Programmers Problem - 타겟 넘버
- n개의 음이 아닌 정수들이 있습니다. 이 정수들을 순서를 바꾸지 않고 적절히 더하거나 빼서 타겟 넘버를 만들려고 합니다.
- 예를 들어 [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]로 숫자 3을 만들려면 다음 다섯 방법을 쓸 수 있습니다.
-1+1+1+1+1 = 3
+1-1+1+1+1 = 3
+1+1-1+1+1 = 3
+1+1+1-1+1 = 3
+1+1+1+1-1 = 3- 사용할 수 있는 숫자가 담긴 배열 numbers, 타겟 넘버 target이 매개변수로 주어질 때 숫자를 적절히 더하고 빼서 타겟 넘버를 만드는 방법의 수를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
- 제한사항
- 주어지는 숫자의 개수는 2개 이상 20개 이하입니다.
- 각 숫자는 1 이상 50 이하인 자연수입니다.
- 타겟 넘버는 1 이상 1000 이하인 자연수입니다.
- 제한사항
Solution
function solution(numbers, target) {
let answer = 0;
dfs(0, 0);
function dfs(index, sum) {
if (index === numbers.length) {
if (sum === target) {
answer++;
}
return;
}
dfs(index + 1, sum + numbers[index]);
dfs(index + 1, sum - numbers[index]);
}
return answer;
}LeetCode Problem : Find if Path Exists in Graph
-
There is a bi-directional graph with
nvertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). The edges in the graph are represented as a 2D integer arrayedges, where eachedges[i] = [ui, vi]denotes a bi-directional edge between vertexuiand vertexvi. Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself. -
You want to determine if there is a valid path that exists from vertex
sourceto vertexdestination. -
Given
edgesand the integersn,source, anddestination, returntrueif there is a valid path from source to destination, orfalseotherwise.- Constraints
- 1 <= n <= 2 * (10^5)
- 0 <= edges.length <= 2 * (10^5)
- edges[i].length == 2
- 0 <= ui, vi <= n - 1
- ui != vi
- 0 <= source, destination <= n - 1
- There are no duplicate edges.
- There are no self edges.
- Constraints
-
Example 1
- Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
- Output: true
- Explanation: here are two paths from vertex 0 to vertex 2 :
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
-
Example 2
- Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
- Output: false
- Explanation: There is no path from vertex 0 to vertex 5.
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @param {number} source
* @param {number} destination
* @return {boolean}
*/
var validPath = function(n, edges, source, destination) {
let adjacencyList = {}, visited = {};
edges.forEach(([vertex1, vertex2]) => {
if (!adjacencyList[vertex1]) adjacencyList[vertex1] = [];
if (!adjacencyList[vertex2]) adjacencyList[vertex2] = [];
adjacencyList[vertex1].push(vertex2);
adjacencyList[vertex2].push(vertex1);
});
let stack = [source];
visited[source] = true;
while (stack.length) {
const current = stack.pop();
if (current === destination) return true;
for (let neighbor of adjacencyList[current]) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true;
stack.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
return false;
};LeetCode Problem : Deepest Leaves Sum
- Given the
rootof a binary tree, return the sum of values of its deepest leaves.- Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 10^4].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 100
- Constraints
Solution
var deepestLeavesSum = function(root) {
let queue = [root];
let lastLevel = [];
while(queue.length) {
let size = queue.length;
let level = [];
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
const node = queue.shift();
level.push(node.val);
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left);
if (node.right) queue.push(node.right);
}
lastLevel = level;
}
return lastLevel.reduce((sum, val) => sum += val, 0);
};- level 출력 예
[ 1 ]
[ 2, 3 ]
[ 4, 5, 6 ]
[ 7, 8 ] // lastLevelLeetCode Problem : Sum of Nodes with Even-Valued Grandparent
- Given the
rootof a binary tree, return the sum of values of nodes with an even-valued grandparent. If there are no nodes with an even-valued grandparent, return 0.- A grandparent of a node is the parent of its parent if it exists.
