설명
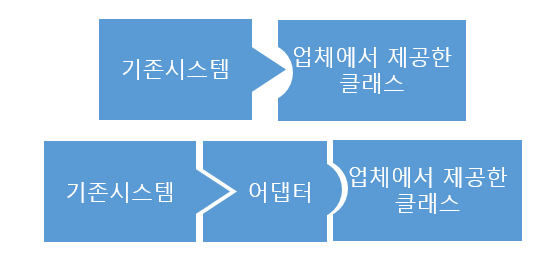
- 어댑터 패턴(Adapter pattern)은 호환되지 않는 인터페이스를 가진 객체들을 연결해서 쓸 수 있도록 하는 구조적 디자인 패턴이다.
-
어댑터 패턴은 래퍼(Wrapper)라고도 불리며, 클라이언트와 구현된 인터페이스를 분리해 후에 인터페이스가 바뀌더라도 그 변경 내역은 어댑터에 캡슐화되기 때문에 클라이언트는 바뀔 필요가 없어진다.
-
어댑터 패턴은
- 클라이언트는 어댑티와 호환되는 인터페이스를 받는다.
- 이 인터페이스를 사용해 클라이언트는 어댑티의 메소드들을 안전하게 호출한다.
- 호출을 수신하면 어댑터는 이 요청을 클라이언트에 그 객체가 예상하는 형식과 순서대로 전달한다.
- 이 과정에서 클라이언트는 어댑터를 모른다.
장단점과 사용 시기
-
장점
-
단일 책임 원칙(SRP) 준수 : 프로그램의 기본 로직에서 인터페이스 또는 데이터 변환 코드를 분리할 수 있다.
-
개방 폐쇄 원칙(OCP) 준수 : 클라이언트가 어댑터와 작동하는 한, 기존 코드를 손상시키지 않고 새로운 어댑터들을 도입할 수 있다.
-
-
단점
- 다수의 새로운 인터페이스와 클래스들을 도입해야 하므로 코드의 전반적인 복잡성이 증가한다.
-
사용 시기
-
기존 클래스를 사용하고 싶지만 그 인터페이스가 나머지 코드와 호환되지 않을 때
-
부모 클래스에 추가할 수 없는 공통 기능들이 없는 여러 기존 자식 클래스들을 재사용하려고 할 때
- 각 자식 클래스를 확장한 후 누락된 기능들을 새 자식 클래스들에 넣을 수 있다.
- 하지만 해당 코드를 모든 새 클래스들에 복제해야 한다.
- 이를 더 깔끔하게 해결하기 위해 위의 누락된 기능을 어댑터 클래스에 넣는다.
- 어댑터 내부에 누락된 기능이 있는 객체들을 래핑하면 필요한 기능들을 동적으로 얻을 수 있다.
-
구조
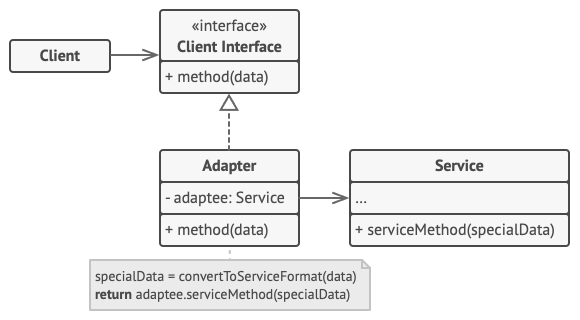
객체 어댑터
-
어댑터는 한 객체의 인터페이스를 구현하고 다른 객체는 래핑한다.
-
합성된 멤버에게 위임을 이용한다.
- 위임이란, 자기가 해야 할 일을 클래스 맴버 객체의 메소드에게 다시 시킴으로써 목적을 달성하는 것이다.
-
런타임 중에 어댑티가 결정되어 유연하다.
-
한 방향으로 역할한다.
-
모든 프로그래밍 언어로 구현할 수 있다.
-
Adaptee(Service): 어댑터 대상 객체, 호환시키려는 객체 -
Target(Client Interface):Adapter가 구현하는 인터페이스 -
Adapter:Client와Adaptee(Service)중간에서 호환성이 없는 둘을 연결Adaptee(Service)를 따로 클래스 멤버로 설정하고 위임을 통해 동작을 매치시킨다.
