1. 에러 (핸들링 불가)
- JVM 문제 발생
StackOverFlowError
- JVM 고유의 스택 공간 범위 벗어났을 때 발생 (보통은 잘못된 재귀호출에 의해 발생)
VirtualMachineError
- JVM 손상되었거나 작동하는데 필요한 자원이 부족했을 때 발생하는 예외
OutOfMemoryError
- JVM의 힙 공간이 과도한 요구 또는 지속적인 누수로 인해 더이상 요청한 메모리를 할당할 수 없거나 OS의 이유로 스레드 생성하는데 실패했을 때 발생
2. 예외 (핸들링 가능)
- 개발자의 구현 실수나 사용자의 입력 실수에 의해 발생
- NullPointException
- ClassCastException
- 개발자가 미리 예측하여 미리 방지하거나 발생했을 경우 핸들링 가능
- 예외 발생되면 프로그램은 바로 종료. 다음 문장 실행되지 않음
- 종료를 막고 정상 실행 상태 유지 <사용자 입장>
- 로그 처리해서 왜 문제가 생겼는지를 개발자가 리팩토링 하기 위함 <개발자 입장>
- UserInputException() -> UserInputTypeException(), UserInputRangeException(), .. 세부적 핸들링 가능
계층도
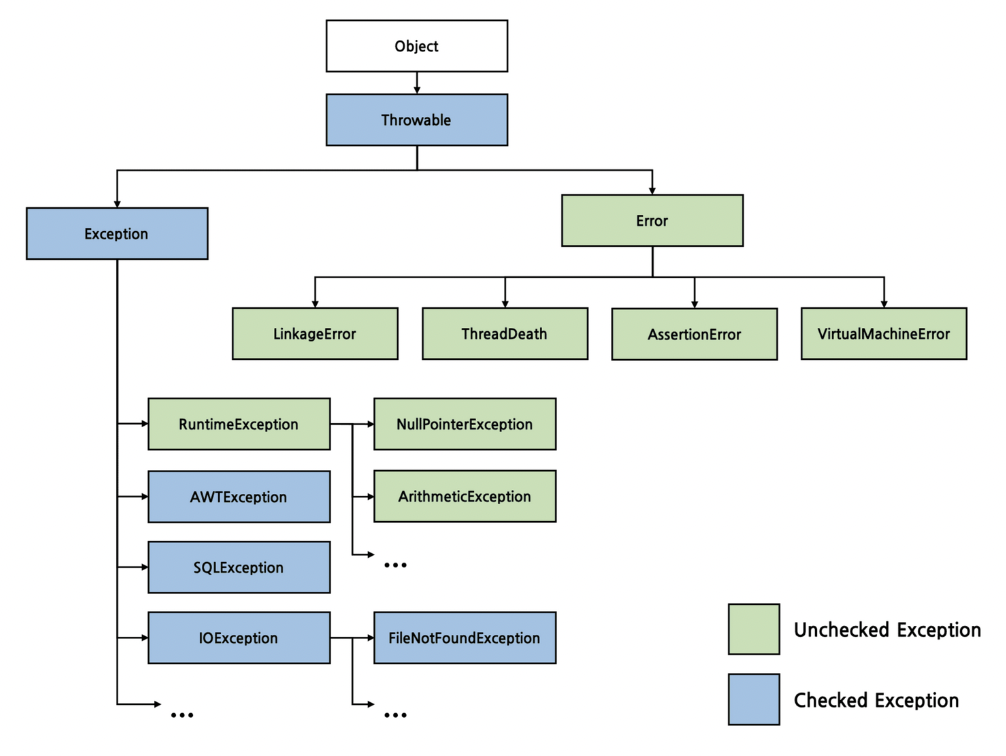
1. Object - Throwable - Exception/Error
- 예외 발생 원인을 메시지로 담을 수 있음
public IOException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause) }
- cause에 해당 예외를 발생시킨 예외도 같이 전달 가능 (Exception이 Trowable 상속하므로)
- 예외가 연결될 때 (chained exception) 연결된 예외 정보들을 기록하기도 함
getMessage()와 printStackTrace() 메소드 정의되어 있음
2. Unchecked (RuntimeException)
- try catch 하지 않아도 컴파일 에러 안뜨지만, 프로그램 중단의 가능성이 있음
Exception 밑의 RuntimeException 상속
NullPointException : null인 참조 변수의 멤버를 호출시 발생ClassCastException : 클래스 간의 형을 잘못 변환 했을 때 발생IndexOutOfBoundException : 배열 범위 벗어났을 때 발생ArithmeticException : 정수를 0으로 나누려고 했을 때 발생
- 대부분
if문으로 제어 가능해서 굳이 try~catch 사용 안함
3. Checked
- 개발자가 체크(try ~ catch) 안하면 컴파일 에러
- => too strict 하여 개발 도중 불편함 -> unchecked exception 으로 wrapping 하여 사용 (ORM)
- SQLException -> DatabaseAccessException (RuntimeException. 컴파일 에러X)
RuntimeException 상속 안하고 그냥 Exception만 상속- Java application 내에서 발생하지 않고, 외부 자원 접근과 관련
SQLException, IOException (파일, 디비)FileNotFoundException : 파일 읽으려고 하는데 파일 시스템에 해당하는 파일이 없다면
=> 다른 전략을 세워야함 (디폴트 이미지나 엑스박스 같은 이미지로 대신함)
try, catch, finally
try {
} catch (Exception1 e1) {
} catch (Exception2 e2) {
...
