
 2021/5/26
2021/5/26
뉴렉처, 자바의 신 시작
구조적 프로그래밍 - O
객체 프로그래밍 -
데이터 구조화
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExamProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exam exam = new Exam(); //-> 아래 풀어서 씀.
// Exam exam;//값(정수,실수 등) 형식이 아닌 참조형식 변수 - 무조건 기본적으로 담고 있는 공간에 연산자 new 통해서 무언갈 만들어 참조 시키지 않는이상, null을 갖고 있다.
// exam = new Exam(); //위의 exam은 현재 null인 상태의 빈 공간이었기 때문에 객체를 생성하여 kor, eng ... 공간을 만들어줌.
exam.kor = 30; // . 이라는 연산자를 통해 exam의 kor 안에 30이라는 값을 담을 수 있게 됨.
exam.eng = 40;
exam.math = 50;
input(exam);
print(exam);
}
public static void print(Exam exam) {
System.out.println("출력 부분");
int total = exam.kor + exam.eng + exam.math;
float avg = total/3.0f;
System.out.printf("국어 : %d\n", exam.kor);
System.out.printf("영어 : %d\n", exam.eng);
System.out.printf("수학 : %d\n", exam.math);
System.out.printf("평균 : %d\n", total);
System.out.printf("총점 : %f\n", avg);
System.out.println("--------------------");
}
public static void input(Exam exam) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("입력부분");
int kor, eng, math ;
do {
System.out.printf("국어 :");
kor = scan.nextInt();
if (kor < 0 || 100 < kor)
System.out.println("0~100만 가능");
}
while (kor < 0 || 100 < kor);
do {
System.out.printf("영어 : ");
eng = scan.nextInt();
if (eng < 0 || 100 < eng)
System.out.println("0~100만 가능");
}
while (eng < 0 || 100 < eng);
do {
System.out.printf("수학 : ");
math = scan.nextInt();
if (math < 0 || 100 < math)
System.out.println("0~100만 가능");
}
while (math < 0 || 100 < math);
exam.kor = kor;
exam.eng = eng;
exam.math = math;
}
}
public class Exam {
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
}
객체생성
Exam exam = new Exam();
Exam exam;값(정수,실수 등) 형식이 아닌 참조형식 변수 - 무조건 기본적으로 담고 있는 공간에 연산자 new 통해서 무언갈 만들어 참조 시키지 않는이상, null을 갖고 있다.
exam = new Exam(); 위의 exam은 현재 null인 상태의 빈 공간이었기 때문에 객체를 생성하여 kor 공간을 만들어줌.
exam.kor = 30;. 이라는 연산자를 통해 exam의 kor 안에 30이라는 값을 담을 수 있게 됨.
구조체 배열
Exam exam = new Exam();이 코드에서의 new : 실제 국어, 영어, 수학이 있는 Exam() 이라는 공간이 만들어진 것.
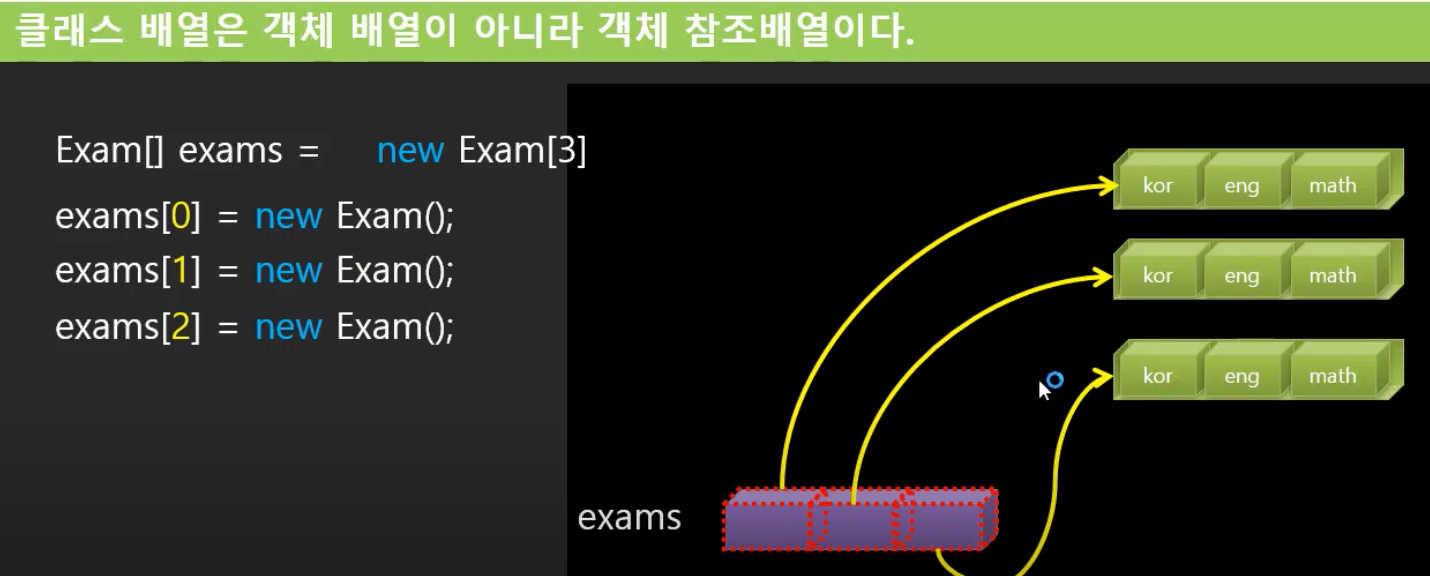
Exam[] exams = new Exam[3];
...
