요구사항
이미 개발 해놓은 컨트롤러와 서비스가 있는 상황에서 json 또는 form-data로 요청이 들어올 때 데이터를 파싱하여 Attribute에 저장해 컨트롤러 코드의 변경이 거의 없이 필요한 데이터를 getAttribute해서 가져올 수 있도록 JsonFilter와 Formdata를 처리하는 filter를 구현해야 한다.
추가적으로 Jwt 를 이용한 유저 인증이 필요하기 때문에 유저가 로그인 하면 DB에서 role과 id 등 User 정보를 가져와 Jwt를 생성하여 Header에 저장하도록 한다.
로그인 시나리오
- LoginController
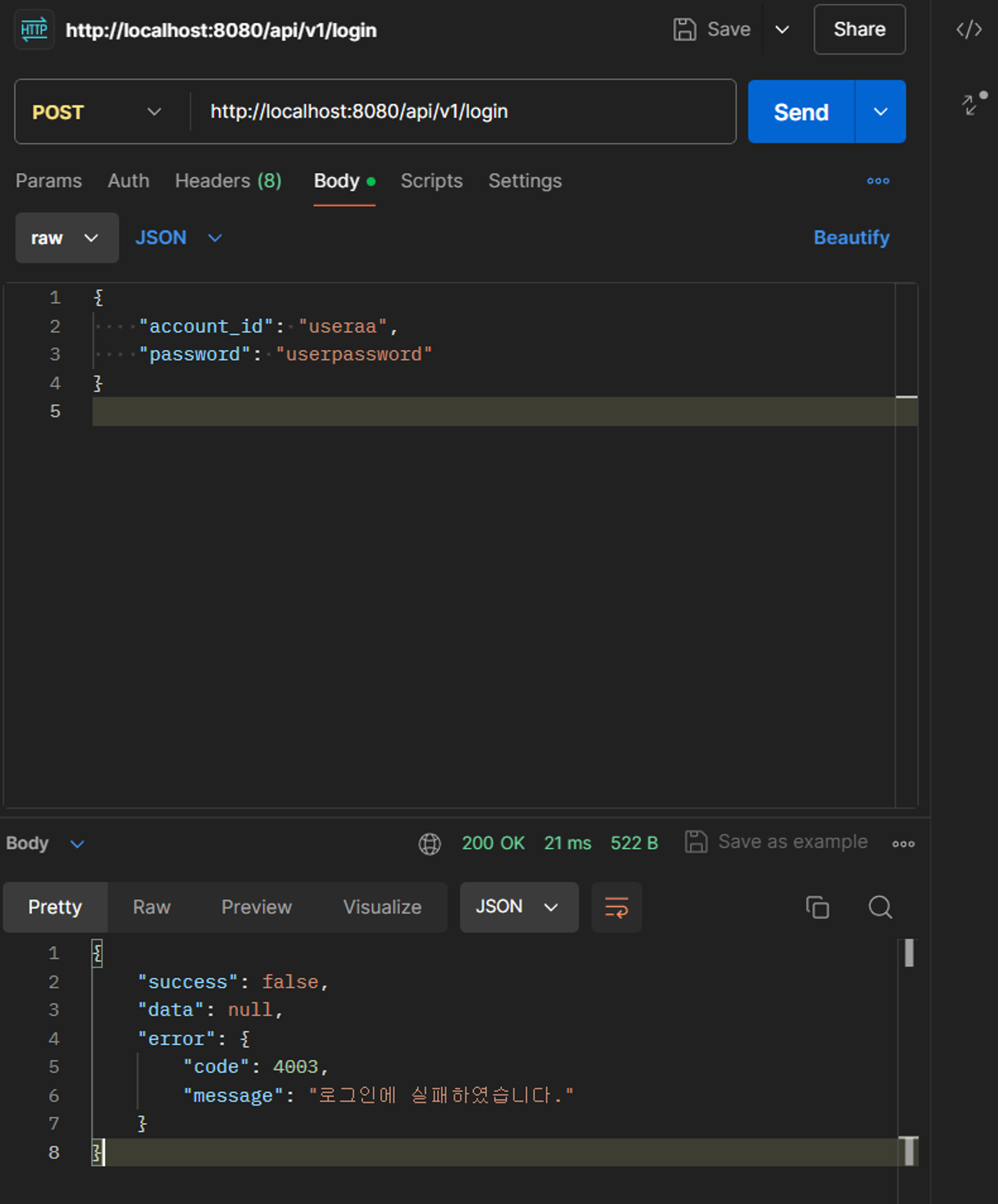
http://localhost:8080/api/v1/login 엔드 포인트로 account_id와 password가 있는 json을 받아 POST 요청이 들어온다.
