LeetCode Problem : N-th Tribonacci Number
-
The Tribonacci sequence Tn is defined as follows:
- T0 = 0, T1 = 1, T2 = 1, and Tn+3 = Tn + Tn+1 + Tn+2 for n >= 0.
-
Given
n, return the value of Tn- Constraints:
- 0 <= n <= 37
- The answer is guaranteed to fit within a 32-bit integer, ie. answer <= 2^31 - 1.
- Constraints:
-
Example 1:
- Input: n = 4
- Output: 4
- Explanation:
- T_3 = 0 + 1 + 1 = 2
- T_4 = 1 + 1 + 2 = 4
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var tribonacci = function(n, memo = []) {
if (memo[n]) return memo[n];
if (n === 0) return 0;
if (n === 1 || n === 2) return 1;
const thirdNumber = tribonacci(n - 1, memo) + tribonacci(n - 2, memo) + tribonacci(n - 3, memo)
memo[n] = thirdNumber;
return thirdNumber;
};LeetCode Problem : Min Cost Climbing Stairs
-
You are given an integer array
costwherecost[i]is the cost ofithstep on a staircase. Once you pay the cost, you can either climb one or two steps. -
You can either start from the step with index
0, or the step with index1. -
Return the minimum cost to reach the top of the floor.
- Constraints:
- 2 <= cost.length <= 1000
- 0 <= cost[i] <= 999
- Constraints:
-
Example 1:
- Input: cost = [10,15,20]
- Output: 15
- Explanation:
- You will start at index 1.
- Pay 15 and climb two steps to reach the top.
- The total cost is 15.
- You will start at index 1.
-
Example 2:
- Input: cost = [1,100,1,1,1,100,1,1,100,1]
- Output: 6
- Explanation:
- You will start at index 0.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 2.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 4.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 6.
- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach index 7.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 9.
- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach the top.
- The total cost is 6.
Solution
/**
* @param {number[]} cost
* @return {number}
*/
var minCostClimbingStairs = function(cost) {
const length = cost.length;
const memo = [];
function dp(cost, index) {
if (index < 0) return 0;
if (index === 0 || index === 1) return cost[index];
if (memo[index]) return memo[index];
memo[index] = cost[index] + Math.min(dp(cost, index - 1), dp(cost, index -2));
return memo[index];
}
return Math.min(dp(cost, length - 1), dp(cost, length - 2));
};LeetCode Problem : Pascal's Triangle II
- Given an integer
rowIndex, return therowIndexth(0-indexed) row of the Pascal's triangle. - In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
- Constraints:
- 0 <= rowIndex <= 33

Solution
/**
* @param {number} rowIndex
* @return {number[]}
*/
var getRow = function(rowIndex) {
if (!rowIndex) return [1];
let memo = [1, 1];
let currRow;
while(--rowIndex) {
currRow = [1];
for (let i = 0; i < memo.length - 1; i++) {
currRow.push(memo[i] + memo[i + 1]);
}
currRow.push(1);
memo = currRow;
}
return memo;
};LeetCode Problem : Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
-
You are given an array
priceswhereprices[i]is the price of a given stock on theithday. -
You want to maximize your profit by choosing a single day to buy one stock and choosing a different day in the future to sell that stock.
-
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return
0.- Constraints:
- 1 <= prices.length <= 10^5
- 0 <= prices[i] <= 10^4
- Constraints:
-
Example 1:
- Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
- Output: 5
- Explanation:
- Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
- Note that buying on day 2 and selling on day 1 is not allowed because you must buy before you sell.
-
Example 2 :
- Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
- Output: 0
- Explanation:
- In this case, no transactions are done and the max profit = 0.