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var sumEvenGrandparent = function(root) {
let result = 0;
traverse(root);
function traverse(node){
if (!node) return 0;
if (node.val % 2 === 0) {
if (node.left && node.left.left) {
result += node.left.left.val;
}
if (node.left && node.left.right) {
result += node.left.right.val;
}
if (node.right && node.right.left) {
result += node.right.left.val;
}
if (node.right && node.right.right) {
result += node.right.right.val;
}
}
traverse(node.left);
traverse(node.right);
}
return result;
};Programmers Problem : 네트워크
- 네트워크란 컴퓨터 상호 간에 정보를 교환할 수 있도록 연결된 형태를 의미합니다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터 A와 컴퓨터 B가 직접적으로 연결되어있고, 컴퓨터 B와 컴퓨터 C가 직접적으로 연결되어 있을 때 컴퓨터 A와 컴퓨터 C도 간접적으로 연결되어 정보를 교환할 수 있습니다. 따라서 컴퓨터 A, B, C는 모두 같은 네트워크 상에 있다고 할 수 있습니다.
- 컴퓨터의 개수 n, 연결에 대한 정보가 담긴 2차원 배열 computers가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 네트워크의 개수를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성하시오.
- 제한사항
- 컴퓨터의 개수 n은 1 이상 200 이하인 자연수입니다.
- 각 컴퓨터는 0부터 n-1인 정수로 표현합니다.
- i번 컴퓨터와 j번 컴퓨터가 연결되어 있으면 computers[i][j]를 1로 표현합니다.
- computer[i][i]는 항상 1입니다.
- 제한사항
Solution
function solution(n, computers) {
var answer = 0;
const length = computers.length;
let visited = new Array(length).fill(false);
function dfs(index) {
visited[index] = true;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (computers[index][i] === 1 && !visited[i]) {
dfs(i);
}
}
}
for (let index = 0; index < n; index++) {
if (!visited[index]) {
dfs(index);
answer++;
}
}
return answer;
}- 풀이
- 컴퓨터 배열을 순회하면서 방문하지 않은 컴퓨터가 있으면 DFS를 하여 해당 컴퓨터와 연결된 모든 다른 컴퓨터들을 탐색함
- 네트워크의 연결 여부와 관계 없이 모든 컴퓨터를 한 번씩 순회할 수 있음
- 한 컴퓨터에 DFS를 하면 해당 컴퓨터와 동일한 네트워크 상에 있는 모든 컴퓨터를 순회하게 되므로, DFS를 실행하는 횟수가 곧 네트워크의 개수가 됨
- 따라서, DFS를 할 때마다 네트워크 개수를 증가시켜서 계산함
- 컴퓨터 배열을 순회하면서 방문하지 않은 컴퓨터가 있으면 DFS를 하여 해당 컴퓨터와 연결된 모든 다른 컴퓨터들을 탐색함
LeetCode Problem : All Paths From Source to Target
- Given a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of
nnodes labeled from0ton - 1, find all possible paths from node0to noden - 1and return them in any order. - The graph is given as follows:
graph[i]is a list of all nodes you can visit from nodei(i.e., there is a directed edge from nodeitonode graph[i][j]).- Constraints:
- n == graph.length
- 2 <= n <= 15
- 0 <= graph[i][j] < n
- graph[i][j] != i (i.e., there will be no self-loops).
- All the elements of graph[i] are unique.
- The input graph is guaranteed to be a DAG.
- Constraints:
Solution
/**
* @param {number[][]} graph
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var allPathsSourceTarget = function(graph) {
const result = [];
const findPath = function(path, node) {
if (node === graph.length - 1) {
result.push([...path, node]);
return;
}
graph[node].forEach((neighbor) => findPath([...path, node], neighbor));
}
findPath([], 0);
return result;
};Programmers Problem : 가장 먼 노드
- n개의 노드가 있는 그래프가 있습니다. 각 노드는 1부터 n까지 번호가 적혀있습니다. 1번 노드에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드의 갯수를 구하려고 합니다. 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드란 최단경로로 이동했을 때 간선의 개수가 가장 많은 노드들을 의미합니다.