- UserService
- UserService의 login이 호출된다.
- login 내부의 authenticate가 호출된다.
- authenticate 내부의 findByAccountId가 호출된다. 입력 받은 account_id가 DB 상에 존재하는지 확인 후 해당 account_id(unique)에 해당하는 user 를 반환한다.
- account_id를 통해 반환된 user의 password를 비교해 인증한다.
- user가 존재하고 authenticate도 true라면 jwt 를 생성한다. (에러인 경우 exception throw)
UserService
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class UserService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
private final JwtService jwtService;
// Find user by accountId
public Optional<User> findByAccountId(String accountId) {
Optional<User> user = userRepository.findByAccountId(accountId);
log.info("Found user for accountId: {}, ROLE: {}", accountId, user.isPresent() ? user.get().getRole() : "not found");
return user;
}
// Authenticate user by accountId and password
public boolean authenticate(String accountId, String password) {
Optional<User> user = findByAccountId(accountId);
boolean isAuthenticated = user.isPresent() && password.equals(user.get().getPassword());
log.info("Authentication attempt for accountId {}, Authenticate: {}", accountId, isAuthenticated ? "success" : "failure");
return isAuthenticated;
}
// Login user by accountId and password
public ResponseDto<?> login(String accountId, String password) {
try {
User user = findByAccountId(accountId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new CommonException(ErrorCode.FAILURE_LOGIN));
if (!authenticate(accountId, password)) {
throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.FAILURE_LOGIN);
}
String token = jwtService.generateToken(user);
log.info("Login successful for account: {}", accountId);
return ResponseDto.ok(new LoginResponseDto(token));
} catch (CommonException e) {
log.warn("Login failed for account: {}", accountId);
return ResponseDto.fail(e);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during login for account: {}", accountId, e);
