이용할 수 있다.
2) Class의 생성
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name = name,
this.first = first,
this.second = second
}
sum(){
return (this.first + this.second);
}
}
const kim = new Person('kim', 10, 20);
console.log(kim) //Person { name: 'kim', first: 10, second: 20 }
console.log(kim.sum()) //30- constructor 는 클래스가 호출되어 객체가 생성될 때, 먼저 호출되는 함수
2. 상속
1) 상속의 기초
- 가져온 라이브러리에서 업데이트를 하면 안될 때
- 클래스의 원형은 최대한 유지해야할 경우
클래스를 수정하는 것은 매우 부담스러운 일이 될 수 있다.
2) 상속의 생성
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
sum(){
return this.first+this.second;
}
}
class PersonPlus extends Person{
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second)/2;
}
}
var kim = new PersonPlus('kim', 10, 20);
console.log(kim);
console.log(kim.sum());
console.log(kim.avg());- 상속을 위한
extends를 활용해서 중복되는 부분을 제거할 수 있다. - 부모 클래스만 바꾸어도 (상속을 받은)자식 클래스까지 동시다발적으로 바꿀 수 있어 유지보수 측면에서 효율적이다.
3) 상속의 문제점
- 예를 들어 부모클래스를 수정하지 않고 인자를 추가해야할 때, 다시 부모클래스의 코드를 중복해서 사용해야하는 문제점이 발생한다.
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
sum(){
return this.first+this.second;
}
}
class PersonPlus extends Person{
constructor(name, first, second, third){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
this.third = third;
}
sum(){
return this.first+this.second+this.third;
}
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.third)/3;
}
} //이 코드는 실행되지 않는다...4) 상속 문제점의 해결: Super
super가 있으면 부모 클래스의 것을 그대로 상속 받을 수 있다.
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
sum(){
return this.first+this.second;
}
}
class PersonPlus extends Person{
constructor(name, first, second, third){
super(name, first, second) //괄호가 붙으면 부모클래스의 생성자가 호출된다
this.third = third;
}
sum(){
return super.sum()+this.third; //super.이 오면 부모클래스 자체를 호출함
}
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.third)/3;
}
}
var kim = new PersonPlus('kim', 10, 20, 30);
console.log(kim);
console.log(kim.sum());
console.log(kim.avg());3. JavaScript와 상속
1) 객체 상속
- 객체를 만들어내는 공장 class
- class를 통해 만들어진 객체(object)
주류객체지향 언어(Java 등)에서는 아래와 같이 super class를 상속받은 sub class에서 object를 생성한다.
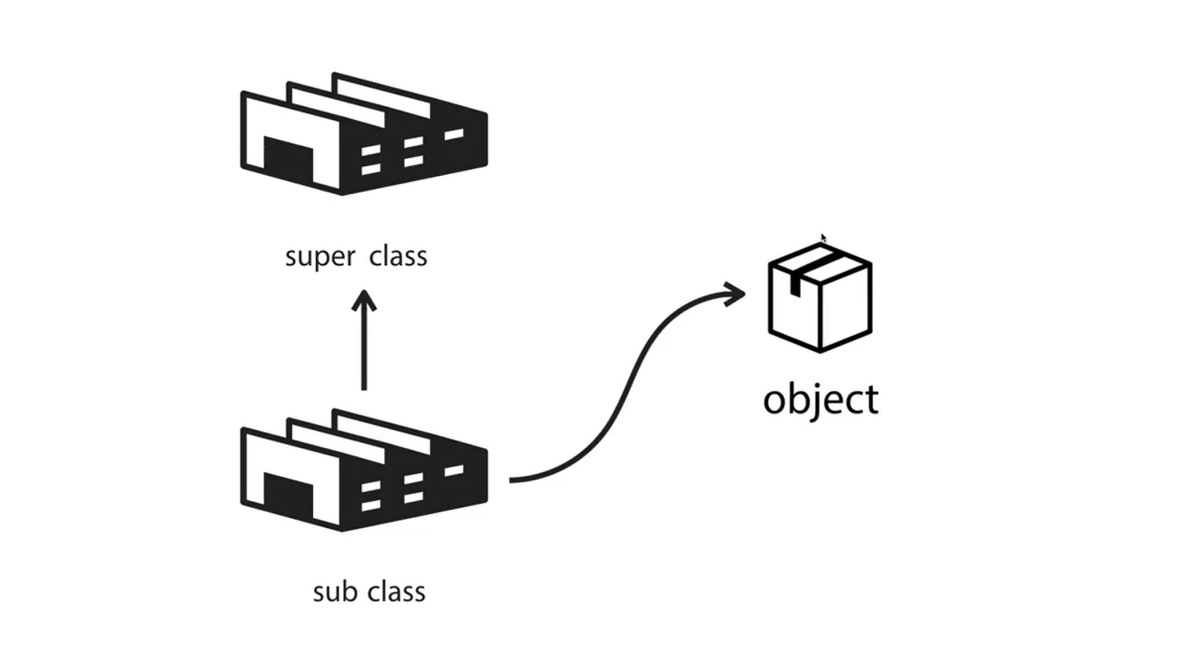
그러나 JavaScript에서는 super object가 sub object 를 상속하는 등 특정 객체가 다른 객체의 상속을 받을 수 있다! 그리고, 우리는 얼마든지 이 상속 관계를 바꿀 수 있다! 상속 관계를 바꿀때는 prototype link만 바꿔주면 된다.
