문제
0에서 n-1이름의 n개 노드로 구성된 무방향 그래프(Undirected Graph)가 주어진다. edges[] 는 각 노드의 엣지(간선)가 리스트업 되어있다. 어떤 노드도 루트노드가 될 수 있다고 할때, 트리의 높이가 가장 낮아지는 루트노드를 모두 구하라.
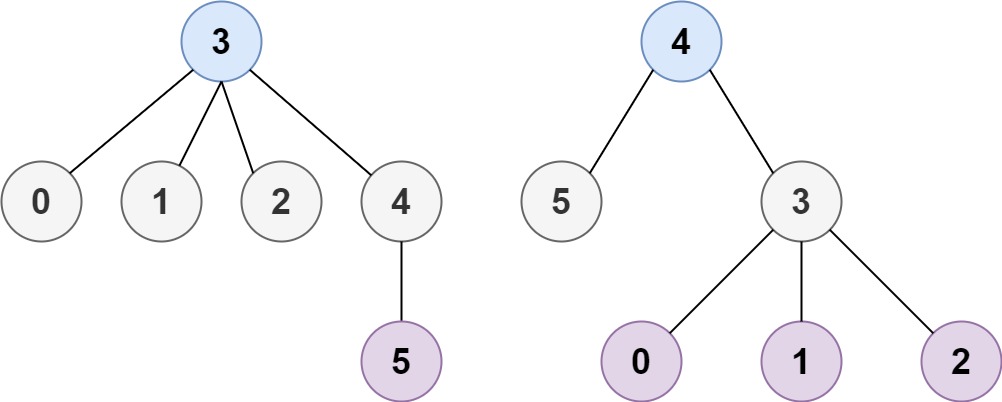
Input: n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]]
Output: [3,4]해결 아이디어
- Brute-force O(n^2) 문제 그대로 모든 노드에서부터 높이를 재서 가장 낮은 높이를 갖는 루트노드를 리턴.
- 2-DFS O(n) 아무노드에서 시작해 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드1를 찾는다. 그리고 그 노드부터 다시 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드2를 찾는다. 노드1 과 노드 2가 해당 그래프에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드가 된다. 여기서 중간의 노드 (1개 혹은 2개)를 리턴하면 된다.
- Topology Sort 방법 O(n) The basic idea is "keep deleting leaves layer-by-layer, until reach the root." 간선 갯수가 1개인 노드부터 단계별로 제거한다. 그러다보면 마지막 까지 남는 노드가 생기는데, 그 노드가 결과값이된다. 이를 위해 Topology Sort 를 사용하면 된다. 이전까지는 방향이 있는 그래프에서 사용했는데 그때는 배열하나에 진입차수 갯수를 저장했다면, 무방향 그래프에서는 노드에 연결된 간선 갯수자체를 저장한다. 간선 갯수가 1개인 노드가 바로 가장 마지막 layer의 노드가 된다. 이 layer별로 q에 삽입후 제거하는 방식으로 동작한다.
풀이1 - Brute-force O(n^2)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> graph;
int get_hight_from(int root, vector<bool> &visit) {
vector<int> depth(visit.size());
queue<int> q;
q.push(root);
int curr = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
curr = q.front();
q.pop();
visit[curr] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[curr].size(); i++) {
if (visit[graph[curr][i]] == true)
continue;
q.push(graph[curr][i]);
depth[graph[curr][i]] = depth[curr] + 1;
}
}
return depth[curr];
}
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<int> ret;
vector<int> hight(n);
int min_hight = n + 1;
graph = vector<vector<int>>(n);
for (auto it: edges) {
graph[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);
graph[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);
}
/*
with edges [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]], the graph will be:
0 -> 3
1 -> 3
2 -> 3
3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 4
4 -> 3 -> 5
*/
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vector<bool> visit(n, false);
hight[i] = get_hight_from(i, visit);
min_hight = std::min(hight[i], min_hight);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (hight[i] == min_hight)
ret.push_back(i);
}
return ret;
}
};풀이2 - 2-DFS방법 O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> graph;
int max_depth = 0;
vector<int> longest_path;
vector<int> tmp;
void get_longest(int node, int depth, vector<bool> &visit) {
if (visit[node] == true)
return;
tmp.push_back(node);
if (depth > max_depth) {
longest_path = tmp;
max_depth = depth;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) {
visit[node] = true;
get_longest(graph[node][i], depth + 1, visit);
}
tmp.pop_back();
}
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
if (n == 1)
return {0};
graph = vector<vector<int>>(n);
for (auto it: edges) {
graph[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);
graph[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);
}
/* 1st dfs */
max_depth = 0;
vector<bool> visit(edges.size(), false);
get_longest(0, 0, visit);
int first_node = longest_path[max_depth];
/* 2st dfs */
max_depth = 0;
visit = vector<bool>(edges.size(), false);
get_longest(first_node, 0, visit);
int second_node = longest_path[max_depth];
/* if max_depth is odd, the number of node in longest path is even
0 1 [2 3] 4 5
else:
0 1 [2] 3 4
*/
int mid = max_depth / 2;
if (max_depth % 2 == 1)
return {longest_path[mid], longest_path[mid + 1]};
return {longest_path[mid]};
}
};풀이3 - Topology Sort 방법 O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(n);
unordered_map<int, int> indeg;
queue<int> q;
if (n == 1)
return {0};
/* generate graph data structure */
for (auto it: edges) {
graph[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);
graph[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);
indeg[it[0]]++;
indeg[it[1]]++;
}
/* push the nodes which is indegree 1 */
for (auto it: indeg) {
if (it.second == 1) {
q.push(it.first);
}
}
/* bfs - topology sort */
vector<int> ret;
while (!q.empty()) {
int nr_leaves = q.size(); // number of leaf nodes current steps.
ret.clear(); //
while (nr_leaves--) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
indeg[node]--;
ret.push_back(node); // so every step, leaf node will be added in ret.
for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) {
int adj = graph[node][i];
indeg[adj]--;
if (indeg[adj] == 1) // the adjacent node is become a leaf
q.push(adj); // a new leaf node is added
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};