//exams[0].kor = 30; 은 존재 불가
exams[0] = new Exam();이 코드에서의 new : Exam[3]; 이라는 객체가 만들어진 것이 아니라 Exam 형식의 배열 3개가 만들어졌다는 뜻. 참조 변수 3개가 만들어진 것. 배열을 만드는데 사용된 new이다. 아직 주소를 저장할 수 있는 상황 밖에 되지 않는다.
그렇기 때문에 예를 들어 exam[0]을 사용하고 싶다면 새로운 객체를 생성하여 참조를 해주어야한다. (exams[0] = new Exam();)
2021/5/28
가변 길이 배열 구현하기

그림상 current에 위치한 곳에 도착했을 때 구분하는 방법
예로 capa가 3개라면 current가 0부터 시작하기 때문에 current 값과 capa의 값이 같으면 공간이 없어 늘려야할 상태인걸 알 수 있다.
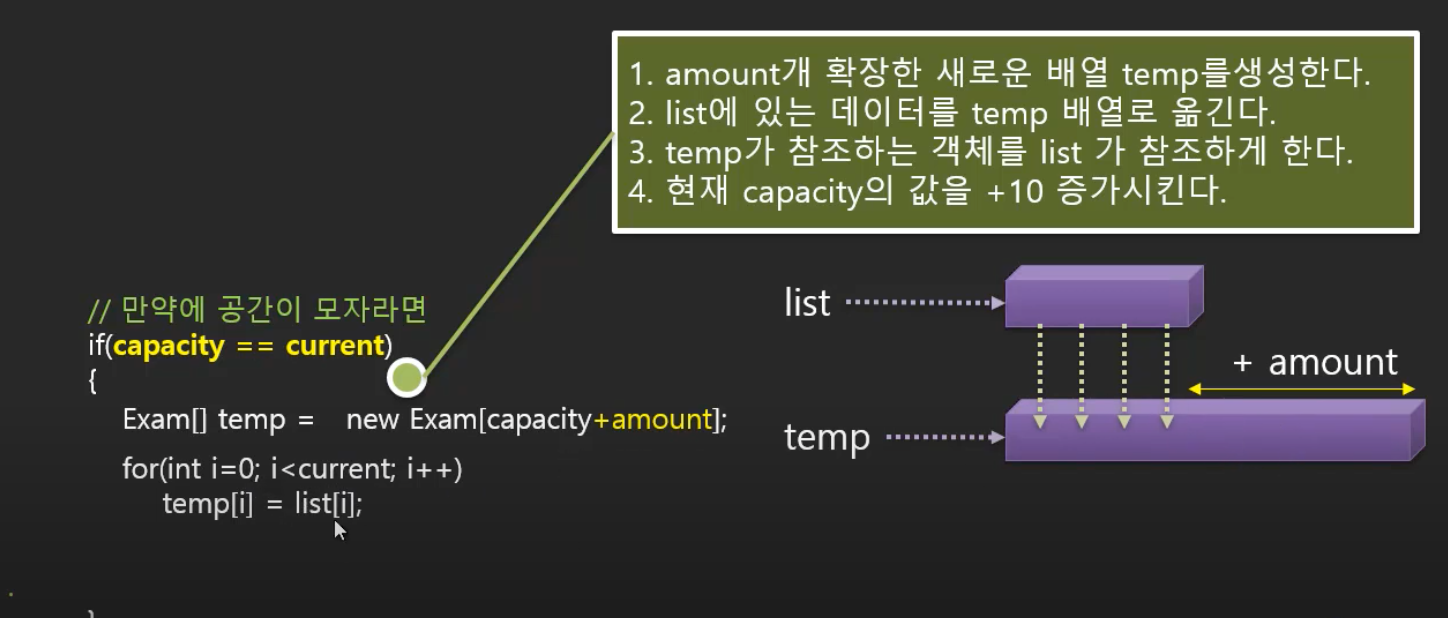 1. 공간을 늘려야하는 양을 알려주는 amount 수 만큼 확장된 capa+amount 크기의 배열을 새로 선언한다.