Solution
/**
* @param {number[]} prices
* @return {number}
*/
var maxProfit = function(prices) {
const length = prices.length;
let profit = 0;
let buyPrice = Infinity;
let sellPrice;
for (let i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
if (prices[i] > buyPrice) continue;
buyPrice = prices[i];
for (let j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
sellPrice = prices[j];
if (sellPrice <= buyPrice) continue;
if (sellPrice - buyPrice > profit) {
profit = sellPrice - buyPrice;
}
}
}
return profit;
};LeetCode Problem : Climbing Stairs
-
You are climbing a staircase. It takes
nsteps to reach the top. -
Each time you can either climb
1or2steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top? -
Constraints:
- 1 <=
n<= 45
- 1 <=
-
Example 1:
- Input: n = 2
- Output: 2
- Explanation:
- 1 step + 1 step
- 2 steps
-
Example 2:
- Input: n = 3
- Output: 3
- Explanation:
- 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
- 1 step + 2 steps
- 2 steps + 1 step
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var climbStairs = function(n) {
let stairs = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
stairs[1] = 1;
stairs[2] = 2;
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
stairs[i] = stairs[i - 1] + stairs[i - 2];
}
return stairs[n];
};// 2 ~ 7의 계단 오르는 방법 경우의 수
2 : 1 + 1 = 2
3 : 1 + 2 = 3
4 : 1 + 3 + 1 = 5
5 : 1 + 4 + 3(2+1) = 8
6 : 1 + 5 + 6(3+2+1) + 1 = 13
7 : 1 + 6 + 10(4+3+2+1) + 4 = 21- 규칙 파악하기
- 점화식 : dp[n] = dp[n - 1] + dp[n - 2]
LeetCode Problem : Count Square Submatrices with All Ones
- Given a
m * nmatrix of ones and zeros, return how many square submatrices have all ones.
Examples
-
Example 1
- Input: matrix = [[0,1,1,1], [1,1,1,1], [0,1,1,1]]
- Output: 15
- Explanation:
- There are 10 squares of side 1.
- There are 4 squares of side 2.
- There is 1 square of side 3.
- Total number of squares = 10 + 4 + 1 = 15.
-
Example 2
- Input: matrix = [[1,0,1], [1,1,0], [1,1,0]]
- Output: 7
- Explanation:
- There are 6 squares of side 1.
- There is 1 square of side 2.
- Total number of squares = 6 + 1 = 7.
Constraints
- 1 <=
arr.length<= 300 - 1 <=
arr[0].length<= 300 - 0 <=
arr[i][j]<= 1
Solution
- 다른 사람 문제 풀이 참고(Python/JS/C++
O(m*n)sol by DP)- 각 배열 요소에 대한 정사각형의 최대 길이를 구하는 문제
- i행, j열 요소에 대한 정사각형의 최대 길이를 DP[i][j]라고할 때,
- i행, j열의 요소가 1일 경우,
- DP[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(DP[i-1][j-1], DP[i-1][j], DP[i][j-1])
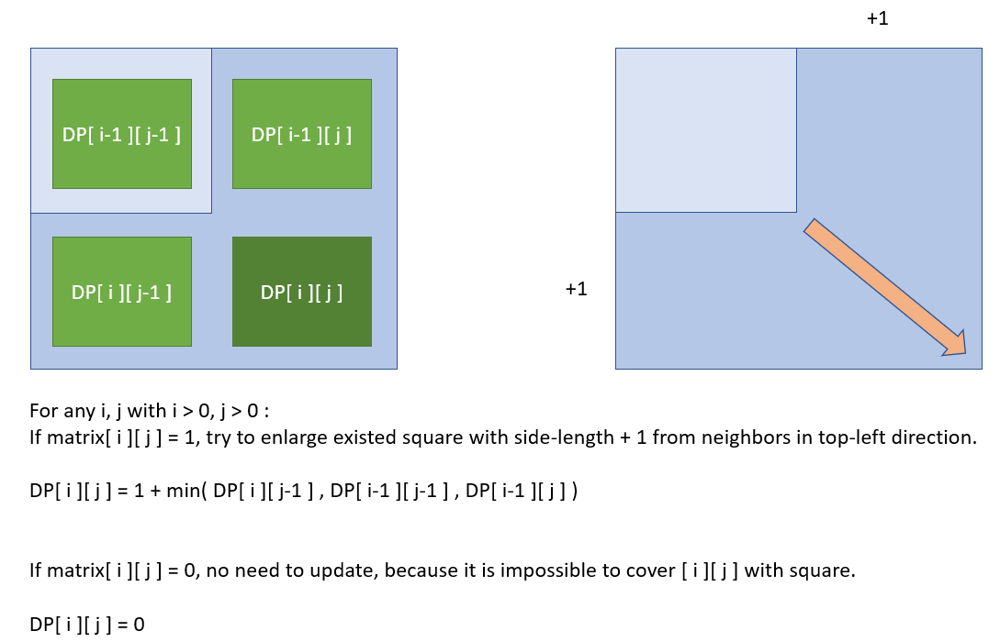
- DP Table
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
- total counts of squares = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 3 = 14
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number}
*/
var countSquares = function(matrix) {
let result = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
if (!matrix[i][j]) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && j > 0) {
matrix[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(matrix[i - 1][j - 1], matrix[i - 1][j], matrix[i][j - 1]);
}
result += matrix[i][j];
}
}
return result;
};