Summary of last class
-
Address space
- illision that the program has its own private memory, where its own code and data reside
-
Address Translation
- Changing the virtual address to a physical address
-
Hardware support
- Privileged mode (user / kernel)
- Base / bounds registers (시작점, 범위를 저장하는 레지스터)
- Ability to translate virtual address and check if within bounds
- Privileged instructions to update base / bounds
- Privileged instructions to register exception handlers
- Ability to raise exceptions
-
OS Issues
- Memory management
- Base / bounds management
- Exception handling
사용중인 물리메모리를 알아야하고, 범위를 벗어나는지 등의 예외를 처리해야하고 context swich 상황에서 값을 셋팅하고 저장할 수 있어야 한다.
Segmentation
Base and Bounding
-
base and bounds registers
-
Big chunk of 'Free' space
- Taking up physical memory when we relocate the entire address space somewhere in physical memory
- Hard to run a program when the entire address space doesn't fit into memory
안 쓰는 공간, 빈 공간이 너무 크면 바로바로 찾아내기 어려울 수 있다.
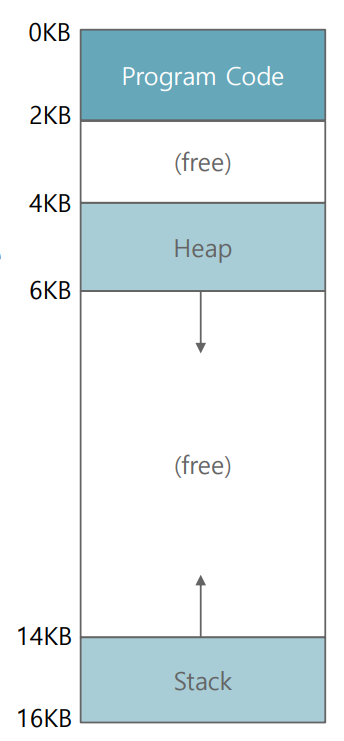
How to Support a Large Address Space
-
How do we support a large address space with a lot of free space between the stack and the heap?
(E.g., 32-bit address space : 4GB)
스택공간과 힙공간을 쌓여가는 거라 미리 공간을 비워놓는데 이 부분이 굉장히 크다. 좀더 효율적으로 관리할 수 있을까?
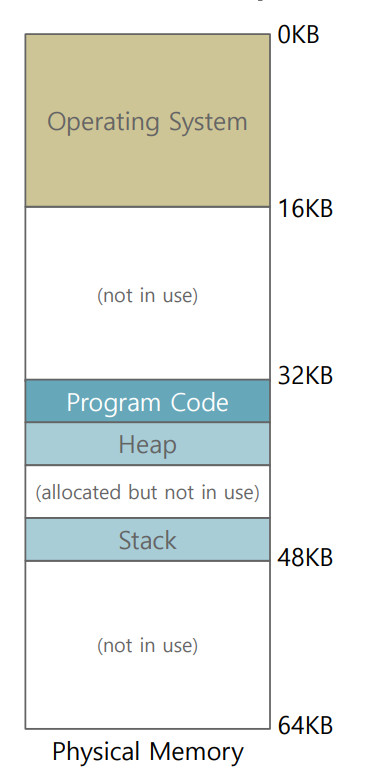
Segmentation
-
Segment
- A contiguous portion of the address space of a particular length
- E.g., code stack, heap
- Each of which has a base and bounds pair
원래 연속적이던 공간을 segment 라는 단위로 자르면서 굳이 연속, 순서적일 필요가 없어짐. 정해진 bounds 가 있음.
또한 사용되는 곳만 할당을 할거라 메모리 효율성이 늘어난다.