return ResponseDto.fail(new CommonException(ErrorCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR));
}
}
}- JwtService
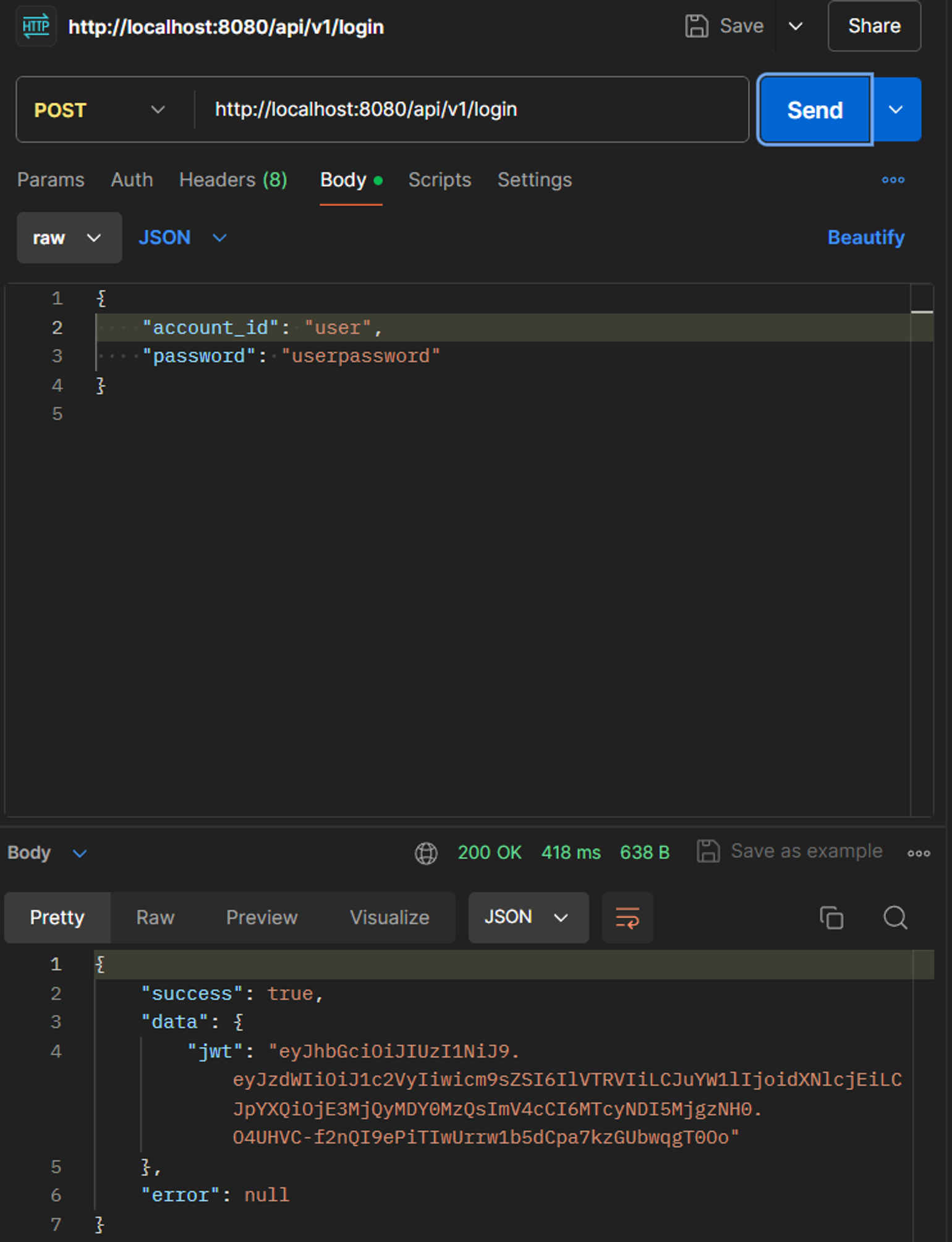
- generateToken에서 account_id, role, name 의 정보가 포함되도록 token을 생성한다.
- 이때 getSignKey의 secretKey는 application.yml에 정의된 secret_key를 사용한다.
- 응답 반환
- 인증 성공 시, 생성된 JWT를 포함한 ResponseDto를 반환한다.
테스트를 위해 JWT를 response에 포함시켰지만 실제 환경에서는 보안상 포함시키지 않는 것이 좋다.JwtService
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class JwtService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
@Value("${jwt.secret-key}")
private String secretKey;
@Value("${jwt.expiration-time}")
private long expirationTime;
// Get the signing key by using the secret key
private SecretKey getSigningKey() {
byte[] keyBytes = secretKey.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
return Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(keyBytes);
}
// Parse the token and get the user's accountId
public String generateToken(User user) {
List<String> authorities = user.getPermissions().stream()
.map(permission -> permission.getUrl() + "_" + permission.getPermission().name())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// Generate the token which contains the user's accountId, role, name, authorities, issuedAt, expiration, and signing key
return Jwts.builder()
.setSubject(user.getAccountId())
.claim("role", user.getRole().getName())
.claim("name", user.getName())
.claim("authorities", authorities)
.setIssuedAt(new Date())
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + expirationTime))
.signWith(getSigningKey(), SignatureAlgorithm.HS256)
.compact();
}
// Parse the token and get the user's accountId
public Claims getClaimsFromToken(String token) {
try {
return Jwts.parserBuilder()
.setSigningKey(getSigningKey())
.build()
.parseClaimsJws(token)
.getBody();
} catch (ExpiredJwtException e) {
log.warn("The token is expired and not valid anymore", e);
return null;
}
}
}로그인 이후 요청 처리
- 클라이언트에서 JWT를 이후 요청의 Authrization 헤더에 포함시킨다.