} catch (ExceptionN eN) {
} finally {
}
throws
- 해당 exception 객체를 메서드 호출부로 전달하여 거기서 try catch
- 계속 상위 메서드로 throws 하다가 main() 에서도 try catch 하지 않는다면 프로그램 종료
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
method();
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
}
}
public void method() throws Exception {
}
throw
throw exception : 해당 함수가 발생시킴method() throws Exception: 해당 함수가 호출 된 곳으로 전달- try catch 해주면 프로그램 종료 되지 않고 에러 메시지 출력 후 다음 코드 실행됨
- 계속 throw 하여 아무것도 핸들링 하지 않은 채 올라가는 것은 좋지 않음
public int nextInt(int radix) {
if ((typeCache != null) && (typeCache instanceof Integer)
&& this.radix == radix) {
int val = ((Integer)typeCache).intValue();
useTypeCache();
return val;
}
setRadix(radix);
clearCaches();
try {
String s = next(integerPattern());
if (matcher.group(SIMPLE_GROUP_INDEX) == null)
s = processIntegerToken(s);
return Integer.parseInt(s, radix);
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
position = matcher.start();
throw new InputMismatchException(nfe.getMessage());
}
}
- nextInt() 이 parseInt()에서 발생할 수 있는 예외를 랩핑 후 throw 했으므로 nextInt() 호출부에서(상위 메서드에서) 핸들링함
try {
age = scanner.nextInt();
} catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.pringln("[ERROR] please input int only.");
}
NullPointException
- 자바에서 제공
- RuntimeException 상속
public class NullPointeExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
if (str != null) {
System.out.println(str.length());
}
System.out.println("finally block");
System.out.println("main method exit...");
try {
System.out.println(str.length());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("finally block");
}
System.out.println("main method exit...");
}
}
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
- 개발자 실수 (코드를 직접적으로 수정해야 함. 실무에서는 이런 경우를 try~catch 사용 안함)
- "main exit..." 이 예외보다 먼저 출력되는 이유
- main, try ~ catch 두개의 스레드가 도는 것
- printStackTrace() 시간이 오래 걸리기 때 (