- 노드의 개수 n, 간선에 대한 정보가 담긴 2차원 배열 vertex가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 1번 노드로부터 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드가 몇 개인지를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
- 제한사항
- 노드의 개수 n은 2 이상 20,000 이하입니다.
- 간선은 양방향이며 총 1개 이상 50,000개 이하의 간선이 있습니다.
- vertex 배열 각 행 [a, b]는 a번 노드와 b번 노드 사이에 간선이 있다는 의미입니다.
- 제한사항
Solution
function solution(n, edge) {
let answer = 0;
let node = Array.from({length: n+1}, () => []);
let visited = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
let queue = [1];
edge.forEach(([start, end]) => {
node[start].push(end);
node[end].push(start);
});
visited[1] = 1;
while(queue.length) {
let current = queue.shift();
node[current].forEach((neighbor) => {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
queue.push(neighbor);
visited[neighbor] = visited[current] + 1;
}
});
}
const max = Math.max(...visited);
answer = visited.filter(edgeCount => edgeCount === max).length;
return answer;
}LeetCode Problem : Number of Provinces
- There are
ncities. Some of them are connected, while some are not. If city a is connected directly with city b, and city b is connected directly with city c, then city a is connected indirectly with city c.- A province is a group of directly or indirectly connected cities and no other cities outside of the group.
- You are given an
nxnmatrixisConnectedwhereisConnected[i][j] = 1if the ith city and thejthcity are directly connected, andisConnected[i][j] = 0otherwise. - Return the total number of provinces.
- Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 200
- n == isConnected.length
- n == isConnected[i].length
- isConnected[i][j] is 1 or 0.
- isConnected[i][i] == 1
- isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
- Constraints:
Solution
/**
* @param {number[][]} isConnected
* @return {number}
*/
var findCircleNum = function(isConnected) {
const visited = {};
let provinceCount = 0;
for (let cityIndex = 0; cityIndex < isConnected.length; cityIndex++){
if (!visited[cityIndex]) {
dfs(cityIndex);
provinceCount++;
}
}
function dfs(cityIndex) {
visited[cityIndex] = true;
for (let neighborIndex = 0; neighborIndex < isConnected[cityIndex].length; neighborIndex++) {
if (!visited[neighborIndex] && isConnected[cityIndex][neighborIndex] === 1) {
dfs(neighborIndex);
}
}
}
return provinceCount;
};LeetCode Problem : Keys and Rooms
- There are
nrooms labeled from0ton - 1and all the rooms are locked except for room0. Your goal is to visit all the rooms. However, you cannot enter a locked room without having its key. - When you visit a room, you may find a set of distinct keys in it. Each key has a number on it, denoting which room it unlocks, and you can take all of them with you to unlock the other rooms.
- Given an array
roomswhererooms[i]is the set of keys that you can obtain if you visited roomi, returntrueif you can visit all the rooms, orfalseotherwise. - Constraints:
- n == rooms.length
- 2 <= n <= 1000
- 0 <= rooms[i].length <= 1000
- 1 <= sum(rooms[i].length) <= 3000
- 0 <= rooms[i][j] < n
- All the values of rooms[i] are unique.
- Example 1:
- Input: rooms = [[1],[2],[3],[]]
- Output: true
- Explanation:
- We visit room 0 and pick up key 1.
- We then visit room 1 and pick up key 2.
- We then visit room 2 and pick up key 3.
- We then visit room 3.
- Since we were able to visit every room, we return true.
- Example 2:
- Input: rooms = [[1,3],[3,0,1],[2],[0]]
- Output: false
- Explanation:
- We can not enter room number 2 since the only key that unlocks it is in that room.
Solution
/**
* @param {number[][]} rooms
* @return {boolean}
*/
var canVisitAllRooms = function(rooms) {
const visited = {};
dfs(0);
function dfs(i) {
visited[i] = true;
rooms[i].forEach((key) => {
if (!visited[key]) {
dfs(key);
}
});
}
for (let i = 0; i < rooms.length; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};LeetCode Problem : Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes
- Given a directed acyclic graph, with
nvertices numbered from0ton-1, and an array edges whereedges[i] = [fromi, toi]represents a directed edge from nodefromito nodetoi. - Find the smallest set of vertices from which all nodes in the graph are reachable. It's guaranteed that a unique solution exists.
