Day06
package class04;
import java.util.Scanner;
// JAVA의 기본단위 == class
// '학생' 코딩 해줘 ==>>학생이라는 기본단위를 만들어야 하는 것 (클래스는 무조건 대문자로 이름붙임)
class Student{ // 대문자로 시작하는 것은 클래스
String name;
int score;
// 상태 : 멤버변수(혹은 필드, 속성, 프로퍼티, 어트리뷰트)라고 불리수 있음
// static == "객체와 무관하게"
void hello() { // 객체와 관련이 있기 때문에 static 붙이지 않음
System.out.println("안녕, 난 "+name+"야"); //<<name변수 함수안에서 선언안해도 에러가 안남. 멤버변수 활용 할 수 있음.
}
// 동작(기능) : 메서드, 멤버함수
// 메서드는 함수에게 주어(주체)가 생긴것! 그래서 메인에서 주어가 없으면 못써요
}
public class Test01OOP { //<=클래스파일을 생성 했을때 생성된 클래스
public static void main(String[] args) { // 학생 / 피카츄 라는 애들 데리고 있어야 함수 호출 가능
int num=10;
double d=3.14;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
String str = new String("apple");
String str2="apple";
String b="banana";
String c="kiwi";
Student student1 = new Student(); //원시타입이 아니므로 클래스류이니까 new 사용
// 클래스 객체 =new 생성자();
// 클래스는 자료형, 붕어빵틀의 역할; Student라는 일종의 새로운 타입을 만든것
// 객체는 변수, 붕어빵의 역할
// 클래스로부터 객체를 생성할 때에는
// new 생성자()가 반드시 필요하며
// 객체화(인스턴스화) 영어로는 생성되는 객체들을 instance라고 함
// 교재, 유튜브, 인강, 블로그 -> "인스턴스" new해서 나온 객체
Student student2 = new Student(); //클래스 하나를 잘 정의하면 여러객체를 만들 수 있다
Student student3 = new Student();
// . 멤버접근 연산자
student1.name="아무무";
student1.score=97;
student2.name="티모";
student2.score=13;
student3.name="아리";
student3.score=56;
//주어가 있으니 인제 메소드임
//주어가 다르다 보니 다르게 나옴
student1.hello();
student2.hello();
student3.hello();
System.out.println(student1); // 주소값이 다 다름
System.out.println(student2); // new : 힙메모리를 사용하기 때문에 각각 다른 주소값이 생성
System.out.println(student3);
}
}
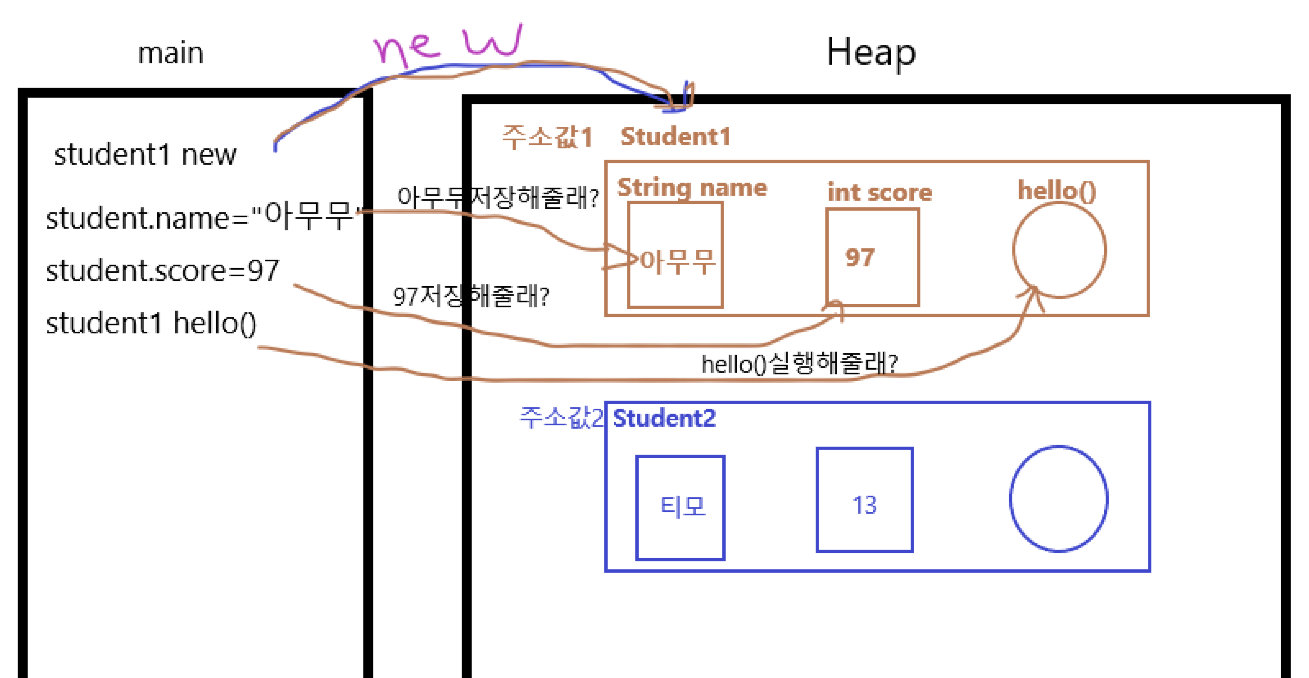
객체도 new 연산자를 사용하기 때문에 Heap메모리 영역에 각기 다른 주소값으로 기억됨
객체화 : 인스턴스화
"인스턴스" new 에서 나온 객체
클래스 하나를 잘 정의하면 객체를 여러개 생성 할 수 있다
static : '객체와 무관하게'; 객체라는 주어로 사용할 함수(객체화 하여 사용할 함수)는 static을 붙이지 않는다
================================================================
객체와 무관하게 사용하는 함수 :
public class BinarySeacrch {
static int[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 20, 35, 99, 100};
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 20, 35, 99, 100};
System.out.println("반복을 이용한 이진 탐색");
System.out.print("찾던 값의 인덱스 : ");
System.out.print(binarySearch(5, 0, arr.length-1));
}
static int binarySearch(int key, int low, int high) {
int mid;
while(low<=high) {
mid = ( low + high ) / 2;
if(key == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
} else if (key < arr[mid]) {
high = mid - 1;
} else { //key > arr[mid]
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1; // 탐색실패
}
}