오호 그런거였구만)
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
try {
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main exit ...");
}
}
public class NumberFormatExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String string1 = "100";
String string2 = "10o";
try {
int intValue1 = Integer.parseInt(string1);
int intValue2 = Integer.parseInt(string2);
System.out.println("intValue1 = " + intValue1);
System.out.println("intValue2 = " + intValue2);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main exit ...");
}
}
ClassCastException
- 부모가 자식으로 캐스팅
- 상속 관계가 아닌 객체 간의 캐스팅
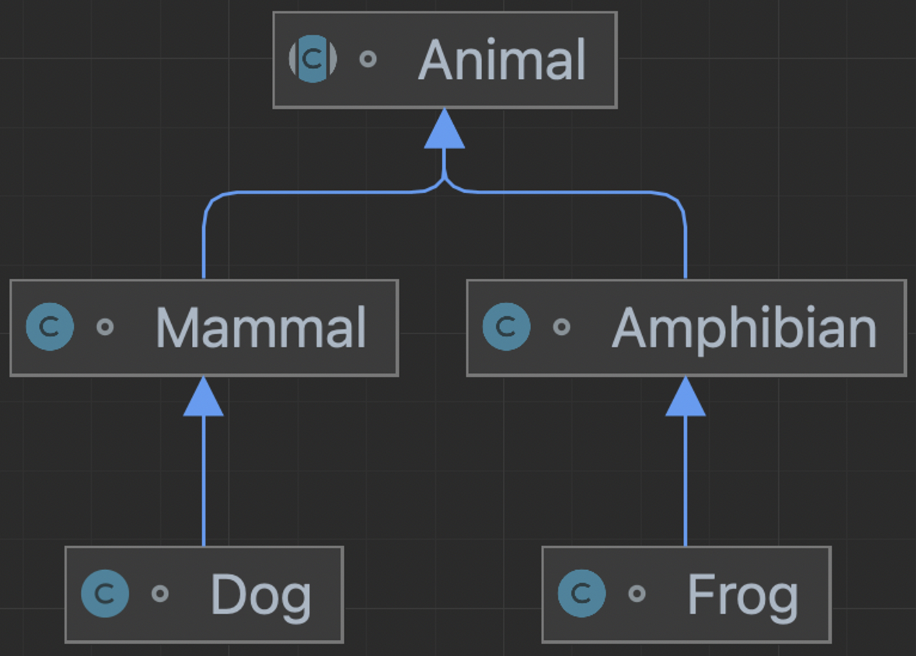
abstract class Animal {
protected abstract String getName();
}
class Mammal extends Animal {
@Override
protected String getName() {
return "Mammal";
}
}
class Amphibian extends Animal {
@Override
protected String getName() {
return "Amphibian";
}
}
class Dog extends Mammal {
@Override
protected String getName() {
return "Dog";
}
}
class Frog extends Amphibian {
@Override
protected String getName() {
return "Frog";
}
}
public class ClassCastExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frog frog = new Frog();
try {
birth(frog);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main exit ...");
}
public static void birth (Animal animal) throws ClassCastException {
Mammal mammal = (Mammal) animal;
System.out.println(mammal.getName() + " give birth to young");
Amphibian amphibian = (Amphibian) animal;
System.out.println(amphibian.getName() + " lay eggs");
}
}
상속 관계의 예외 객체 catch하기
- 모든 예외를 최상위 부모가 한번에 잡는 건 편하지만, 어떤 예외가 발생했는지 로그를 찍을 수 없다
- 부모 예외 객체의 로그 그대로 사용 (하나로 공통) => 자식 클래스의 캐치 블록을 최상단으로 올리면 구체적인 로깅 가능
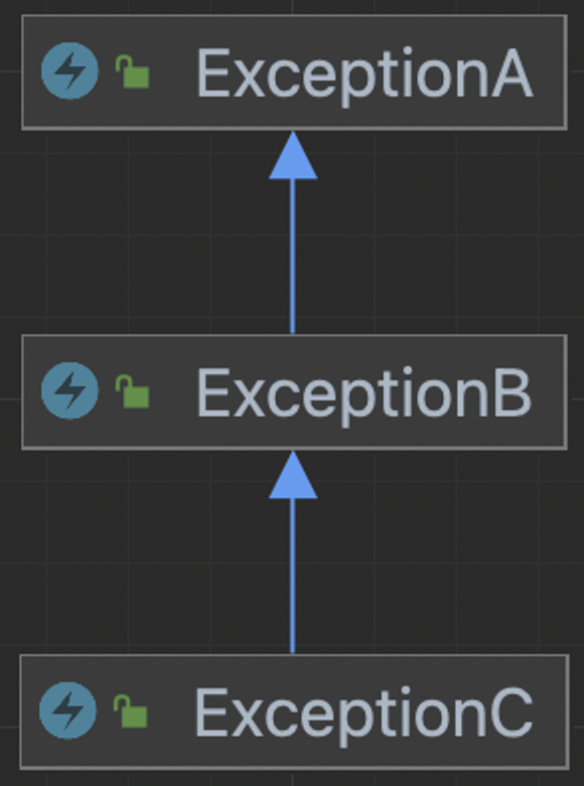
public class InheritedExceptionBadCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
throw new ExceptionC();
} catch (ExceptionA e) {