-
Client: 기존 시스템(어댑티)을 어댑터를 통해 이용하려는 쪽.Client Interface를 통하여Service를 이용할 수 있게 된다.
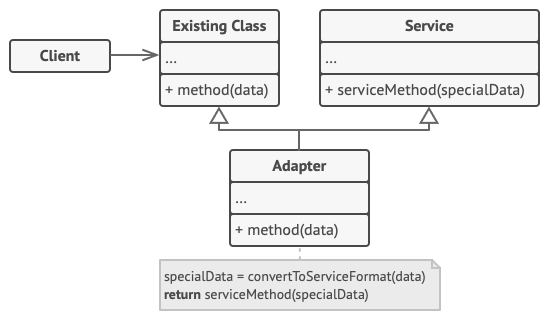
클래스 어댑터
-
어댑터가 동시에 두 객체의 인터페이스를 상속한다.
-
객체를 래핑할 필요가 없고, 따로 객체 구현없이 바로 코드 재사용이 가능하다.
-
양방향으로 역할한다.
-
다중 상속이 가능한 언어에서만 사용이 가능하며, 죽음의 다이아몬드 문제 등 다중 상속의 문제 때문에 권장되지 않는 방법이다.
-
Adaptee(Service): 어댑터 대상 객체, 호환시키려는 객체 -
Target(Cient Interface):Adapter가 구현하는 인터페이스. -
Adapter:Client와Adaptee(Service)중간에서 호환성이 없는 둘을 연결 -
Client: 기존 시스템(어댑티)을 어댑터를 통해 이용하려는 쪽.Existing Class를 통하여Service를 이용할 수 있게 된다.
구현 및 예시
구현 방법
-
호환되지 않는 인터페이스가 있는 클래스들이 있다.
-
클라이언트 인터페이스를 선언하고 클라이언트들이 어댑티(서비스)와 통신하는 방법을 기술한다.
-
어댑터 클래스를 생성하고 클라이언트 인터페이스를 상속한다.
-
어댑티 객체에 참조를 저장하기 위해 어댑터 클래스에 필드를 추가한다.
-
클라이언트 인터페이스의 모든 메소드를 어댑터 클래스에서 구현한다.
- 어댑터는 인터페이스 혹은 데이터 형식 변환만 처리해야 하며, 실제 작업의 대부분을 어댑티에 위임해야 한다.
- 클라이언트들은 클라이언트 인터페이스를 통해 어댑터를 사용해야 한다. 이렇게 클라이언트 코드에 영향을 주지 않고도 어댑터들을 변경하고 확장할 수 있다.
예시
의사코드
- 서로 맞지 않는 정사각형 못과 둥근 구멍이 있다.
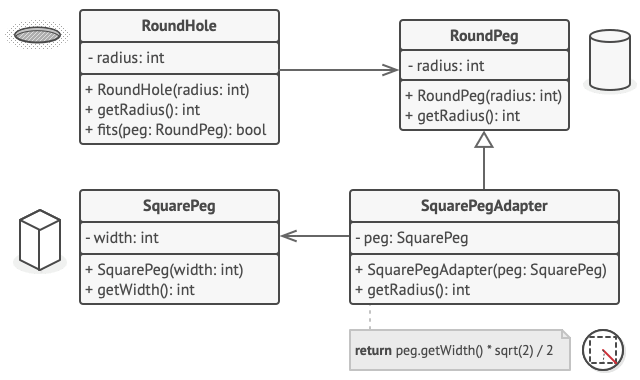
- 어댑터는 정사각형 대각선 길이의 절반(즉, 사각형 못을 수용할 수 있는 가장 작은 원의 반지름)을 반지름으로 가진 둥근 못인 척 한다.
// RoundHole(둥근 구멍) 및 RoundPeg(둥근 못)라는 호환되는 인터페이스들이 있는
// 두 개의 클래스가 있다고 가정해봅시다.
class RoundHole is
constructor RoundHole(radius) { ... }
method getRadius() is
// 구멍의 반지름을 반환하세요.
method fits(peg: RoundPeg) is
return this.getRadius() >= peg.getRadius()
class RoundPeg is
constructor RoundPeg(radius) { ... }
method getRadius() is
// 못의 반지름을 반환하세요.
// 그러나 SquarePeg(직사각형 못)라는 호환되지 않는 클래스가 있습니다.
class SquarePeg is
constructor SquarePeg(width) { ... }
method getWidth() is
// 직사각형 못의 너비를 반환하세요.