- JwtAuthenticationFilter
-
모든 요청에 대해 JWT를 검증한다.
검증 과정
- extractToken을 통해 요청 헤더에서 토큰 추출
- JwtService의 validateToken을 통해 토큰 검증
- 유효하다면 getClaimsFromToken을 통해 사용자 정보와 권한 추출
- 유효성 확인 후 Authentication 객체를 생성하고 Security Context에 저장
-
- 권한 기반 접근 제어
- SecurityConfig에 정의된 규칙에 따라 접근 제어
- 예를 들어 /admin 경로는 ADMIN 역할만 접근 가능, /user 경로는 ADMIN, USER, MANAGER 접근 가능
JwtAuthenticationFilter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Slf4j
public class JwtAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private final CustomUserDetailService customUserDetailService;
private final JwtService jwtService;
private final SecurityContextRepository securityContextRepository;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
String token = extractToken(request);
Claims claims = jwtService.getClaimsFromToken(token);
String accountId = claims.getSubject();
// Load user details from the database by account Id
CustomUserDetails userDetails = (CustomUserDetails) customUserDetailService.loadUserByUsername(accountId);
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
userDetails, null, userDetails.getAuthorities());
authentication.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
// Set the authentication in the SecurityContext
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);
securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response); // Save the SecurityContext using the SecurityContextRepository
} catch (Exception e) {
// If an exception occurs, clear the SecurityContext
log.error("Unable to set user authentication: {}", e.getMessage());
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
// Continue the filter chain
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private String extractToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String bearerToken = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (bearerToken != null && bearerToken.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return bearerToken.substring(7);
}
return null;
}
}XSS 방지 (json)
- HTMLCharacterEscapes
- XSS방지 처리할 특수 문자 지정, StringEscapeUtils를 사용해 Escape 처리
- XssConfig
- *ObjectMapper에 HTMLCharacterEscapes 설정
- MessageConverter에 등록해 XSS 방지 처리
JSON을 Java 객체로 역직렬화 하거나 Java 객체를 JSON으로 직렬화할 때 사용하는 Jackson 라이브러리의 클래스이다.
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter의 생성자에서 ObjectMapper를 생성해 가지고 있다.
- 이 방식은 필터처럼 요청이 들어와서 컨트롤러로 전달되기 전에 처리되는 것이 아니라, JSON 데이터가 직렬화되거나 역직렬화될 때 자동으로 이스케이프 처리를 수행하여 XSS 공격을 예방한다.
- lucy-xss-servlet-filter는 Servlet Filter 단에서 < 등의 특수 문자를 < 등으로 변환해주지만 form-data에만 적용된다는 단점이 있다. 따라서 JSON에 대해서 처리할 수 있도록 Response를 클라이언트로 내보내는 단계에서 처리하기 위해 ObjectMapper를 MessageConverter에 등록하고 특수문자를 처리하는 방법을 사용하였다.
HTMLCharacterEscapes
public class HTMLCharacterEscapes extends CharacterEscapes {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final int[] asciiEscapes;
public HTMLCharacterEscapes() {
// Define ASCII characters to escape
asciiEscapes = CharacterEscapes.standardAsciiEscapesForJSON();
asciiEscapes['<'] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
asciiEscapes['>'] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
asciiEscapes['&'] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
asciiEscapes['\"'] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
asciiEscapes['('] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
asciiEscapes[')'] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
asciiEscapes['#'] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
asciiEscapes['\''] = CharacterEscapes.ESCAPE_CUSTOM;
}
@Override
public int[] getEscapeCodesForAscii() {
return asciiEscapes;
}
@Override
public SerializableString getEscapeSequence(int ch) {
return new SerializedString(StringEscapeUtils.escapeHtml4(Character.toString((char) ch)));
}
}XssConfig
@Configuration
public class XssConfig {
@Bean
public ObjectMapper objectMapper() {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
objectMapper.getFactory().setCharacterEscapes(new HTMLCharacterEscapes());
return objectMapper;
}
@Bean
public MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter jsonEscapeConverter(ObjectMapper objectMapper) {
return new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(objectMapper);
}
}Xss 방지 (form-data)
form-data에서의 Xss 방지는 Apache text 라이브러리에서 제공하는 StringEscapeUtils의 escapeHtml4 메서드를 사용하여 처리해주었다.
