Problem 290. Word Pattern
-
Given a
patternand a strings, find ifsfollows the same pattern. -
Here follow means a full match, such that there is a bijection between a letter in
patternand a non-empty word ins.
Examples
-
Example 1:
- Input: pattern = "abba", s = "dog cat cat dog"
- Output: true
-
Example 2:
- Input: pattern = "abba", s = "dog cat cat fish"
- Output: false
-
Example 3:
- Input: pattern = "aaaa", s = "dog cat cat dog"
- Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= pattern.length <= 300patterncontains only lower-case English letters.1 <= s.length <= 3000scontains only lowercase English letters and spaces' '.sdoes not contain any leading or trailing spaces.- All the words in
sare separated by a single space.
Solution
/**
* @param {string} pattern
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var wordPattern = function(pattern, s) {
const strArr = s.split(' ');
const keyMap = new Map();
const valueMap = new Map();
if (pattern.length !== strArr.length) {
return false;
}
for (let i = 0; i < pattern.length; i++) {
const key = pattern[i];
const value = strArr[i];
if ((keyMap.has(key) && keyMap.get(key) !== value) ||
(valueMap.has(value) && valueMap.get(value) !== key)) {
return false;
}
keyMap.set(key, value);
valueMap.set(value, key);
}
return true;
};Problem 2305. Fair Distribution of Cookies
-
You are given an integer array
cookies, wherecookies[i]denotes the number of cookies in theithbag. You are also given an integerkthat denotes the number of children to distribute all the bags of cookies to. All the cookies in the same bag must go to the same child and cannot be split up. -
The unfairness of a distribution is defined as the maximum total cookies obtained by a single child in the distribution.
-
Return the minimum unfairness of all distributions.
Examples
- Example 1:
- Input: cookies = [8,15,10,20,8], k = 2
- Output: 31
- Explanation:
- One optimal distribution is [8,15,8] and [10,20]
- The 1st child receives [8,15,8] which has a total of 8 + 15 + 8 = 31 cookies.
- The 2nd child receives [10,20] which has a total of 10 + 20 = 30 cookies.
- The unfairness of the distribution is max(31,30) = 31.
- It can be shown that there is no distribution with an unfairness less than 31.
- Example 2:
- Input: cookies = [6,1,3,2,2,4,1,2], k = 3
- Output: 7
- Explanation:
- One optimal distribution is [6,1], [3,2,2], and [4,1,2]
- The 1st child receives [6,1] which has a total of 6 + 1 = 7 cookies.
- The 2nd child receives [3,2,2] which has a total of 3 + 2 + 2 = 7 cookies.
- The 3rd child receives [4,1,2] which has a total of 4 + 1 + 2 = 7 cookies.
- The unfairness of the distribution is max(7,7,7) = 7.
- It can be shown that there is no distribution with an unfairness less than 7.
Constraints:
2 <= cookies.length <= 81 <= cookies[i] <= 10^52 <= k <= cookies.length
Solution
/**
* @param {number[]} cookies
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var distributeCookies = function(cookies, k) {
const totalCookies = cookies.length;
const children = new Array(k).fill(0);
let answer = Infinity;
const backtracking = (index, children, cookies) => {
if (index === totalCookies) {
const maxCookie = Math.max(...children);
answer = Math.min(answer, maxCookie);
return;
}
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
children[i] += cookies[index];
backtracking(index + 1, children, cookies);
children[i] -= cookies[index];
}
}
backtracking(0, children, cookies);
return answer;
};Problem 86. Partition List
-
Given the
headof a linked list and a valuex, partition it such that all nodes less thanxcome before nodes greater than or equal tox. -
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Examples
- Example 1:
- Input: head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
- Output: [1,2,2,4,3,5]
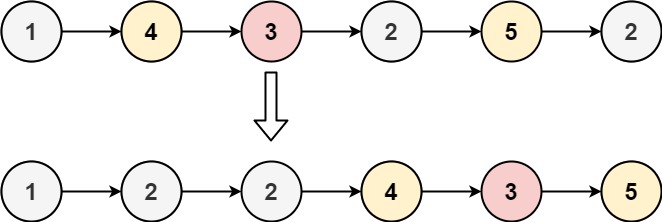
- Example 2:
- Input: head = [2,1], x = 2
- Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 200]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100-200 <= x <= 200
Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} x
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var partition = function(head, x) {
let beforeNodes = new ListNode(0);
let afterNodes = new ListNode(0);
let beforeCurr = beforeNodes;
let afterCurr = afterNodes;
while (head) {
if (head.val < x) {
beforeCurr.next = head;
beforeCurr = beforeCurr.next;
} else {
afterCurr.next = head;
afterCurr = afterCurr.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
afterCurr.next = null;
beforeCurr.next = afterNodes.next;
return beforeNodes.next;
};
Problem 2181. Merge Nodes in Between Zeros
-
You are given the
headof a linked list, which contains a series of integers separated by0's. The beginning and end of the linked list will haveNode.val == 0. -
For every two consecutive
0's, merge all the nodes lying in between them into a single node whose value is the sum of all the merged nodes. The modified list should not contain any0's. -
Return the
headof the modified linked list.
Examples
- Example 1:
- Input: head = [0,3,1,0,4,5,2,0]
- Output: [4,11]
- Explanation:
- The above figure represents the given linked list. The modified list contains
- The sum of the nodes marked in green: 3 + 1 = 4.
- The sum of the nodes marked in red: 4 + 5 + 2 = 11.

- Example 2:
- Input: head = [0,1,0,3,0,2,2,0]
- Output: [1,3,4]
- Explanation:
- The above figure represents the given linked list. The modified list contains
- The sum of the nodes marked in green: 1 = 1.
- The sum of the nodes marked in red: 3 = 3.
- The sum of the nodes marked in yellow: 2 + 2 = 4.

Constraints
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[3, 2 * 10^5]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000- There are no two consecutive nodes with
Node.val == 0. - The beginning and end of the linked list have
Node.val == 0.
Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeNodes = function(head) {
const nodes = new ListNode(0);
let currNode = nodes;
let sum = 0;
head = head.next;
while (head) {
if (head.val > 0) {
sum += head.val;
} else {
const node = new ListNode(sum);
currNode.next = node;
currNode = currNode.next;
sum = 0;
}
head = head.next;
}
return nodes.next;
};
정보 감사합니다.