System.out.println(ExceptionA.class.getName() + " => catch");
}
}
}
public class InheritedExceptionGoodCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
throw new ExceptionC();
} catch (ExceptionC e) {
System.out.println(ExceptionC.class.getName() + " => catch");
} catch (ExceptionB e) {
System.out.println(ExceptionB.class.getName() + " => catch");
} catch (ExceptionA e) {
System.out.println(ExceptionA.class.getName() + " => catch");
}
}
}
사용자 정의 예외
- 예외 직접 만들기
- extends Exception/RuntimeException
- message, cause
- 사용자 정의 예외 클래스는 특정 어플리케이션에서만 사용하는 예외로서
특정 어플리케이션에 대한 내용을 알아야만 사용할 수 있으므로외부 리소스와 관련된 예외로 취급함
- 강제로 체크하라고 만든 예외 클래스 이므로 또는 강제로 체크하고 싶은 예외인 경우
- 회사마다 다름
- 직접 만든 예외 사용하기
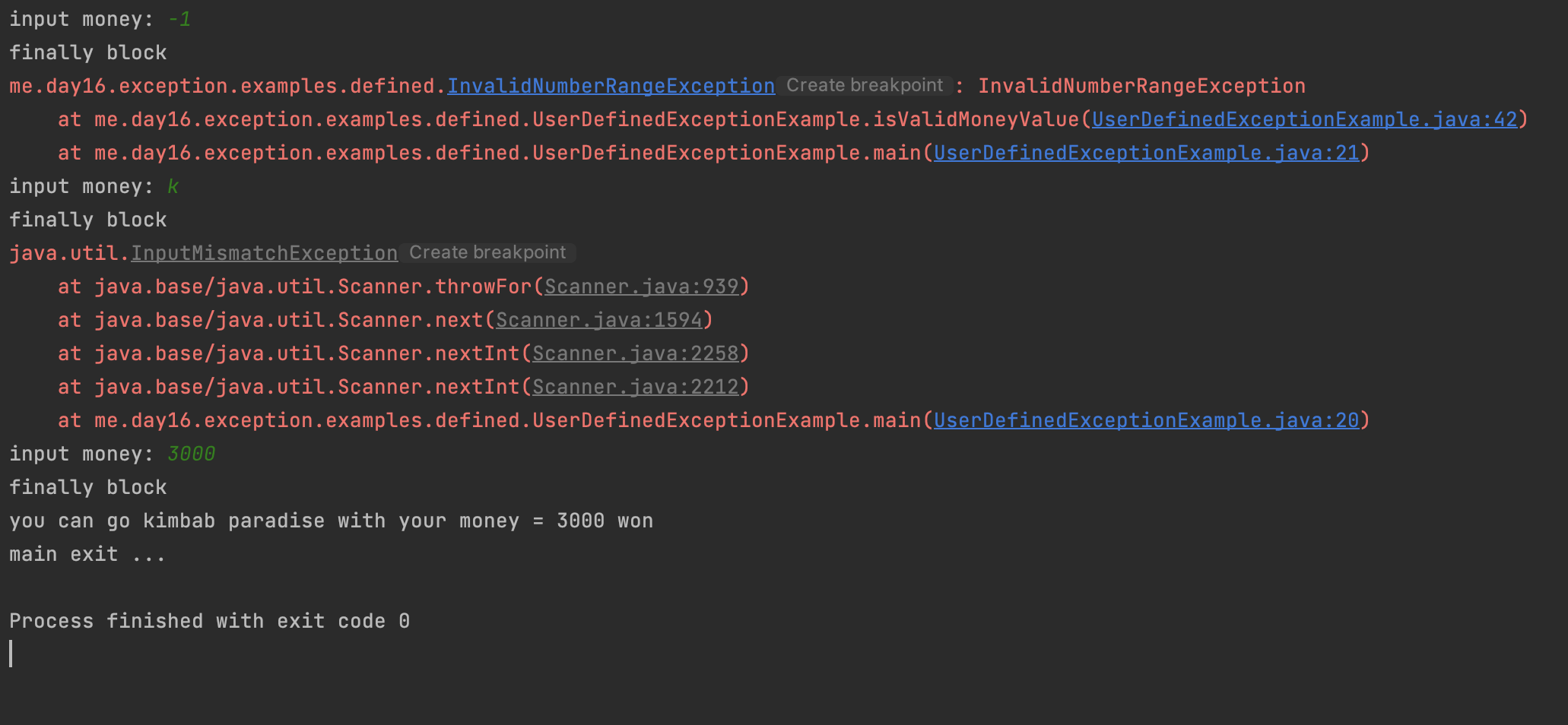
public class InvalidNumberRangeException extends Exception {
private final static String MESSAGE = "InvalidNumberRangeException";
public InvalidNumberRangeException() { super(MESSAGE); }
public InvalidNumberRangeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public InvalidNumberRangeException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}
public class UserDefinedExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int money;
while (true) {
try {
System.out.print("input money: ");
money = scanner.nextInt();
isValidMoneyValue(money);
break;
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
scanner.nextLine();
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidNumberRangeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("finally block");
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
System.out.print("you can go kimbab paradise ");
System.out.println("with your money = " + money + " won");
System.out.println("main exit ...");
scanner.close();
}
public static boolean isValidMoneyValue(int money) throws InvalidNumberRangeException {
if (money < 0) {
throw new InvalidNumberRangeException();
}
return true;
}
}