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
@Order(2) // After Excute JSONFilter, which is Order(1)
public class MultipartFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private final MultipartResolver multipartResolver;
private final FileService fileService;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
// Check if the request is a multipart request
if (multipartResolver.isMultipart(request) && !(request instanceof ContentCachingRequestWrapper)) {
MultipartHttpServletRequest multipartRequest = multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request);
try {
processMultipartRequest(multipartRequest); // Process the multipart request
filterChain.doFilter(multipartRequest, response); // Continue the filter chain with the multipart request
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error in MultipartFilter", e);
throw new ServletException(e);
}
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response); // Continue the filter chain with the not multipart request
}
}
private void processMultipartRequest(MultipartHttpServletRequest multipartRequest) throws IOException {
// Store all request parameters as attributes
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = multipartRequest.getParameterMap();
for (Map.Entry<String, String[]> entry : parameterMap.entrySet()) {
String[] sanitizedValues = new String[entry.getValue().length];
for (int i = 0; i < entry.getValue().length; i++) {
sanitizedValues[i] = StringEscapeUtils.escapeHtml4(entry.getValue()[i]);
}
multipartRequest.setAttribute(entry.getKey(), sanitizedValues);
}
// Process file upload
MultipartFile file = multipartRequest.getFile("file");
if (file != null) {
try {
FileUploadResponseDto responseDto = fileService.uploadFile(file); // Upload the file
multipartRequest.setAttribute("fileUploadResult", responseDto); // Set the file upload result as a request attribute
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error during file upload: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.FILE_UPLOAD_FAILED);
}
} else {
log.warn("No file found in the multipart request");
}
}
}
파일 처리
Json
파일 처리는 json 의 경우에는 클라이언트에서 파일을 Base64 형식으로 인코딩해서 보내기 때문에 body의 형식을 보고 구분할 수 없었다. 따라서 어떤 uri로 request가 들어오는지를 확인하여 특정 url인 경우 파일 처리를 설정 하였다.
form-data
form-data로 요청이 오는 경우, 파일은 Multipart/form-data 형식으로 들어오기 때문에 body의 type을 확인하여 multipart 형식이라면 파일 처리를 하도록 하였다.
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class FileService {
private final FileInfoRepository fileInfoRepository;
private final FilePathRepository filePathRepository;
private final FileUploadProperties fileUploadProperties;
@Transactional
public FileUploadResponseDto uploadFileWithPathType(MultipartFile file, String pathType) throws IOException {
FilePath filePath = filePathRepository.findByPathType(pathType)
.orElseThrow(() -> new CommonException(ErrorCode.INVALID_PATH_TYPE));
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
String extension = getFileExtension(originalFilename);
if (!isAllowedExtension(extension)) {
throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.FILE_EXTENSION_NOT_ALLOWED);
}
String renamedFilename = generateUniqueFilename(originalFilename);
Path fullPath = Paths.get(filePath.getPath(), renamedFilename);
Files.createDirectories(fullPath.getParent());
Files.copy(file.getInputStream(), fullPath);
setFilePermissions(fullPath);
FileInfo fileInfo = FileInfo.builder()
.originalName(originalFilename)
.renamedName(renamedFilename)
.path(fullPath.toString())
.size(file.getSize())
.contentType(file.getContentType())
.build();
FileInfo savedFileInfo = fileInfoRepository.save(fileInfo);
return new FileUploadResponseDto(
savedFileInfo.getId(),
savedFileInfo.getOriginalName(),
savedFileInfo.getRenamedName(),
savedFileInfo.getPath(),
savedFileInfo.getSize(),
savedFileInfo.getContentType()
);
}
@Transactional
public FileUploadResponseDto uploadFile(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