- Notice that you can return the vertices in any order.
- Constraints:
- 2 <= n <= 10^5
- 1 <= edges.length <= min(10^5, n * (n - 1) / 2)
- edges[i].length == 2
- 0 <= fromi, toi < n
- All pairs (fromi, toi) are distinct.
- Constraints:
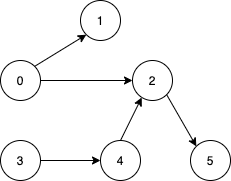
- Example 1:
- Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,5],[3,4],[4,2]]
- Output: [0,3]
- Explanation:
- It's not possible to reach all the nodes from a single vertex.
- From 0 we can reach [0,1,2,5].
- From 3 we can reach [3,4,2,5]. So we output [0,3].
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findSmallestSetOfVertices = function(n, edges) {
const visited = new Array(n).fill(0);
const result = [];
edges.forEach(([start, end]) => visited[end]++);
visited.forEach((visitedCount, index) => {
if (!visitedCount) {
result.push(index);
}
});
return result;
};Programmers Problem : 단어 변환
- 두 개의 단어 begin, target과 단어의 집합 words가 있습니다. 아래와 같은 규칙을 이용하여 begin에서 target으로 변환하는 가장 짧은 변환 과정을 찾으려고 합니다.
- 한 번에 한 개의 알파벳만 바꿀 수 있습니다.
- words에 있는 단어로만 변환할 수 있습니다.
- 두 개의 단어
begin,target과 단어의 집합words가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 최소 몇 단계의 과정을 거쳐 begin을 target으로 변환할 수 있는지 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.- 제한 사항
- 각 단어는 알파벳 소문자로만 이루어져 있습니다.
- 각 단어의 길이는 3 이상 10 이하이며 모든 단어의 길이는 같습니다.
- words에는 3개 이상 50개 이하의 단어가 있으며 중복되는 단어는 없습니다.
- begin과 target은 같지 않습니다.
- 변환할 수 없는 경우에는 0를 return 합니다.
- 제한 사항
- 입출력 예 1
- 입력 : begin = "hit", target = "cog", words = ["hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"]
- 출력 : 4
- 설명 : "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog"와 같이 4단계를 거쳐 변환
- 입출력 예 2
- 입력 : begin = "hit", target = "cog", words = ["hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log"]
- 출력 : 0
- 설명 : target인 "cog"는 words 안에 없기 때문에 변환할 수 없음
Solution
function solution(begin, target, words) {
let answer = 0;
const hasTarget = words.includes(target);
if (!hasTarget) return 0;
function checkSimilarity(word1, word2) {
let differentLength = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < word1.length; i++) {
if (word1[i] !== word2[i]) {
differentLength++;
}
}
return differentLength === 1;
}
const visited = { [begin] : 0 };
const queue = [begin];
while (queue.length) {
const currWord = queue.shift();
if (currWord === target) break;
words.forEach((word) => {
if (!visited[word] && checkSimilarity(word, currWord)) {
visited[word] = visited[currWord] + 1;
queue.push(word);
}
});
}
return visited[target];
}LeetCode Problem : Number of Operations to Make Network Connected
-
There are n computers numbered from
0ton - 1connected by ethernet cablesconnectionsforming a network whereconnections[i] = [ai, bi]represents a connection between computers ai and bi. Any computer can reach any other computer directly or indirectly through the network. -
You are given an initial computer network
connections. You can extract certain cables between two directly connected computers, and place them between any pair of disconnected computers to make them directly connected. -
Return the minimum number of times you need to do this in order to make all the computers connected. If it is not possible, return
-1.- Constraints
- 1 <= n <= 10^5
- 1 <= connections.length <= min(n * (n - 1) / 2, 105)
- connections[i].length == 2
- 0 <= ai, bi < n
- ai != bi
- There are no repeated connections.
- No two computers are connected by more than one cable.