※ 이것이 바로 자바스크립트가 prototype base langauge 라고도 불리는 이유다!
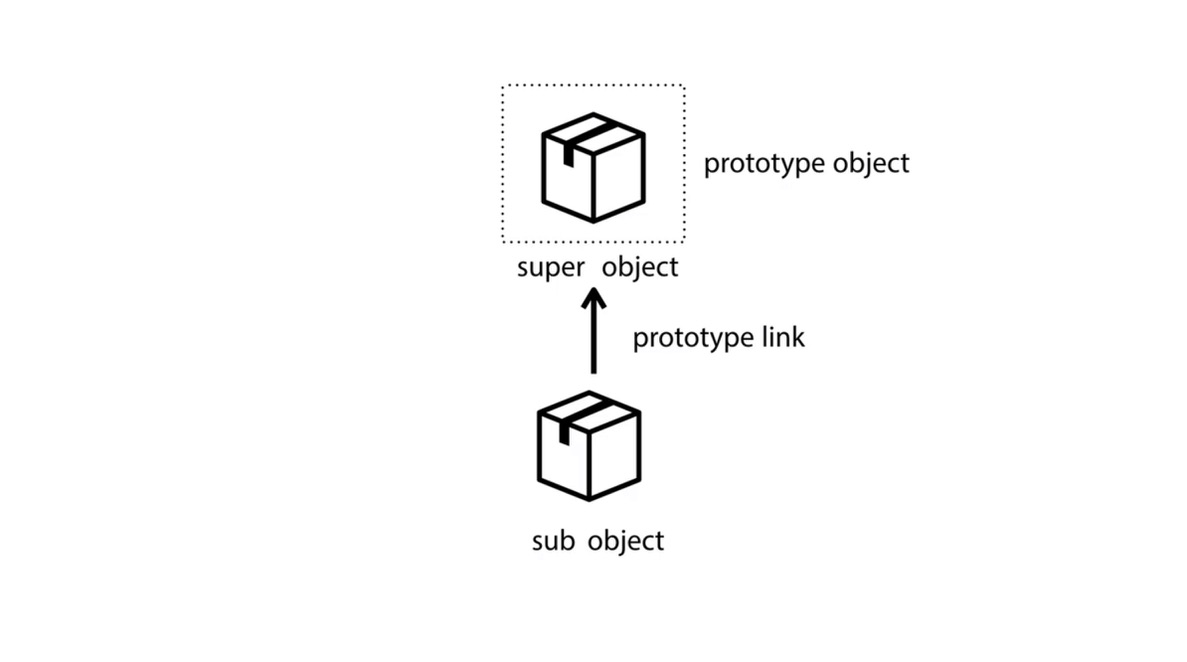
2) .__proto__
.__proto__를 통해서 객체사이에 상속관계를 만들어 낼 수 있다.- 해당 객체가 그 속성을 찾고 없으면, (
.__proto__로 연결된) 그 객체의 부모 객체에서 속성을 찾는다.
const superObj = {superVal: 'super'}
const subObj = {subVal: 'sub'}
subObj.__proto__ = superObj; //subObj의 원형(부모객체)이 무엇인가?라는 속성을 주는 것.
console.log(subObj.subVal); //sub
console.log(subObj.superVal); //super그러나, 자식객체에서 값을 바꾸는 것은 부모객체의 값을 바꾸지 않는다.
subObj.superVal = 'sub';
console.log(superObj.superVal); //super3) Object.create()
__proto__의 대체재(표준화 된 방법)const 새로운 자식 객체 = object.create(부모객체);
const superObj = {superVal: 'super'}
const subObj = Object.create(superObj);
subObj.subVal = 'sub'
console.log(subObj.subVal); //sub
console.log(subObj.superVal); //super자바스크립트 디버거 기능 참고
JavaScript 객체 지향 프로그래밍 - 13.3. Object.create() - YouTube
4) 객체상속의 활용
(1) __proto___의 활용
const kim = {
name : 'kim',
first: 10,
second: 20,
sum:function(){
return this.first + this.second
}
}
const lee = {
name: 'lee',
first: 10,
second: 10,
avg:function(){
return (this.first + this.second)/2
}
}
lee.__proto__ = kim;
console.log(kim.sum()); //30
console.log(lee.sum()); //20
console.log(lee.avg()); //10(2) Object.create()의 활용
const kim = {
name : 'kim',
first: 10,
second: 20,
sum:function(){
return this.first + this.second
}
}
const lee = Object.create(kim);
lee.name = 'lee';
lee.first = 10;
lee.second = 10;
lee.avg = function (){
return (this.first + this.second)/2
}
console.log(kim.sum()); //30
console.log(lee.sum()); //20
console.log(lee.avg()); //10