- A contiguous portion of the address space of a particular length
Example : Relocation
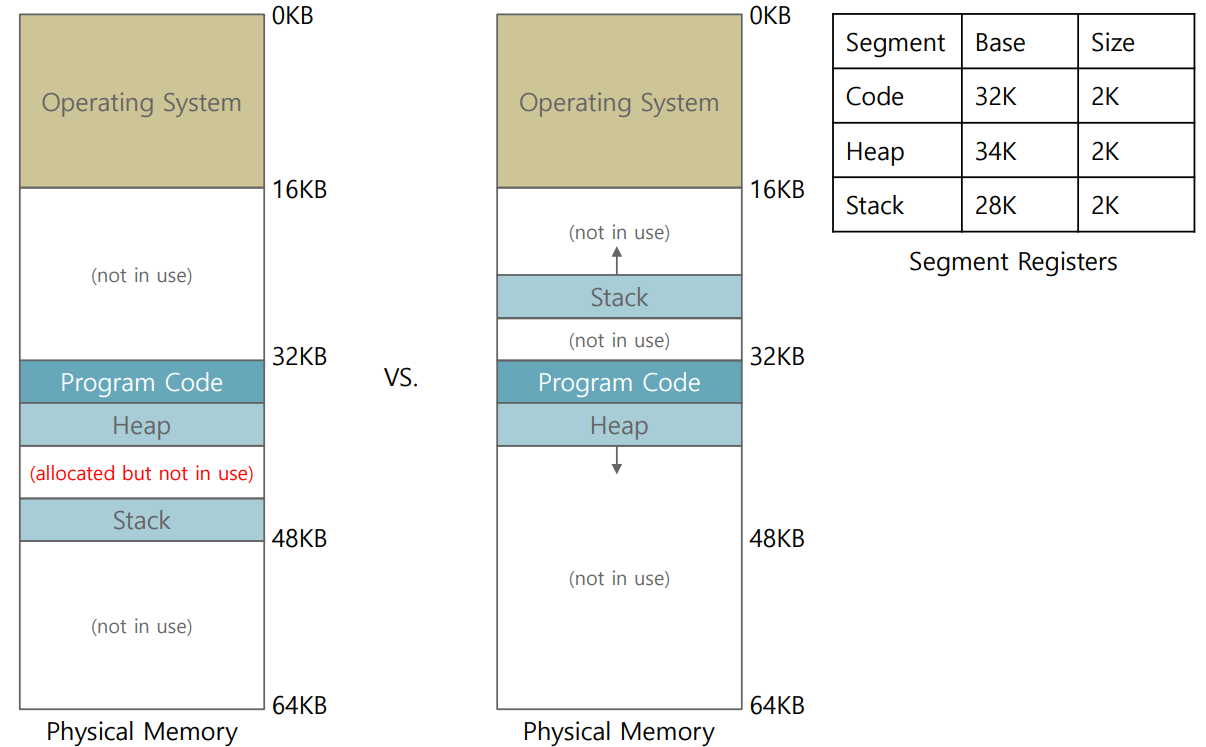
안 쓰는 공간을 좀 더 줄였다.
Example : Address Translation
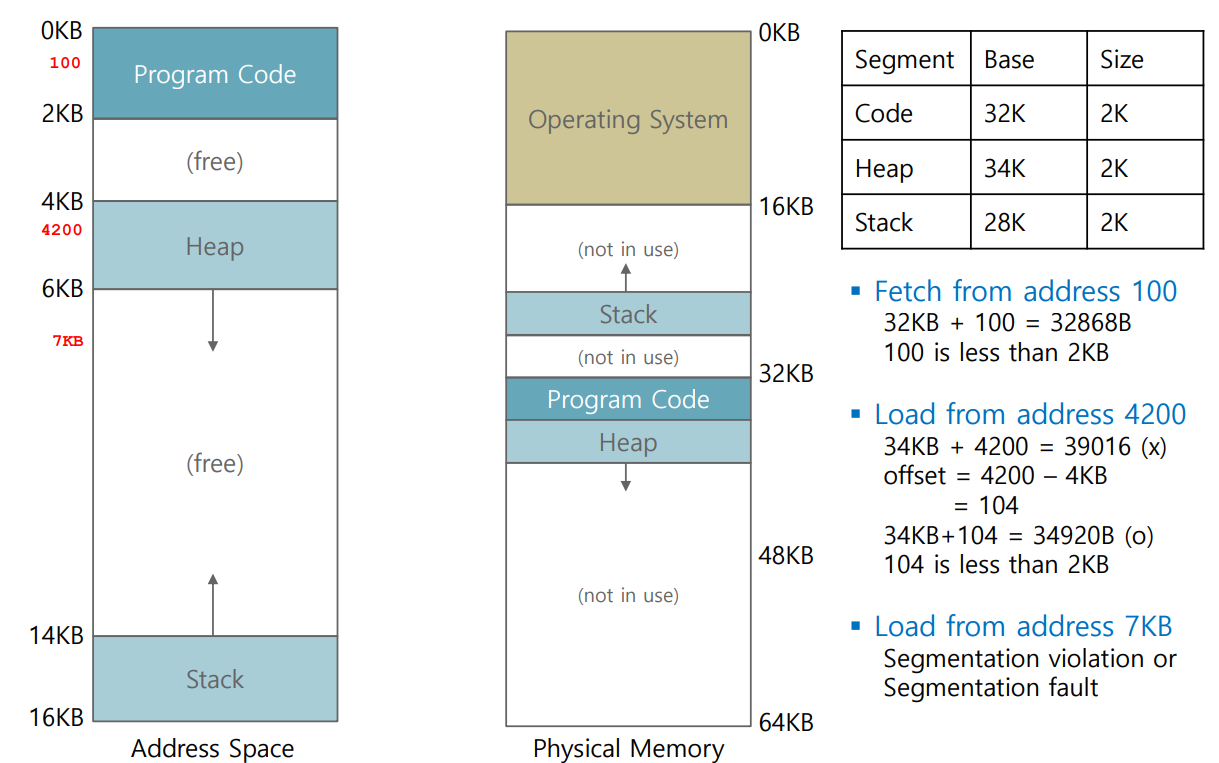
Which segment are we referring to?
-
Explicit approach
-
Chops up the address space into segments based on the top few bits of the virtual address
-
Example : 14-bits addressing (16 KB address space)