- Constraints
-
Example 1:
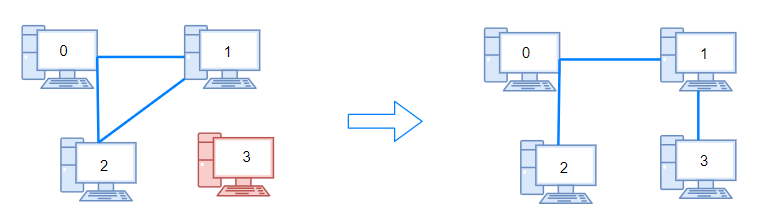
- Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]
- Output: 1
- Explanation: Remove cable between computer 1 and 2 and place between computers 1 and 3.
- Example 2:
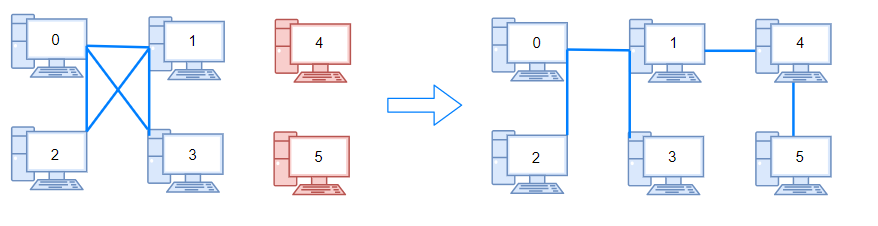
- Input: n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3]]
- Output: 2
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} connections
* @return {number}
*/
var makeConnected = function(n, connections) {
if (connections.length < n - 1) return -1;
let answer = 0;
const graph = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
const visited = Array(n).fill(false);
connections.forEach(([start, end]) => {
graph[start].push(end);
graph[end].push(start);
});
const dfs = function(node) {
visited[node] = true;
graph[node].forEach((neighbor) => {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
dfs(neighbor);
}
});
}
for (let index = 0; index < n; index++) {
if (!visited[index]) {
dfs(index);
answer++;
}
}
return answer - 1;
};Programmers Problem : 게임 맵 최단거리
-
ROR 게임은 두 팀으로 나누어서 진행하며, 상대 팀 진영을 먼저 파괴하면 이기는 게임입니다. 따라서, 각 팀은 상대 팀 진영에 최대한 빨리 도착하는 것이 유리합니다.
-
지금부터 당신은 한 팀의 팀원이 되어 게임을 진행하려고 합니다. 다음은 5 x 5 크기의 맵에, 당신의 캐릭터가 (행: 1, 열: 1) 위치에 있고, 상대 팀 진영은 (행: 5, 열: 5) 위치에 있는 경우의 예시입니다.

-
위 그림에서 검은색 부분은 벽으로 막혀있어 갈 수 없는 길이며, 흰색 부분은 갈 수 있는 길입니다. 캐릭터가 움직일 때는 동, 서, 남, 북 방향으로 한 칸씩 이동하며, 게임 맵을 벗어난 길은 갈 수 없습니다.
-
아래 예시는 캐릭터가 상대 팀 진영으로 가는 두 가지 방법을 나타내고 있습니다.
-
첫 번째 방법은 11개의 칸을 지나서 상대 팀 진영에 도착했습니다.

- 두 번째 방법은 15개의 칸을 지나서 상대팀 진영에 도착했습니다.

-
위 예시에서는 첫 번째 방법보다 더 빠르게 상대팀 진영에 도착하는 방법은 없으므로, 이 방법이 상대 팀 진영으로 가는 가장 빠른 방법입니다.
- 따라서 첫 번째 방법으로 상대 팀 진영에 간다면 캐릭턱 총 11칸을 지나갔으므로, 11을 return 하면 됩니다.
-
만약, 상대 팀이 자신의 팀 진영 주위에 벽을 세워두었다면 상대 팀 진영에 도착하지 못할 수도 있습니다. 예를 들어, 다음과 같은 경우에 당신의 캐릭터는 상대 팀 진영에 도착할 수 없습니다.