1. 공간을 늘려야하는 양을 알려주는 amount 수 만큼 확장된 capa+amount 크기의 배열을 새로 선언한다.
2. capa+amount 크기를 나타내는 temp 배열에 list의 배열을 반복문을 통해 옮겨준다.
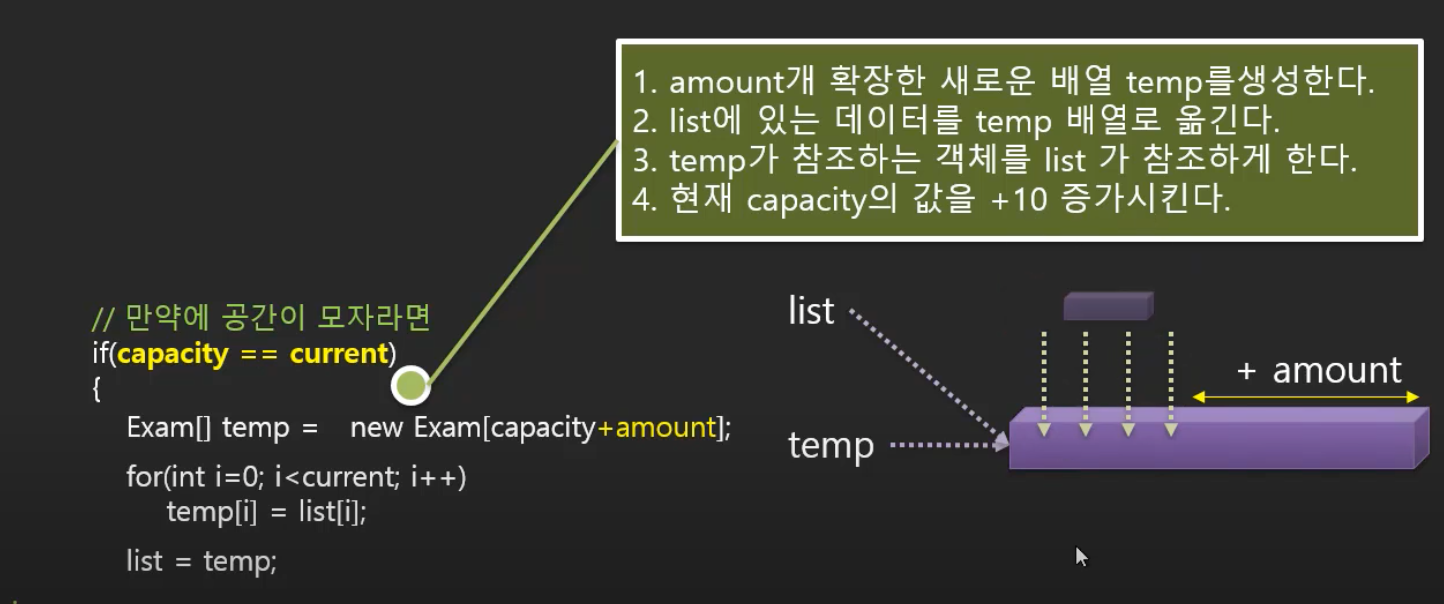 3. list가 temp를 참조하는 객체를 참조하게 한다.
3. list가 temp를 참조하는 객체를 참조하게 한다.
list = temp;
4. list는 사용하지 않기 때문에 자바에서는 list를 쓰레기 값으로 수거하게 된다.
