try-with-resources
finally
FileReader in = null;
try{
in = new FileReader(...);
char c = (char)in.read();
System.out.println(c);
} catch(IOException e){
//IOException 처리
} finally{
if (in != null)
in.close();
}ex1)
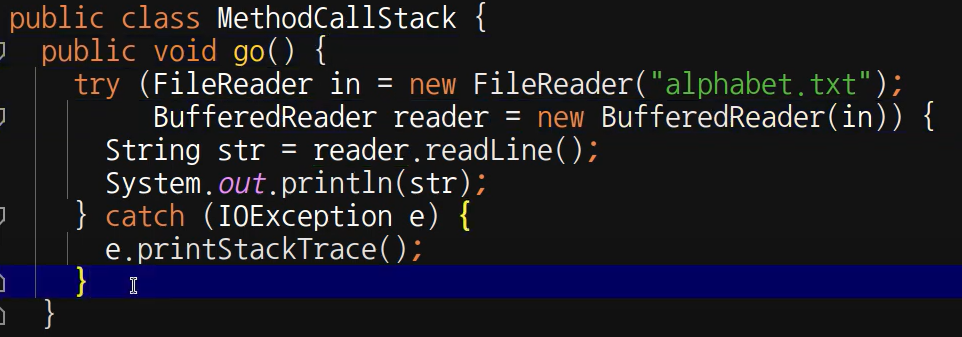
try-with-resources
try(FileReader in = new FileReader(...)){
char c = (char) in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
//IOException 처리
}ex1)
Exception의 중요한 특징
-어떤 메서드가 Exception을 던지면 method call stack을 따라 자신을 호출하는 메서드로 Exception이 전달된다.
-Runtime exception은 try~catch를 해도 되고 안해도 된다. try~catch를 안할 경우 자동적으로 던져진다.
-Checked exception은 반드시 try~catch를 하거나 throws로 던져야한다.
-자원을 사용하면 반드시 해제해야 memory leak이 발생하지 않는다. 자원의 해제는 finally에서 해야한다. 그렇지 않을 경우 exception이 발생하면 해제가 안되어 memory leak 생긴다.
-AutoCloseable 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스들은 try-with-resources 구문을 사용하면 finally를 사용하지 않고도 자동으로 해제된다.
