문제
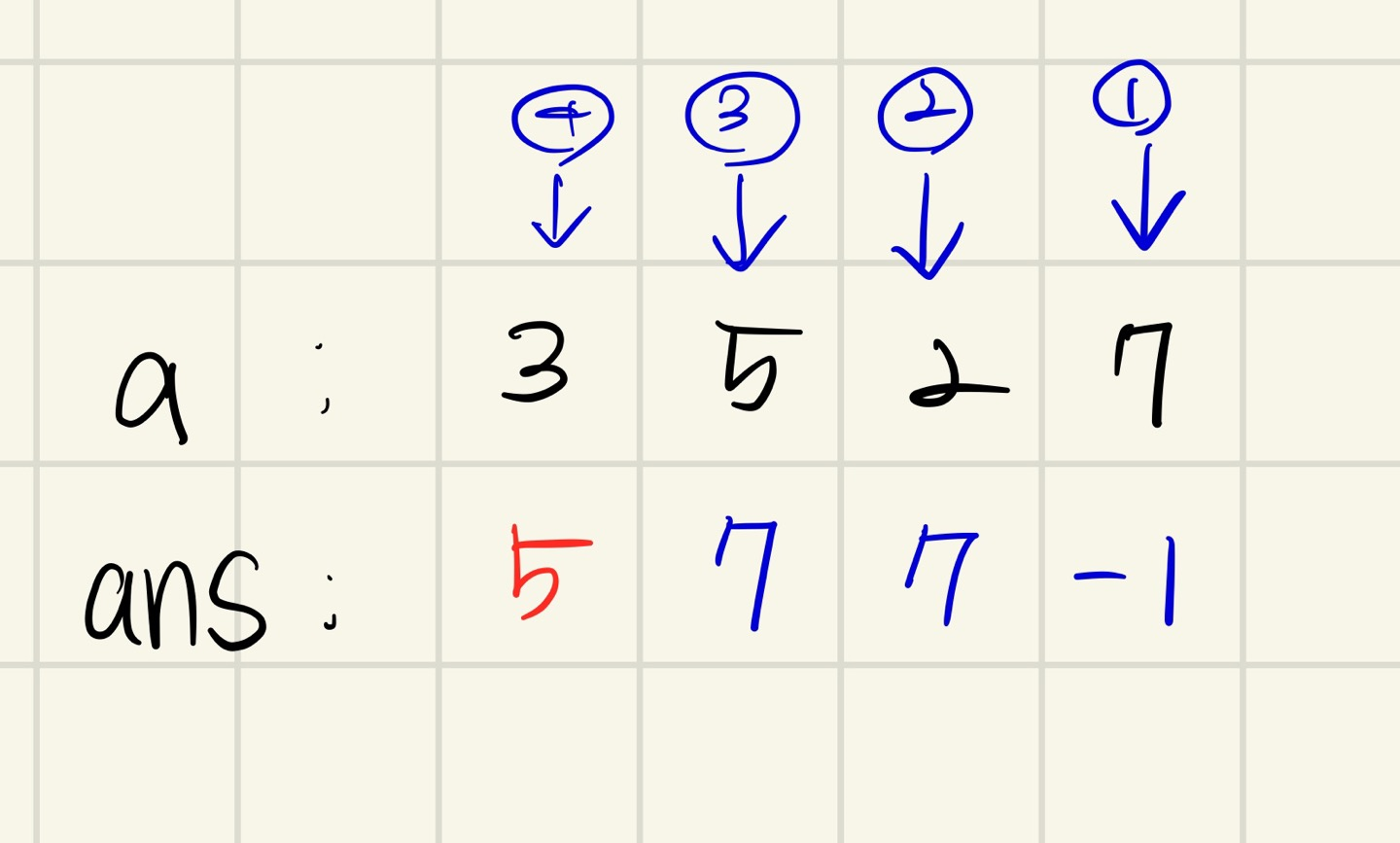
크기가 N인 수열 A = A1, A2, ..., AN이 있다. 수열의 각 원소 Ai에 대해서 오큰수 NGE(i)를 구하려고 한다. Ai의 오큰수는 오른쪽에 있으면서 Ai보다 큰 수 중에서 가장 왼쪽에 있는 수를 의미한다. 그러한 수가 없는 경우에 오큰수는 -1이다.
예를 들어, A = [3, 5, 2, 7]인 경우 NGE(1) = 5, NGE(2) = 7, NGE(3) = 7, NGE(4) = -1이다. A = [9, 5, 4, 8]인 경우에는 NGE(1) = -1, NGE(2) = 8, NGE(3) = 8, NGE(4) = -1이다.
