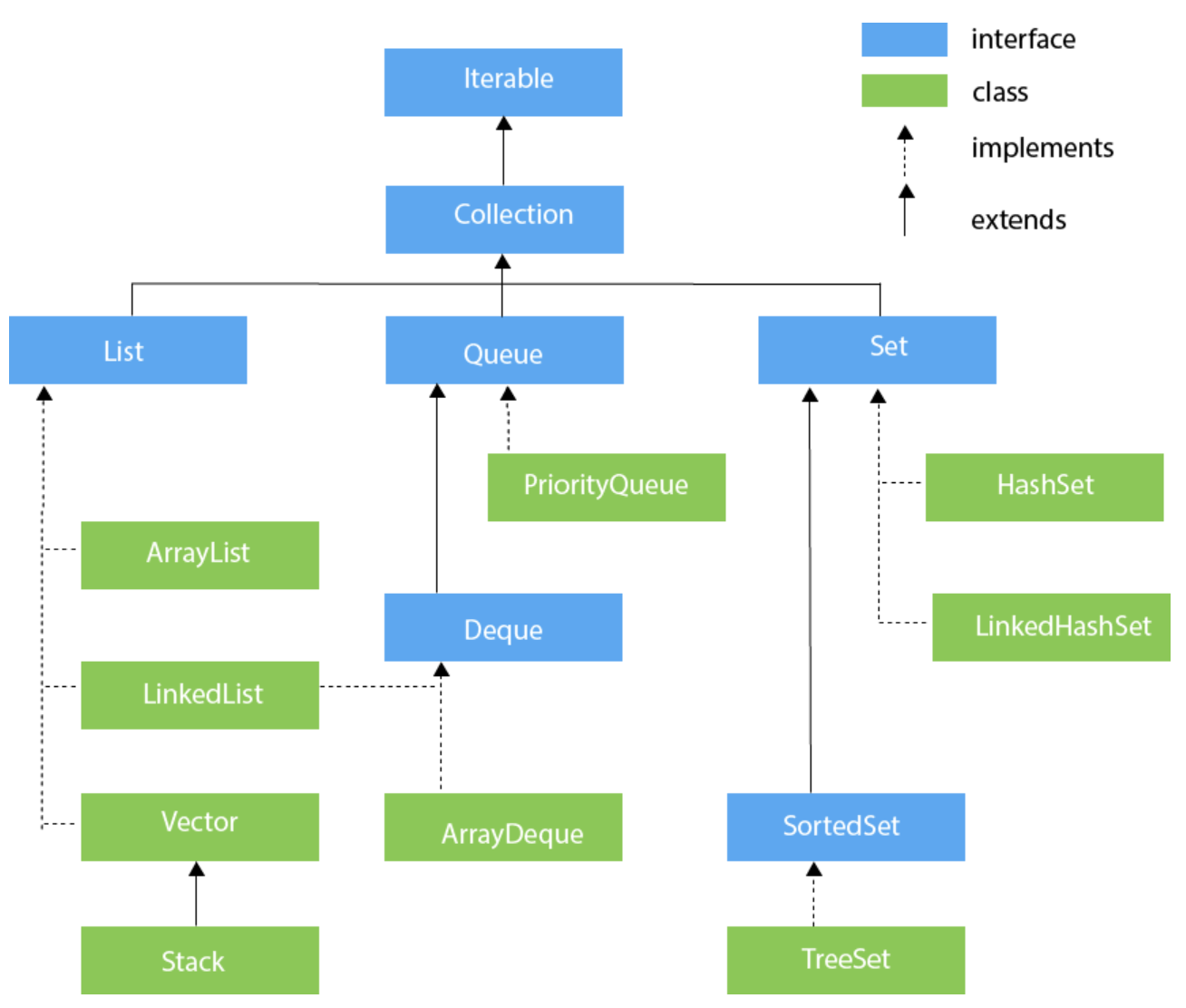
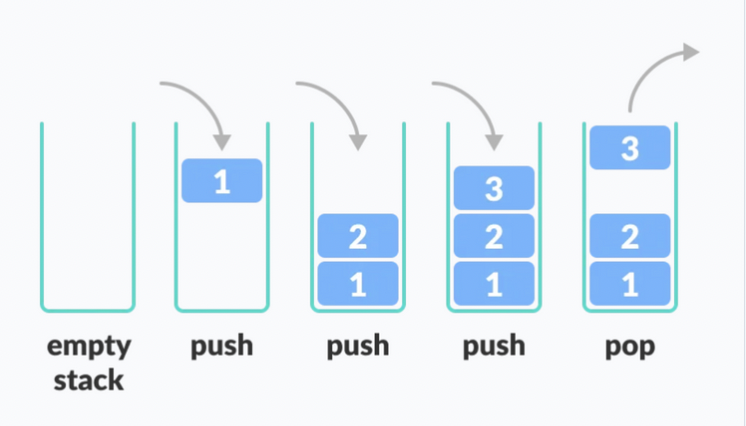
Stack
- last in, first out
- 입력 1 2 3 4 => 출력 4 3 2 1
package me.day21.collection.stack;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
class Book {
private String title;
public Book() {
}
public Book(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"title=" + title +
'}';
}
}
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Book> books = new Stack<>(); // Set 으로 왜 캐스팅 안하냐
// push()
books.push(new Book("Harry Potter"));
// add() : Stack 이 Vector 상속 하므로 List 인터페이스 메소드도 사용 가능
books.add(new Book("Christmas Carol"));
// addAll()
// List.of()
books.addAll(List.of(
new Book("Effective Java"), new Book("Clean Code"), new Book("Spring Framework Bible")));
System.out.println("books = " + books);
System.out.println("books.size() = " + books.size());
System.out.println();
// get(i)
for (int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("books.get(i) = " + books.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
// peek() : 스택에서 맨 위의(맨 뒤에 삽입한) 객체를 가져옴 (제거 ❌)
Book peekBook = books.peek();
System.out.println("peekBook = " + peekBook);
System.out.println("books = " + books);
System.out.println("books.size() = " + books.size());
System.out.println();
// pop() : 스택에서 맨 위의 객체를 가져옴 (제거 ⭕️)
Book popBook = books.pop();
System.out.println("popBook = " + popBook);
System.out.println("books = " + books);
System.out.println("books.size() = " + books.size());
System.out.println();
// remove() : Stack 이 Vector 상속 하므로 List 인터페이스 메소드도 사용 가능
// Stack의 순서 무시 하므로 권장하지 않음
Book popBook2 = books.remove(1);
System.out.println("popBook2 = " + popBook2);
System.out.println("books = " + books);
System.out.println("books.size() = " + books.size());
System.out.println();
// 삽입의 역순(맨 위의) 꺼내옴 (제거O)
while(!books.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("books.pop() = " + books.pop());
}
}
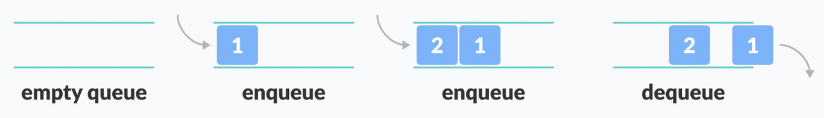
}Queue
- first in, first out
- 입력 1 2 3 4 => 출력 1 2 3 4
ADT: 추상적인 자료구조- queue는 인터페이스!
- 인터페이스만 있고, LinkedList가 구현 (실제 객체는 LinkedList에 저장)
``java
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("========= 큐 =========");
// Queue는 순서대로 유지하면 되므로 LinkedList를 사용해서 구현
