회고 리스트
1. 자바스크립트에서 이벤트란?
이벤트(event)는 자바스크립트에서 사용자나 브라우저가 발생시키는 사건 또는 동작을 의미한다.
예를 들어, 사용자가 버튼을 클릭하거나 입력창에 텍스트를 입력하거나 페이지가 로드되는 것 등이 이벤트이다.
2.
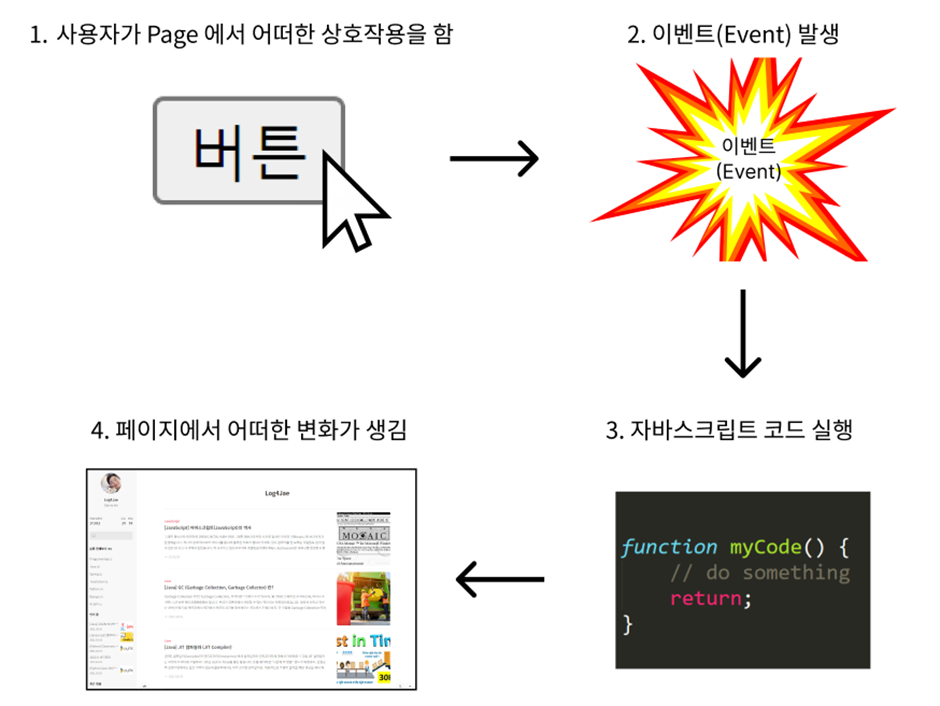
3. 이벤트 종류를 정리 해 보세요.
참고: https://jenny-daru.tistory.com/17
-
마우스 이벤트 🖱️
click: 요소를 클릭했을 때
dblclick: 더블 클릭했을 때
mouseover: 요소 위에 마우스를 올렸을 때
mouseout: 요소에서 마우스가 벗어났을 때
mousedown, mouseup: 마우스를 눌렀을 때와 뗐을 때 -
키보드 이벤트 ⌨️
keydown: 키를 눌렀을 때 (누르고 있는 동안 반복 발생)
keyup: 키에서 손을 뗐을 때
keypress: 문자를 입력했을 때 (deprecated, 대신 keydown 또는 keyup 사용 권장) -
폼(Form) 이벤트 📝
submit: 폼이 제출될 때
change: 입력값이 변경될 때
focus: 요소에 포커스가 맞춰질 때
blur: 요소의 포커스가 해제될 때 -
브라우저 이벤트 🌐
load: 페이지나 이미지가 로드될 때
resize: 브라우저 창 크기가 변경될 때
scroll: 사용자가 페이지를 스크롤할 때
unload: 사용자가 페이지를 떠날 때
4. 아래 두개체의 차이점에 대하여 설명하시오?
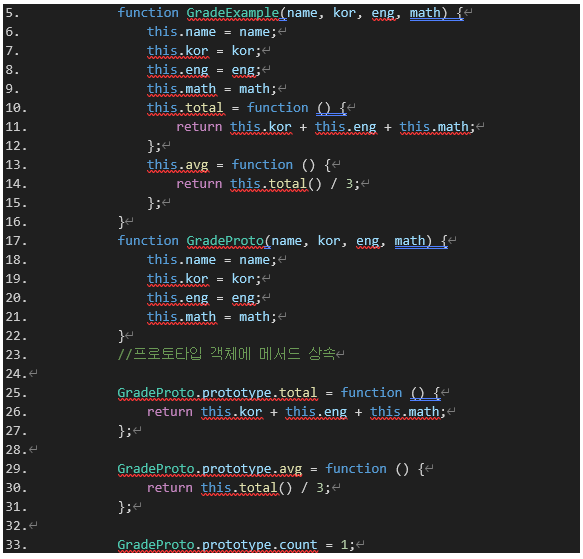
-
GradeExample (일반 생성자 함수)
: 메서드가 객체마다 개별로 생성된다.