풀이
풀이 1 - 정답코드
- 나보다 오른쪽에 있음
- 나보다 크면서 가장 왼쪽에 있음
두 조건을 만족하는 수를 출력하기
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[1000000]; //수열의 크기에 맞춘 공간
int ans[1000000]; //정답 배열 공간
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
stack<int> tower;
cin >> n;
//수열 입력받기
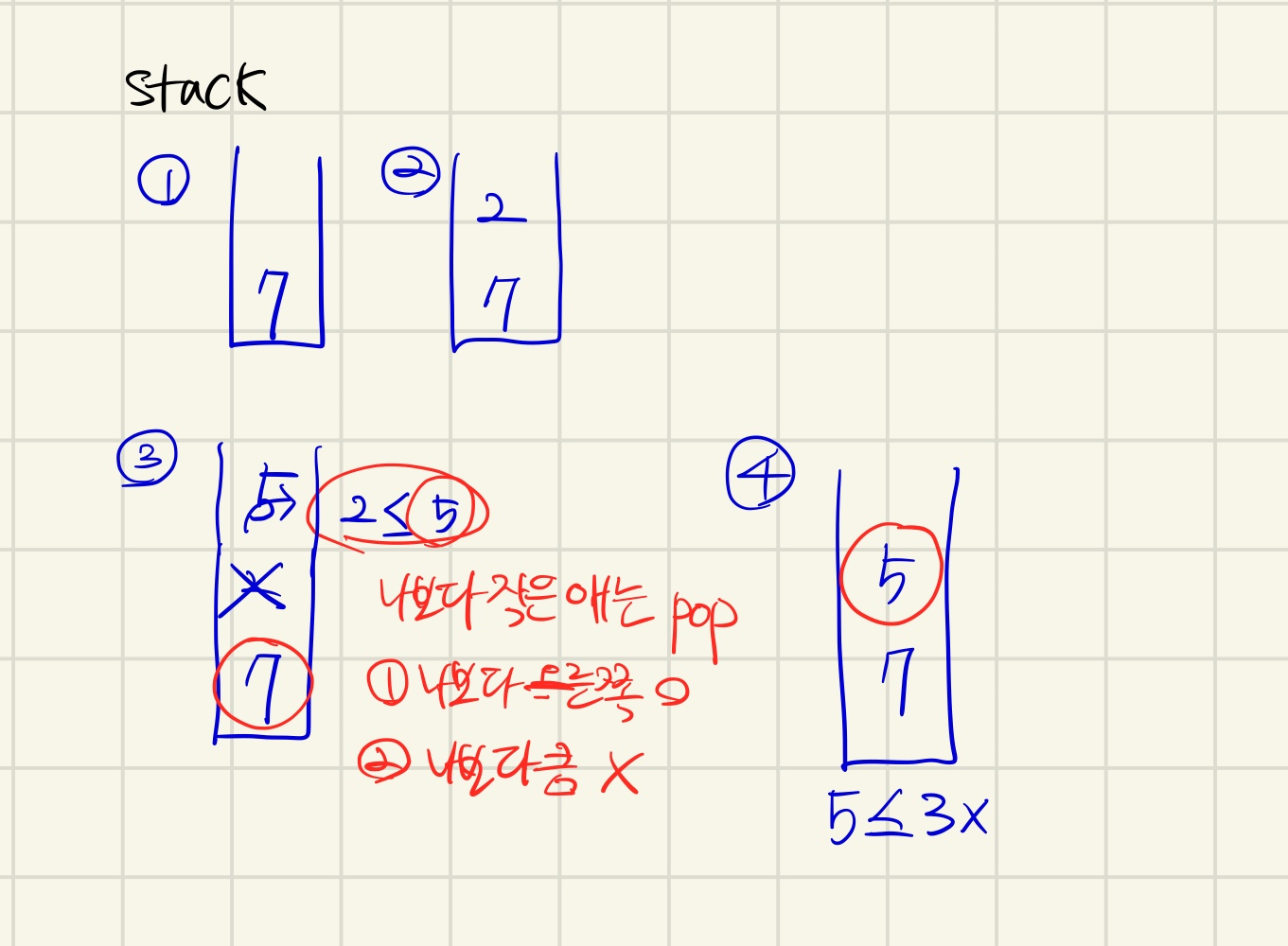
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) cin >> a[i]; //3 5 2 7
//입력받은 수열 뒤에서부터 읽기
for (int i =n-1; i >=0; i--) {
while (!tower.empty() && tower.top() <= a[i])
tower.pop();
if(tower.empty()) ans[i] = -1; //만족하는 오큰수가 없으므로 -1
else ans[i] = tower.top();
tower.push(a[i]);
}
//출력
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) cout << ans[i]<< ' ';
}
풀이 2 - 채연 코드
중간에 런타임에러가 뜬다.
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int k;
int arr[k];
stack<int> st;
//입력
cin>>k;
for(int i=0; i<k; i++){
cin>>arr[i];
}
for(int i=k-1; i>=0; i--){
if(i==k-1){ //마지막 원소일때
st.push(-1);
}
else{
for(int j=i+1; j<k; j++){
if(arr[i]<arr[j]){
st.push(arr[j]);
break;
}
if(j==k-1){ //오른쪽에 있는 수가 모두 작다면
if(arr[i]>arr[j]) st.push(-1);
}
}
}
}
//출력
while(k--){
cout<<st.top()<<" ";
st.pop();
}
return 0;
}-> 같은 숫자가 들어왔을 떄 -1을 출력하는 코드가 없어서 그럼
if(j==k-1){ //오른쪽에 있는 수가 모두 작다면
if(arr[i]>arr[j]) st.push(-1);이 부분을 >=으로 고쳐주면된다.
if(arr[i]>=arr[j]) st.push(-1);