-
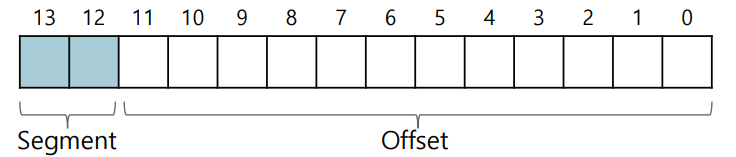
- 00 : code segment
- 01 : heap segment
- 11 : stack segment
- One segment (10) of the address space goes unused
- Some systems use only one bit (put code in the same segment as the heap)
> segment 부분에서 0 으로 시작하면 code + heap
>
> 1로 시작하면 stack 영역이다.- Example : 14 - bit addressing (16KB address space)
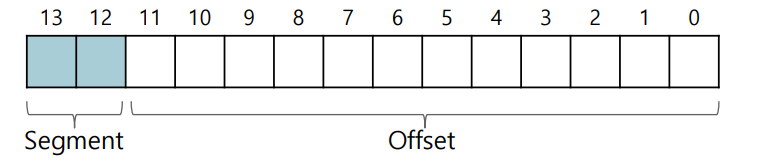
-
Max size of each segment 4KB - heap영역이 4KB 부터 시작한 이유, code공간 여유를 위해
- Offset : 12bits / 2^10 4 = 1KB 4
-
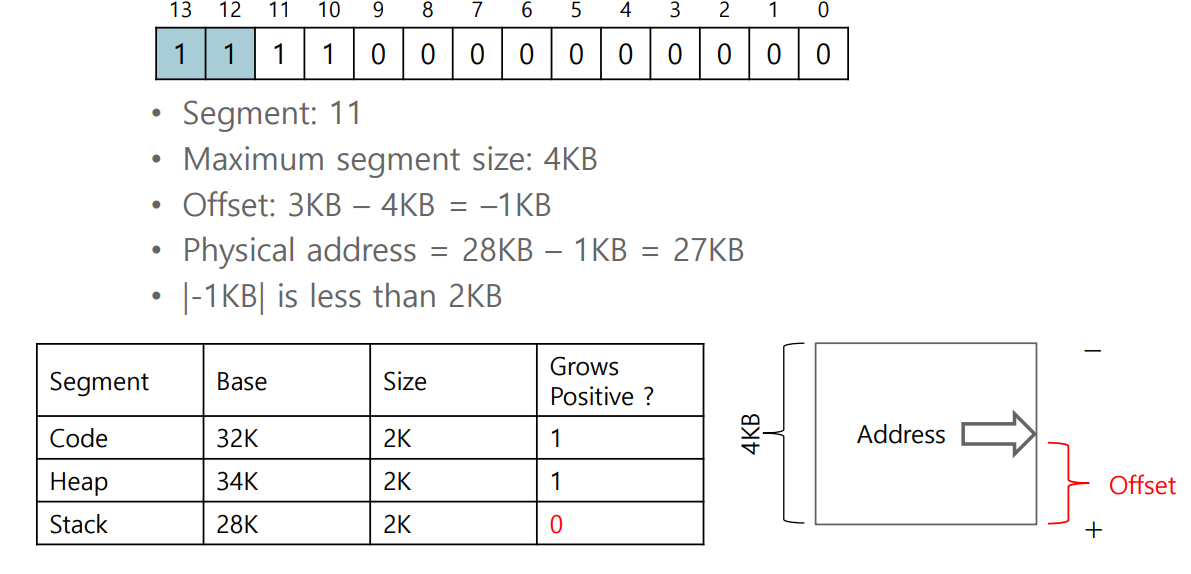
Address 4200
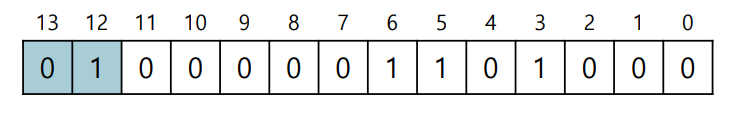
- Address 7KB
- Address translation (by hardware)
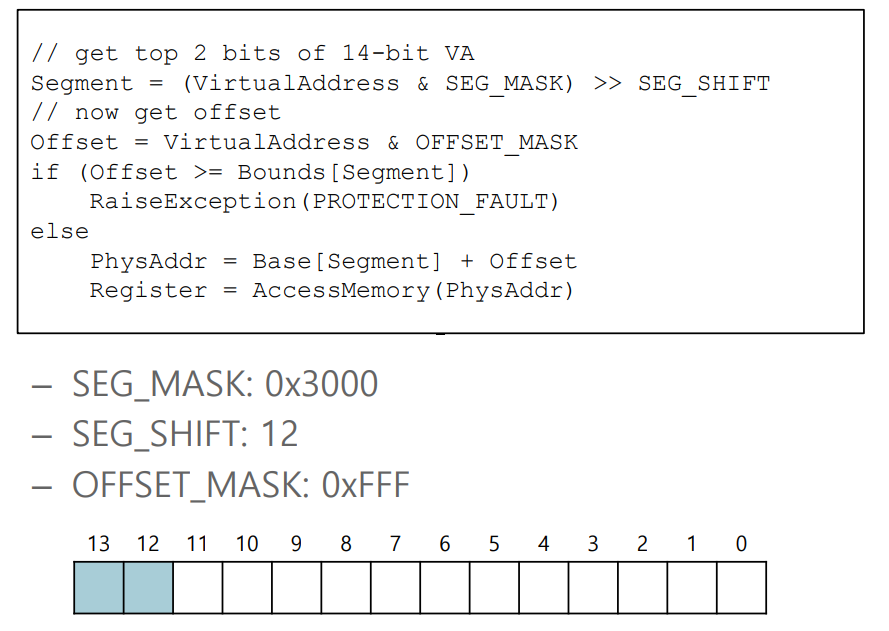
SEG_MASK 에서 한 칸당 4bit로 표현, 0x3000 - 3은 세그먼트, 000은 12bit
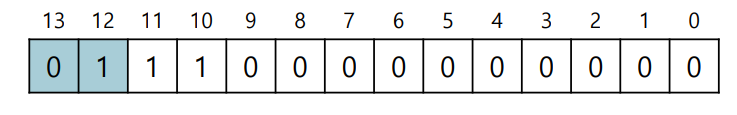
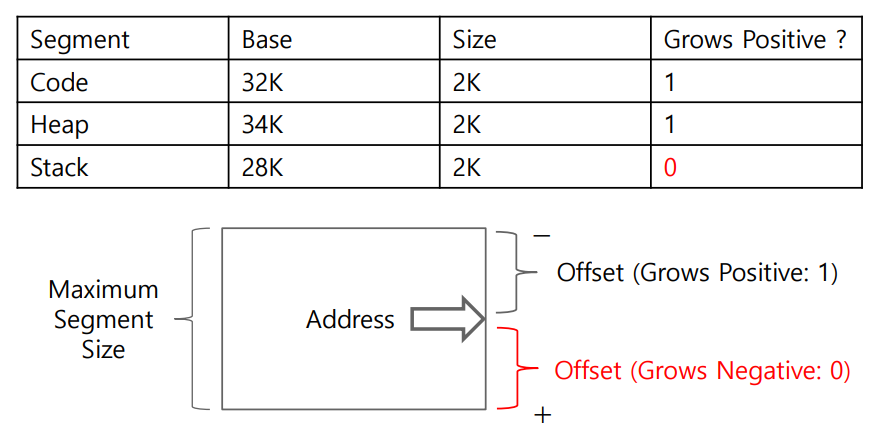
What about the Stack?