String extension = getFileExtension(originalFilename);
if (!isAllowedExtension(extension)) {
throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.FILE_EXTENSION_NOT_ALLOWED);
}
// Generate unique filename
String renamedFilename = generateUniqueFilename(originalFilename);
Path filePath = Paths.get(fileUploadProperties.getPath(), renamedFilename);
Files.copy(file.getInputStream(), filePath);
setFilePermissions(filePath);
FileInfo fileInfo = FileInfo.builder()
.originalName(originalFilename)
.renamedName(renamedFilename)
.path(filePath.toString())
.size(file.getSize())
.contentType(file.getContentType())
.build();
FileInfo savedFileInfo = fileInfoRepository.save(fileInfo);
return new FileUploadResponseDto(
savedFileInfo.getId(),
savedFileInfo.getOriginalName(),
savedFileInfo.getRenamedName(),
savedFileInfo.getPath(),
savedFileInfo.getSize(),
savedFileInfo.getContentType()
);
}
private String getFileExtension(String filename) {
return filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf(".") + 1).toLowerCase();
}
private boolean isAllowedExtension(String extension) {
log.info("Allowed extensions: {}", fileUploadProperties.getAllowedExtensions());
return fileUploadProperties.getAllowedExtensions().contains(extension);
}
// Generate unique filename using UUID
private String generateUniqueFilename(String originalFilename) {
String extension = getFileExtension(originalFilename);
return UUID.randomUUID().toString() + extension;
}
private void setFilePermissions(Path filePath) throws IOException {
File file = filePath.toFile();
if (!file.setReadable(true, false)) {
throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.FILE_PERMISSION_SETTING_FAILED);
}
if (!file.setWritable(true, true)) {
throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.FILE_PERMISSION_SETTING_FAILED);
}
// Window os does not support setExecutable
// if (!file.setExecutable(false, false)) {
// throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.FILE_PERMISSION_SETTING_FAILED);
// }
}
}Security Config
위에서 구현한 총 3개의 필터 (JwtAuthenticationFilter, JsonFilter, MultipartFilter) 는 각각 @Order를 통해 실행 순서를 정하고 Security Config에서 addFilterBefore과 addFilterAfter를 활용하여 실행된다.
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class SecurityConfig {
private final CustomUserDetailService customUserDetailService;
private final JwtService jwtService;
private final MultipartFilter multipartFilter;
private final JsonFilter jsonFilter;
private final PermissionService permissionService;
@Bean
public JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter() {
return new JwtAuthenticationFilter(customUserDetailService, jwtService, securityContextRepository());
}
// Password encoder for testing purposes (not bcrypt)
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new PasswordEncoder() {
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
return rawPassword.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword) {
return rawPassword.toString().equals(encodedPassword);
}
};
}
// Security filter chain
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// Get all permissions from DB
List<PermissionDto> permissions = permissionService.getAllPermissions();
Map<String, Set<String>> urlRoles = new HashMap<>();
permissions.forEach(permission -> {
urlRoles.computeIfAbsent(permission.url(), k -> new HashSet<>())
.add(permission.role().name());
});
http
.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.authorizeHttpRequests(authorizeRequests -> {
authorizeRequests
// Permit all requests to login, submit, file upload
.requestMatchers(
"/login", "/api/v1/login",
"/api/v1/submit/danger", "/api/v1/submit/formdata",
"/api/v1/jsonfile/upload", "/api/v1/multipart/upload", "/api/v1/submit/total")
.permitAll();
// Set up permissions for each URL, ROLE from DB
urlRoles.forEach((url, roles) -> {
authorizeRequests.requestMatchers(url)
.hasAnyRole(roles.toArray(new String[0]));
});