Queue<Student> queue = new LinkedList<>();// List queue = new LinkedList<>(); 와 다른 점은 Queue 인터페이스의 api 이용??
// offer()
queue.offer(new Student("20211111", "이순신"));
queue.offer(new Student("20219873", "자바킹"));
queue.offer(new Student("20212222", "이제이"));
queue.offer(new Student("20171234", "이텔리"));
queue.offer(new Student("20045555", "이초잉"));
// add(), addAll(List.of())
// Queue는 LinkedList로 구현하므로 List 인터페이스 메소드도 사용 가능
queue.add(new Student("20089212", "이수근"));
queue.addAll(List.of(
new Student("20011222", "강호동"),
new Student("20071231", "유재석")));
System.out.println("queue = " + queue);
System.out.println("queue.size() = " + queue.size());
System.out.println();
// peek() : 큐 원소 가져옴 (제거 ❌)
Student peekStudent = queue.peek();
System.out.println("peekStudent = " + peekStudent);
System.out.println("queue = " + queue);
System.out.println("queue.size() = " + queue.size());
System.out.println();
// poll() : 큐 원소 가져옴 (제거 ⭕️)
Student pollStudent = queue.poll();
System.out.println("pollStudent = " + pollStudent);
System.out.println("queue = " + queue);
System.out.println("queue.size() = " + queue.size());
System.out.println();
//
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Student pollStudent2 = queue.poll();
System.out.println("pollStudent2 = " + pollStudent2);
System.out.println("queue = " + queue);
System.out.println("queue.size() = " + queue.size());
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("========= 우선 순위 큐=========");
// 우선순위가 존재하는 Queue (최소 힙 / 최대 힙을 통해 구현)
PriorityQueue<Student> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
// offer()
// PriorityQueue Queue에 원소 추가
priorityQueue.offer(new Student("20211111", "이순신"));
priorityQueue.offer(new Student("20219873", "자바킹"));
priorityQueue.offer(new Student("20212222", "이제이"));
priorityQueue.offer(new Student("20171234", "이텔리"));
priorityQueue.offer(new Student("20045555", "이초잉"));
// poll()
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
Student pollStudent2 = priorityQueue.poll();
System.out.println("pollStudent2 = " + pollStudent2);
System.out.println("priorityQueue = " + priorityQueue);
System.out.println("priorityQueue.size() = " + priorityQueue.size());
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}}