-
Hardware also nedds to know which way the segment grows
-
Example
- A bit is set to 1 when the segment grows in the positive direction, and 0 for negative
-
-
Address translation
- Example : accessing virtual addresss 15KB
Support for Sharing
-
Code sharing
-
To save memory, sometimes it is useful to share certain memory segments between address spaces
- Code segment
-
Protection bits
-
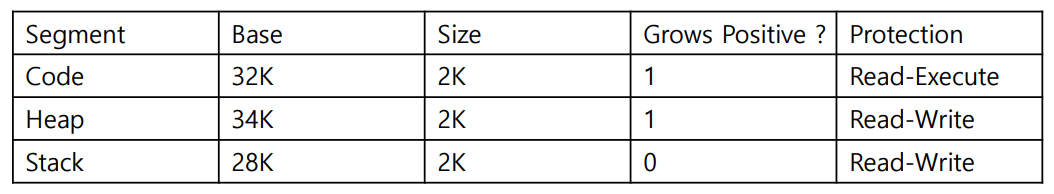
- By setting a code segment to read-only, the same code can be shared across multiple processes- In addition to checking whether a virtual addresss is within bounds, the hardware also has to check whether a particular access is permissible
hardware는 bounds 뿐만 아니라 Protection도 같이 확인하게 된다.
Fine-grained vs Coarse-grained
-
Coarse - grained segmentation
- Code, stack, and heap
1bit / 0 -> heap, code 1 -> stacak
2bit / 00 code 01 heap , 11 stack
-
Fine - grained segmentation
- Supporting many segments requires even further hardware support
- Segment table
- Supporting many segments requires even further hardware support
segment 종류가 많아지면 종류가 명시된 table이 필요하고 register가 필요해진다.