// 어댑터 클래스를 사용하면 정사각형 못을 둥근 구멍에 맞출 수 있습니다. 어댑터
// 객체들은 RoundPeg(둥근 못) 클래스를 확장해 둥근 못들처럼 작동하게 해줍니다.
class SquarePegAdapter extends RoundPeg is
// 실제로 어댑터에는 SquarePeg(정사각형 못) 클래스의 인스턴스가 포함되어
// 있습니다.
private field peg: SquarePeg
constructor SquarePegAdapter(peg: SquarePeg) is
this.peg = peg
method getRadius() is
// 어댑터는 이것이 어댑터가 실제로 감싸는 정사각형 못에 맞는 반지름을
// 가진 원형 못인 것처럼 가장합니다.
return peg.getWidth() * Math.sqrt(2) / 2
// 클라이언트 코드 어딘가에…
hole = new RoundHole(5)
rpeg = new RoundPeg(5)
hole.fits(rpeg) // 참
small_sqpeg = new SquarePeg(5)
large_sqpeg = new SquarePeg(10)
hole.fits(small_sqpeg) // 이것은 컴파일되지 않습니다(호환되지 않는 유형)
small_sqpeg_adapter = new SquarePegAdapter(small_sqpeg)
large_sqpeg_adapter = new SquarePegAdapter(large_sqpeg)
hole.fits(small_sqpeg_adapter) // 참
hole.fits(large_sqpeg_adapter) // 거짓C# 예시 코드 1
using System;
namespace RefactoringGuru.DesignPatterns.Adapter.Conceptual
{
// The Target defines the domain-specific interface used by the client code.
public interface ITarget
{
string GetRequest();
}
// The Adaptee contains some useful behavior, but its interface is
// incompatible with the existing client code. The Adaptee needs some
// adaptation before the client code can use it.
class Adaptee
{
public string GetSpecificRequest()
{
return "Specific request.";
}
}
// The Adapter makes the Adaptee's interface compatible with the Target's
// interface.
class Adapter : ITarget
{
private readonly Adaptee _adaptee;
public Adapter(Adaptee adaptee)
{
this._adaptee = adaptee;
}
public string GetRequest()
{
return $"This is '{this._adaptee.GetSpecificRequest()}'";
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Adaptee adaptee = new Adaptee();
ITarget target = new Adapter(adaptee);
Console.WriteLine("Adaptee interface is incompatible with the client.");
Console.WriteLine("But with adapter client can call it's method.");
Console.WriteLine(target.GetRequest());
}
}
}- 실행 결과
Adaptee interface is incompatible with the client.
But with adapter client can call it's method.
This is 'Specific request.'C# 예시 코드 2
namespace Wikipedia.Examples;
using System;
interface ILightningPhone
{
void ConnectLightning();
void Recharge();
}
interface IUsbPhone
{
void ConnectUsb();
void Recharge();
}
sealed class AndroidPhone : IUsbPhone
{
private bool isConnected;
public void ConnectUsb()
{
this.isConnected = true;
Console.WriteLine("Android phone connected.");
}
public void Recharge()
{
if (this.isConnected)
{
Console.WriteLine("Android phone recharging.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Connect the USB cable first.");
}
}
}
sealed class ApplePhone : ILightningPhone
{
private bool isConnected;
public void ConnectLightning()
{
this.isConnected = true;
Console.WriteLine("Apple phone connected.");
}
public void Recharge()
{
if (this.isConnected)
{
Console.WriteLine("Apple phone recharging.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Connect the Lightning cable first.");
}
}
}
sealed class LightningToUsbAdapter : IUsbPhone
{
private readonly ILightningPhone lightningPhone;
private bool isConnected;
public LightningToUsbAdapter(ILightningPhone lightningPhone)
{
this.lightningPhone = lightningPhone;
}
public void ConnectUsb()
{
this.lightningPhone.ConnectLightning();
}
public void Recharge()
{
this.lightningPhone.Recharge();
}
}
public class AdapterDemo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ILightningPhone applePhone = new ApplePhone();
IUsbPhone adapterCable = new LightningToUsbAdapter(applePhone);
adapterCable.ConnectUsb();
adapterCable.Recharge();
}
}- 실행 결과
Apple phone connected.
Apple phone recharging.