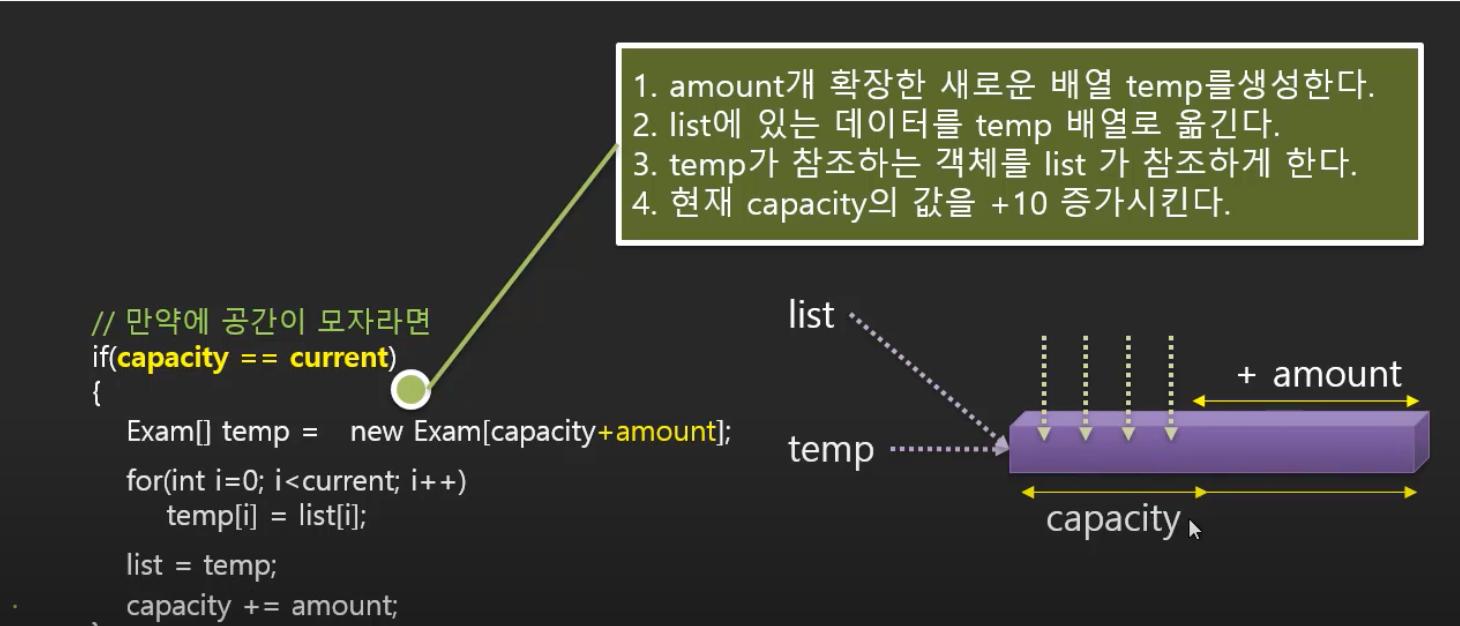 5. capa가 현재 3을 가리키고 있을 때 amount 만큼 더해진 부분으로 값을 변경해야하기 때문에 capa의 값을 amount만큼의 크기로 증가시켜준다.
5. capa가 현재 3을 가리키고 있을 때 amount 만큼 더해진 부분으로 값을 변경해야하기 때문에 capa의 값을 amount만큼의 크기로 증가시켜준다.
capa += amount;
2021/5/29
함수의 캡슐화
6월 멈춰..!!
자바 구조적프로그래밍 완강!
자바 객체지향 강의 시작 ^<^
캡슐화의 장점 : 묶은 캡슐들 안으로 코드의 오류가 한정된다.
캡슐화 이전의 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Program
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExamList list = new ExamList();
list.exams = new Exam[3];
list.current = 0;
//exams와 current를 포함하여 묶여있는 list라는 클래스를 전달하여 메소드에서 인자로 받을 때에서 List로 보내준다.