OS Support
-
Context switch
- Segment registers must be saved and restored
모든 상황에 대해 잘 저장하고 있어야 한다.
-
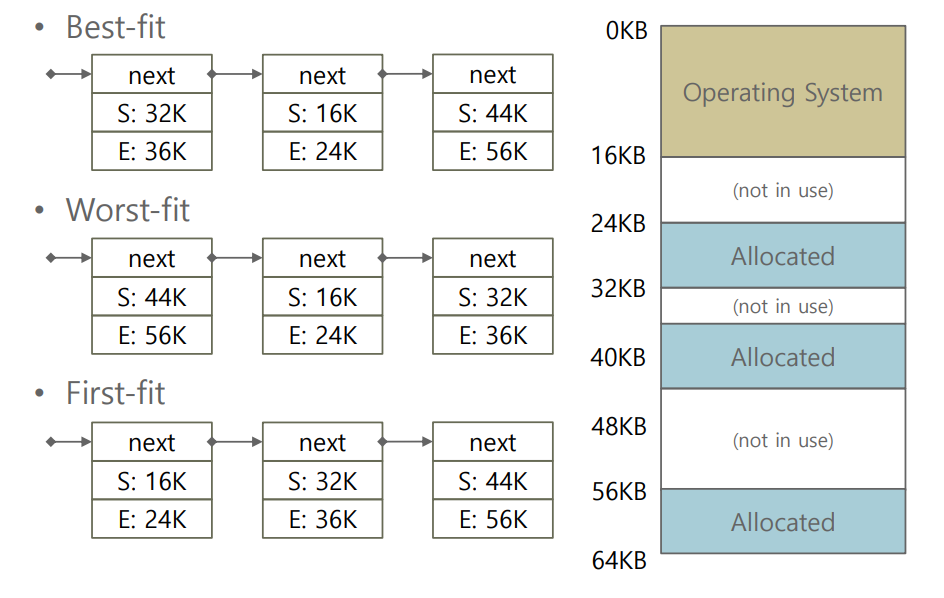
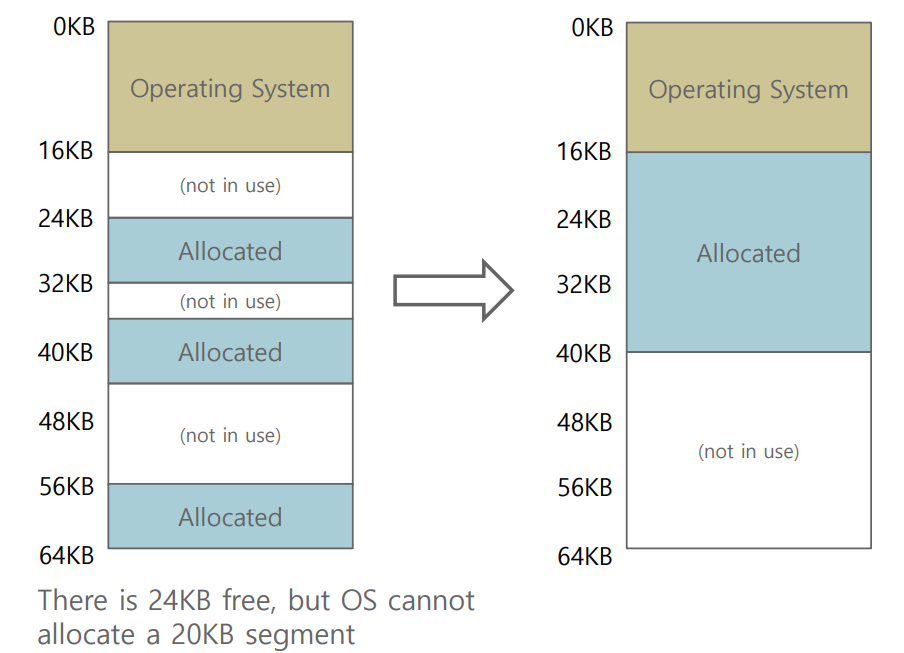
Managing free space in physical memory
- When a new address space is created, the OS has to be able to find space in physical memory for its segments
- Now, we have a number of segments per process, and each segment might be a different size
- External fragmentation
- Physical memory quickly becomes full of little holes of free space, making it difficult to allocate new segments
- When a new address space is created, the OS has to be able to find space in physical memory for its segments
-
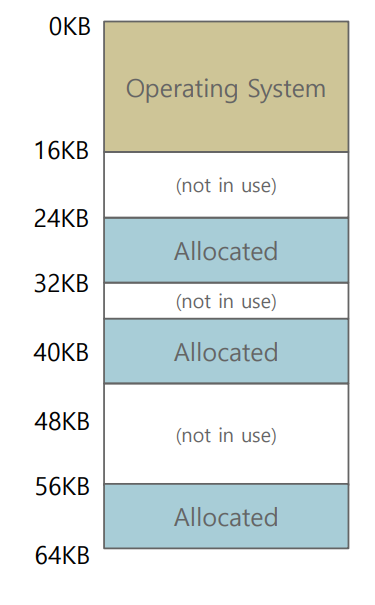
Physical memory compaction
virtual -> physical 이동은 크게 어렵지 않다.
하지만 중간중간 빈 곳을 모으기 메모리공간을 정렬시킬때는 base위치도 달라지고 모든 데이터를 copy해야 하기 때문에 큰 runtime이 생긴다. 효율적이긴 하지만 실행하기에 너무 시간이 걸린다.
- free-list management algorithms
-
Best-fit - 가장 남는 공간이 적은, 할당할 공간과 비슷한 크기로 배정
-
Worst-fit - 가장 큰 공간에 배정
-
First-fit - 주소순으로 빈 공간을 찾으면 배정
-
Buddy algorithm - paging
free 공간들을 linked list 로 관리.