-
게임 맵의 상태
maps가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 캐릭터가 상대 팀 진영에 도착하기 위해서 지나가야 하는 칸의 개수의 최솟값을 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요. 단, 상대 팀 진영에 도착할 수 없을 때는-1을 return 해주세요. -
제한사항
- maps는 n x m 크기의 게임 맵의 상태가 들어있는 2차원 배열로, n과 m은 각각 1 이상 100 이하의 자연수입니다.
- n과 m은 서로 같을 수도, 다를 수도 있지만, n과 m이 모두 1인 경우는 입력으로 주어지지 않습니다.
- maps는 0과 1로만 이루어져 있으며, 0은 벽이 있는 자리, 1은 벽이 없는 자리를 나타냅니다.
- 처음에 캐릭터는 게임 맵의 좌측 상단인 (1, 1) 위치에 있으며, 상대방 진영은 게임 맵의 우측 하단인 (n, m) 위치에 있습니다.
- maps는 n x m 크기의 게임 맵의 상태가 들어있는 2차원 배열로, n과 m은 각각 1 이상 100 이하의 자연수입니다.
Solution
function solution(maps) {
let answer = -1;
const n = maps.length;
const m = maps[0].length;
const dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0];
const dy = [0, 1, 0, -1];
const isOutBoundary = (x, y) => {
return x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m;
}
const bfs = () => {
const queue = [[0, 0, 1]];
maps[0][0] = 0;
while(queue.length) {
const [x, y, count] = queue.shift();
if (x === n - 1 && y === m - 1) {
answer = count;
break;
}
for (let i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
let nx1 = x + dx[i];
let ny1 = y + dy[i];
if (isOutBoundary(nx1, ny1)) {
continue;
}
if (maps[nx1][ny1] === 1) {
maps[nx1][ny1] = 0;
queue.push([nx1, ny1, count + 1]);
}
}
}
}
bfs();
return answer;
}Programmers Problem : 여행경로
-
주어진 항공권을 모두 이용하여 여행경로를 짜려고 합니다. 항상 "ICN" 공항에서 출발합니다.
-
항공권 정보가 담긴 2차원 배열
tickets가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 방문하는 공항 경로를 배열에 담아 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요. -
제한사항
- 모든 공항은 알파벳 대문자 3글자로 이루어집니다.
- 주어진 공항 수는 3개 이상 10,000개 이하입니다.
tickets의 각 행 [a, b]는 a 공항에서 b 공항으로 가는 항공권이 있다는 의미입니다.- 주어진 항공권은 모두 사용해야 합니다.
- 만일 가능한 경로가 2개 이상일 경우 알파벳 순서가 앞서는 경로를 return 합니다.
- 모든 도시를 방문할 수 없는 경우는 주어지지 않습니다.
-
입출력 예
- 입력 : [["ICN", "SFO"], ["ICN", "ATL"], ["SFO", "ATL"], ["ATL", "ICN"], ["ATL","SFO"]]
- 출력 : ["ICN", "ATL", "ICN", "SFO", "ATL", "SFO"]
- 설명 :
- ["ICN", "SFO", "ATL", "ICN", "ATL", "SFO"] 순으로 방문할 수도 있지만 ["ICN", "ATL", "ICN", "SFO", "ATL", "SFO"] 가 알파벳 순으로 앞섭니다.
