Trie 자료구조는 효율적인 문자열 검색 자료구조이다.
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/5052 이 문제는 Trie 자료구조를 사용해서 풀어야 한다.
Trie 자료구조
Trie는 tree 구조의 일종으로 문자열 검색에 효율적인 자료구조이다.
문자열 검색에 배열 등을 사용한다면 모든 경우의 수를 다 비교해야 하므로 비효율적이다.
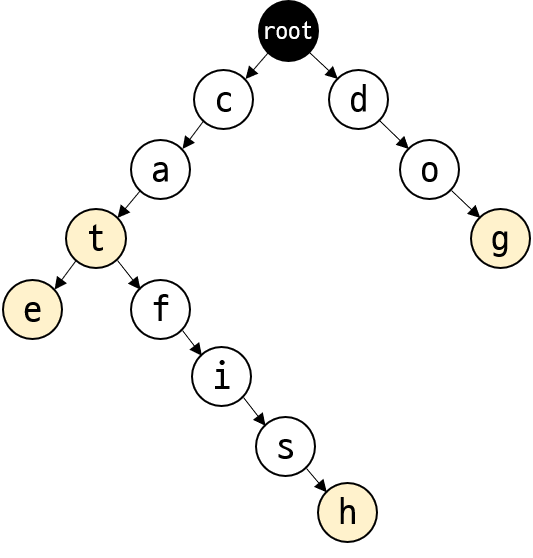
예를 들어 cat, dog, catfish, cate를 Trie 자료구조에 삽입하면 아래와 같이 저장된다.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define LEN 10
int get_index(const char c) {
return c - '0';
}
class Trie {
private:
Trie *next[LEN];
bool is_leaf;
public:
Trie();
~Trie();
void insert(const char *key);
bool find(const char *key);
};
Trie::Trie() {
this->is_leaf = false;
memset(this->next, 0, sizeof(this->next));
}
Trie::~Trie() {
for (int i = 0; i < LEN; i++) {
if (this->next[i])
delete this->next[i];
}
}
void Trie::insert(const char *key) {
if (*key == '\0') {
this->is_leaf = true;
return;
}
int index = get_index(*key);
if (this->next[index] == 0) {
this->next[index] = new Trie();
}
return this->next[index]->insert(key + 1);
}
bool Trie::find(const char *key) {
if (*key == '\0') {
return false;
}
if (this->is_leaf) return true;
int index = get_index(*key);
return this->next[index]->find(key + 1);
}
int main() {
int T, N;
bool ans = false;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
Trie * root = new Trie();
char phone_numbers[10001][11];
ans = false;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> phone_numbers[i];
root->insert(phone_numbers[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (root->find(phone_numbers[i])) {
ans = true;
}
}
cout << (ans ? "NO" : "YES") << endl;
delete root;
}
return 0;
}