int menu;
boolean Loop = true;
while(Loop)
{
menu = inputMenu();
switch(menu) {
case 1:
inputList(list);
break;
case 2:
printList(list);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Bye");
Loop = false;
break;
default:
System.out.println("error 1~3 입력");
}
}
}
static void printList(ExamList list) {
printList(list, list.current);
}
static void printList(ExamList list, int size) {
System.out.println("성적 출력");
//int size = list.current;
Exam[] exams = list.exams;
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++) {
Exam exam = exams[i];
int kor = exam.kor;
int eng = exam.eng;
int math = exam.math;
int total = kor+eng+math;
float avg = total/3.0f;
System.out.printf("국어: %d\n ", kor);
System.out.printf("영어: %d\n ", eng);
System.out.printf("수학: %d\n ", math);
System.out.printf("총점: %d\n ", total);
System.out.printf("평균: %f\n ", avg);
}
}
static void inputList(ExamList list) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("성적입력");
int kor, eng, math;
do {
System.out.printf("국어 : ");
kor = scan.nextInt();
if (kor < 0 || 100 < kor)
System.out.println("국어 성적 범위는 1~100");
} while (kor < 0 || 100 < kor);
do {
System.out.printf("영어 : ");
eng = scan.nextInt();
if (eng < 0 || 100 < eng)
System.out.println("영어 성적 범위는 1~100");
} while (eng < 0 || 100 < eng);
do {
System.out.printf("수학 : ");
math = scan.nextInt();
if (math < 0 || 100 < math)
System.out.println("국어 성적 범위는 1~100");
} while (math < 0 || 100 < math);
Exam exam = new Exam();
exam.kor = kor;
exam.eng = eng;
exam.math = math;
Exam[] exams = list.exams;
int size = list.current;
if (exams.length == size) {
//1. 크기가 더 큰 배열을 생성하기
Exam[] temp = new Exam[size + 5];
// 2. 값을 이주 시키기
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
temp[i] = exams[i];
//3. list.exams가 새로 만든 temp배열을 넘겨받아 참조할 수 있게 한다.
list.exams = temp;
}
list.exams[list.current] = exam;
list.current++;
}
static int inputMenu() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("메인 메뉴");
System.out.println("1. 성적입력");
System.out.println("2. 성적출력");
System.out.println("3. 종료");
int menu = scan.nextInt();
return menu;
}
}public class ExamList {
Exam[] exams;
int current;
}public class Exam {
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
}함수 캡슐화 이후의 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Program
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExamList list = new ExamList();
ExamList.init(list);
//exams와 current를 포함하여 묶여있는 list라는 클래스를 전달하여 메소드에서 인자로 받을 때에서 List로 보내준다.
int menu;
boolean Loop = true;
while(Loop)
{
menu = inputMenu();
switch(menu) {
case 1:
ExamList.inputList(list);
break;
case 2:
ExamList.printList(list);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Bye");
Loop = false;
break;
default:
System.out.println("error 1~3 입력");
}
}
}
static int inputMenu() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("메인 메뉴");
System.out.println("1. 성적입력");
System.out.println("2. 성적출력");
System.out.println("3. 종료");
int menu = scan.nextInt();
return menu;
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExamList {
Exam[] exams;
int current;
static void printList(ExamList list) {
printList(list, list.current);
}
static void printList(ExamList list, int size) {
System.out.println("성적 출력");
//int size = list.current;
Exam[] exams = list.exams;
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++) {
Exam exam = exams[i];
int kor = exam.kor;
int eng = exam.eng;
int math = exam.math;
int total = kor+eng+math;
float avg = total/3.0f;
System.out.printf("국어: %d\n ", kor);
System.out.printf("영어: %d\n ", eng);
System.out.printf("수학: %d\n ", math);
System.out.printf("총점: %d\n ", total);
System.out.printf("평균: %f\n ", avg);
}
}
static void inputList(ExamList list) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("성적입력");
int kor, eng, math;
do {
System.out.printf("국어 : ");
kor = scan.nextInt();
if (kor < 0 || 100 < kor)
System.out.println("국어 성적 범위는 1~100");
} while (kor < 0 || 100 < kor);
do {
System.out.printf("영어 : ");
eng = scan.nextInt();
if (eng < 0 || 100 < eng)
System.out.println("영어 성적 범위는 1~100");
} while (eng < 0 || 100 < eng);
do {
System.out.printf("수학 : ");
math = scan.nextInt();
if (math < 0 || 100 < math)
System.out.println("국어 성적 범위는 1~100");
} while (math < 0 || 100 < math);
Exam exam = new Exam();
exam.kor = kor;
exam.eng = eng;
exam.math = math;
Exam[] exams = list.exams;
int size = list.current;
if (exams.length == size) {
//1. 크기가 더 큰 배열을 생성하기
Exam[] temp = new Exam[size + 5];
// 2. 값을 이주 시키기
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
temp[i] = exams[i];
//3. list.exams가 새로 만든 temp배열을 넘겨받아 참조할 수 있게 한다.
list.exams = temp;
}
list.exams[list.current] = exam;
list.current++;
}
public static void init(ExamList list) {
list.exams = new Exam[3];
list.current = 0;
}
}public class Exam {
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
}