Solution
function solution(tickets) {
const totalTicketCount = tickets.length;
const visited = new Array(totalTicketCount).fill(false);
let answer;
tickets.sort();
const dfs = (airport, airportCount, path) => {
console.log(path);
if (airportCount === totalTicketCount && !answer) {
answer = path;
return;
}
for (let ticketIndex = 0; ticketIndex < totalTicketCount; ticketIndex++) {
if (visited[ticketIndex]) {
continue;
}
let [startAirport, endAirport] = tickets[ticketIndex];
if (airport === startAirport) {
visited[ticketIndex] = true;
dfs(endAirport, airportCount + 1, [...path, endAirport]);
visited[ticketIndex] = false;
}
}
}
dfs('ICN', 0, ['ICN']);
return answer;
}LeetCode Problem : Battleships in a Board
-
Given an
m x nmatrix board where each cell is a battleship'X'or empty'.', return the number of the battleships on board. -
Battleships can only be placed horizontally or vertically on board. In other words, they can only be made of the shape
1 x k(1row,kcolumns) ork x 1(krows,1column), wherekcan be of any size. At least one horizontal or vertical cell separates between two battleships (i.e., there are no adjacent battleships). -
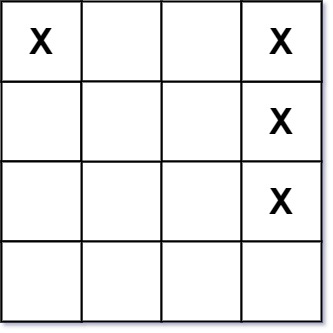
Example 1:
- Input: board = [["X",".",".","X"],[".",".",".","X"],[".",".",".","X"]]
- Output: 2
Solution
/**
* @param {character[][]} board
* @return {number}
*/
var countBattleships = function(board) {
const m = board.length;
const n = board[0].length;
const visited = Array.from({length: m}, () => new Array(n).fill(false));
let battleshipsCount = 0;
const dfs = (row, col) => {
visited[row][col] = true;
if ( col + 1 < n && board[row][col+1] === 'X') {
for (let nextCol = col + 1; nextCol < n; nextCol++) {
if (board[row][nextCol] === 'X') {
visited[row][nextCol] = true;
continue;
}
if (board[row][nextCol] === '.') {
return;
}
}
}
if ( row + 1 < m && board[row+1][col]=== 'X') {
for (let nextRow = row + 1; nextRow < m; nextRow++) {
if (board[nextRow][col] === 'X') {
visited[nextRow][col] = true;
continue;
}
if (board[nextRow][col] === '.') {
return;
}
}
}
}
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (!visited[row][col] && board[row][col] === 'X') {
dfs(row, col);
battleshipsCount++;
}
}
}
return battleshipsCount;
};Programmers Problem : 마법의 엘리베이터
- 마법의 세계에 사는 민수는 아주 높은 탑에 살고 있습니다. 탑이 너무 높아서 걸어 다니기 힘든 민수는 마법의 엘리베이터를 만들었습니다.
- 마법의 엘리베이터에는 -1, +1, -10, +10, -100, +100 등과 같이 절댓값이 10^c (c ≥ 0 인 정수) 형태인 정수들이 적힌 버튼이 있습니다.
- 마법의 엘리베이터의 버튼을 누르면 현재 층 수에 버튼에 적혀 있는 값을 더한 층으로 이동하게 됩니다.
- 단, 엘리베이터가 위치해 있는 층과 버튼의 값을 더한 결과가 0보다 작으면 엘리베이터는 움직이지 않습니다.
- 민수의 세계에서는 0층이 가장 아래층이며 엘리베이터는 현재 민수가 있는 층에 있습니다.
- 마법의 엘리베이터를 움직이기 위해서 버튼 한 번당 마법의 돌 한 개를 사용하게 됩니다.
- 예를 들어, 16층에 있는 민수가 0층으로 가려면 -1이 적힌 버튼을 6번, -10이 적힌 버튼을 1번 눌러 마법의 돌 7개를 소모하여 0층으로 갈 수 있습니다.
- 하지만, +1이 적힌 버튼을 4번, -10이 적힌 버튼 2번을 누르면 마법의 돌 6개를 소모하여 0층으로 갈 수 있습니다.
- 민수와 마법의 엘리베이터가 있는 층을 나타내는 정수
storey가 주어졌을 때, 0층으로 가기 위해 필요한 마법의 돌의 최소값을 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성하세요. - 제한사항
- 1 ≤
storey≤ 100,000,000
- 1 ≤
Solution
function solution(storey) {
let answer = 100000000;
const dfs = (num, movement) => {
if (movement >= answer) {
return;
}
if (num === 0) {
answer = movement;
return;
}
const digit = num % 10;
// 층을 내려갔을 경우
dfs(Math.floor(num/10), movement + digit);
// 층을 올라갔을 경우
dfs(Math.floor(num/10) + 1, movement + 10 - digit);
};
dfs(storey, 0);
return answer;
}