
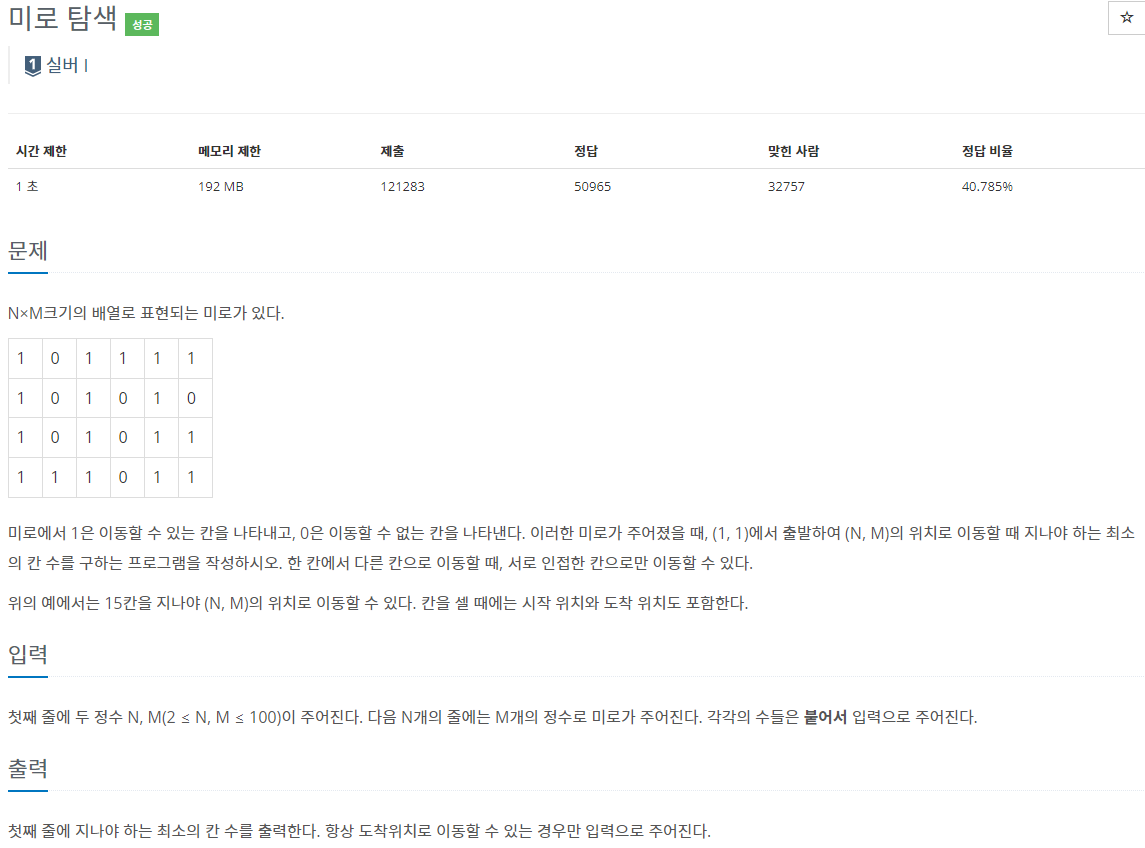
🔗 Problem
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2178
👩💻 Code
package baekjoon;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
// 미로 탐색
public class BJ2178 {
static class Pos {
int x;
int y;
int cnt;
Pos(int x, int y, int cnt){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.cnt = cnt;
}
}
static int n;
static int m;
static boolean[][] maze;
static boolean[][] visited;
static Queue<Pos> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
maze = new boolean[n+2][m+2];
visited = new boolean[n+2][m+2];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
String input = br.readLine();
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if(input.charAt(j) == '1') {
maze[i][j+1] = true;
}
}
}
queue.add(new Pos(1, 1, 1));
bfs();
}
static void bfs() {
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pos poll = queue.poll();
if(visited[poll.x][poll.y]) continue;
visited[poll.x][poll.y] = true;
if(poll.x == n && poll.y == m) {
System.out.println(poll.cnt);
System.exit(0);
}
if(maze[poll.x-1][poll.y] && !visited[poll.x-1][poll.y]) { // 상
queue.add(new Pos(poll.x-1, poll.y, poll.cnt+1));
}
if(maze[poll.x+1][poll.y] && !visited[poll.x+1][poll.y]) { // 하
queue.add(new Pos(poll.x+1, poll.y, poll.cnt+1));
}
if(maze[poll.x][poll.y-1] && !visited[poll.x][poll.y-1]) { // 좌
queue.add(new Pos(poll.x, poll.y-1, poll.cnt+1));
}
if(maze[poll.x][poll.y+1] && !visited[poll.x][poll.y+1]) { // 우
queue.add(new Pos(poll.x, poll.y+1, poll.cnt+1));
}
}
}
}
📌 Note
아이디어
- 오랜만에
BFS구현하느라 조금 해맸다. 맞았습니다후 메모리 효율이 높은 다른 풀이를 확인해보니,
상/하/좌/우 탐색을 배열에 담아서 탐색하는 방식으로 if문 4개를 1개로 합쳐 구현하였다.