authorizeRequests.anyRequest().authenticated();
})
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class) // Add JWT filter before UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
.addFilterAfter(jsonFilter, JwtAuthenticationFilter.class) // Add JSON filter after JWT filter
.addFilterAfter(multipartFilter, JsonFilter.class); // Add Multipart filter after JSON filter
return http.build();
}
// Security context repository, purpose for saving security context
// SpringContextPersistenceFilter deprecated in Spring 6.3.x
@Bean
public SecurityContextRepository securityContextRepository() {
return new DelegatingSecurityContextRepository(
new RequestAttributeSecurityContextRepository(),
new HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository()
);
}
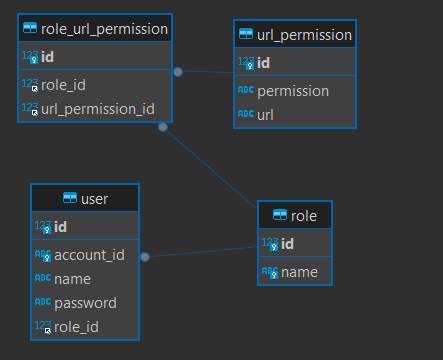
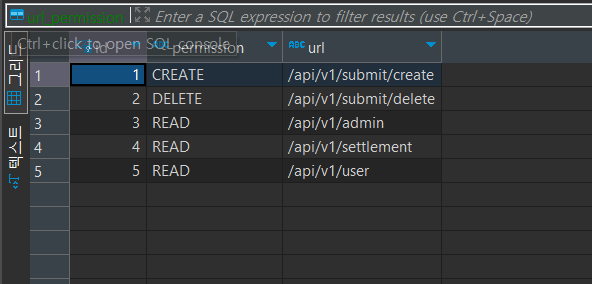
}이때 유저의 permission은 DB에 저장된 데이터를 가져와서 설정한다.
User의 Role을 기준으로 api마다 권한을 설정한다.
Controller
결과적으로 Controller에서는 getAttribute 또는 Requestattribute를 통하여 원하는 데이터를 가져올 수 있다.
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class LoginController {
private final UserService userService;
@PostMapping("/login")
public ResponseDto<?> login(@RequestAttribute("account_id") String accountId,
@RequestAttribute("password") String password) {
log.info("Login attempt for account: {}", accountId);
try {
return userService.login(accountId, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Login error for account: {}", accountId, e);
return ResponseDto.fail(new CommonException(ErrorCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR));
}
}
}또는 정의된 Dto 에 데이터를 넣어 사용할 수도 있다.
@PostMapping("/submit/formdata")
public ResponseDto<?> formDataSubmit(@ModelAttribute FormDataSubmitRequestDto formDataSubmitDto, Authentication authentication) {
log.info("Form data submit attempt with input: {}", formDataSubmitDto.text());
try {
SubmitResponseDto response = submitService.processFormDataSubmit(formDataSubmitDto);
return ResponseDto.ok(response);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error processing form data submit", e);
return ResponseDto.fail(new CommonException(ErrorCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR));
}
}트러블 슈팅
SecurityContextHolder의 getContext().getAuthentication() 했을 때 JwtAuthenticationFilter 내부 에서는 값이 들어있지만 filter가 끝나면 null 로 초기화 되는 문제.
따라서 filter 외부에서 SecurityContext가 null 값만을 가져서 사용자의 권한을 확인할 수 없는 문제가 있었다.
Security Context Null 이라는 키워드로 구글링 한 결과 Spring Security 6 이상 버전에서 SecurityContextPersistenceFilter 의 지원중단으로 인해 SecurityContext가 유지되지 않는 현상이 있다는 것을 알게 되었다.
해결
SecurityContextRepository 를 Bean 등록한 후 context의 내용을 저장하는 것으로 해결할 수 있었다.
SecurityConfig.java
@Bean
public SecurityContextRepository securityContextRepository() {
return new DelegatingSecurityContextRepository(
new RequestAttributeSecurityContextRepository(),
new HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository()
);
}JwtAuthentication.java
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
String token = extractToken(request);
Claims claims = jwtService.getClaimsFromToken(token);
String accountId = claims.getSubject();
// Load user details from the database by account Id
CustomUserDetails userDetails = (CustomUserDetails) customUserDetailService.loadUserByUsername(accountId);
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
userDetails, null, userDetails.getAuthorities());
authentication.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
// Set the authentication in the SecurityContext
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);
securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response); // Save the SecurityContext using the SecurityContextRepository
} catch (Exception e) {
// If an exception occurs, clear the SecurityContext
log.error("Unable to set user authentication: {}", e.getMessage());
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
// Continue the filter chain
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}