📍 1. 문제
📍 2. 풀이
📌 최초 풀이 - Brute Force
방법
반복문 내부 반복문에서 배열 내부를 모두 순회
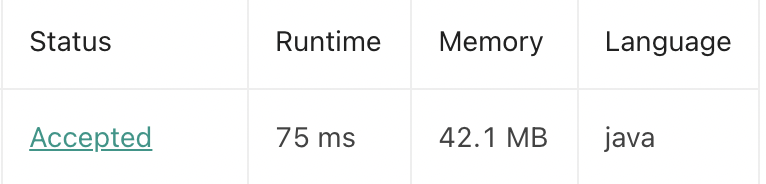
시간복잡도가 O(n2)
코드
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for(int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if(i + j == target) {
result[0] = i;
result[1] = j;
return result;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}결과
📌 두번째 풀이
방법
- 해시테이블에 배열의 값을 key로, index를 value로 저장.
- 배열을 순회하면서 검색값(nums[i] - target)을 해시테이블에서 찾는다.
2-1. 검색값이 해시테이블에 있고, 검색값이 해시테이블의 자기자신이 아니면 return
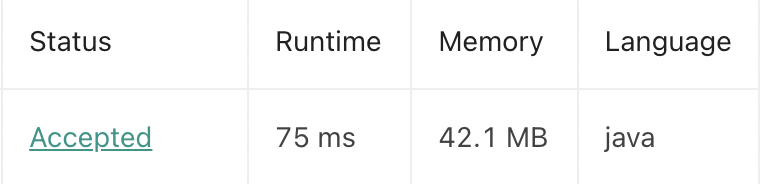
배열을 해시테이블에 복제, 배열순회 두번 하기 때문에 시간복잡도는 O(2n)
코드
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) map.put(nums[i], i);
for(int x = 0; x < nums.length; x++) {
Integer y = map.get(target - nums[x]);
if(y != null && y != x) {
result[0] = x;
result[1] = y;
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
}결과
📌 세번째 풀이
방법
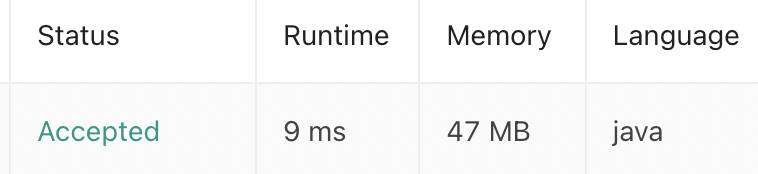
위 방법과 비슷하나 해시테이블을 복사하지 않아 시간복잡도가 O(n)이다.
코드
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for(int x = 0; x < nums.length; x++) {
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[x])) {
result[0] = x;
result[1] = map.get(target - nums[x]);
return result;
}else {
map.put(nums[x] , x);
}
}
return result;
}
}
결과
📍 2. 결론
어쩌면 브루트포스가 가장 인간적인 풀이법이 아닐까..