: 캡슐화가 쉽지만 메모리 비효율적이다.
(각 객체마다 메서드를 복제하므로 객체가 많아질수록 메모리 사용량이 증가한다.) -
GradeProto (프로토타입을 사용하는 생성자 함수)
: 메서드가 모든 객체에 공유된다.
(total과 avg 메서드는 프로토타입 체인을 통해 한 번만 메모리에 저장되며 모든 객체가 이를 참조한다.)
: 메모리 효율이 높다.
(메서드가 개별 객체에 복제되지 않으므로 메모리를 절약할 수 있다.)
: 모든 객체가 공유하는 속성 추가 가능하다.
(count는 GradeProto 인스턴스가 공유하는 속성이다.)
5. 아래가 돌아 가도록 Grade 생성자 함수를 만드시오.
<script>
let hong = new Grade('홍길동', 100, 90, 80);
document.write(hong.total() + '<br>');
document.write(hong.avg() + '<br>');
</script><script>
function Grade(name, kor, eng, math) {
this.name = name;
this.kor = kor;
this.eng = eng;
this.math = math;
}
Grade.prototype.total = function() {
return this.kor + this.eng + this.math;
};
Grade.prototype.avg = function() {
return this.total() / 3;
};
// 사용 예시
let hong = new Grade('홍길동', 100, 90, 80);
document.write(hong.total() + '<br>'); // 출력: 270
document.write(hong.avg() + '<br>'); // 출력: 90
</script>6. 아래를 구현하시오
회원정보<br>
주소<input type="text" name="address1" id="address1" value="서울시 강남구"><br>
전화번호<input type="text" name="phone1" id="phone1" value="010-1234-1234"><br>
<hr>
동일<input type="checkbox" name="chk" onclick="check(this)">
<hr>
배송지 정보<br>
주소<input type="text" name="address2" id="address2" value=""><br>
전화번호<input type="text" name="phone2" id="phone2" value=""><br><script>
function check(t) {
if (t.checked) {
document.getElementById("address2").value = document.getElementById('address1').value;
document.getElementById("phone2").value = document.getElementById('phone1').value;
}
else {
document.getElementById("address2").value = "";
document.getElementById("phone2").value = "";
}
};
</script>7. 아래를 구현하시오.
<h1>1. +연산</h1>
<input type="text" name="v1" id="v1" value="10">+
<input type="text" name="v2" id="v2" value="20">=
<input type="text" name="result" id="result" value="">
<button onclick="sum()">연산</button><br><script>
function sum() {
let v1 = document.getElementById("v1").value;
let v2 = document.getElementById("v2").value;
document.getElementById("result").value = parseInt(v1) + parseInt(v2);
}
</script>Q. 값을 받아올 때 getElementById를 쓸 때도 있고 querySelector를 쓸 때도 있는데 무슨 차이일까?
A.
- getElementById()
- 용도: id 속성을 기준으로 요소를 가져옴.
- 문법: document.getElementById("id명")
- 반환값: 첫 번째로 찾은 요소 하나만 반환. (항상 단일 요소)
- 특징: id는 고유해야 하므로 보통 한 요소만 가져오고 사용법이 단순하고 빠름.
- querySelector()
- 용도: CSS 선택자 문법을 사용해 요소를 가져옴.
- 문법: document.querySelector("CSS선택자")
- 반환값: 첫 번째로 일치하는 요소 하나만 반환. (단일 요소)
- 특징: CSS 선택자(.class, #id, tag, div > p 등)를 사용해서 더 유연하지만 특정 상황에선 약간 느릴 수 있음(특히 대규모 DOM에서는).
<비교>
속도: getElementById가 더 빠름(직접 ID를 찾기 때문).
유연성: querySelector는 CSS 선택자를 사용해서 더 다양한 요소를 가져올 수 있음.
호환성: 둘 다 대부분의 브라우저에서 잘 작동하지만, querySelector는 더 최신 방식임.
<언제 어떤 걸 써야 할까?>
ID로만 요소를 가져와야 한다면 👉 getElementById()
클래스나 태그 등 다양한 조건이 필요하다면 👉 querySelector()
→ 요즘은 더 범용적인 querySelector() 를 자주 쓰지만 간단히 ID만 가져올 때는 getElementById() 가 더 효율적
3줄 요악
1. 자바스크립트 함수에 new 를 붙이면, 객체로 변환이 된다.
2. Prototype 객체는 공용 변수, 공용함수를 등록하기 위한 객체이다.
3. 이벤트 처리란 특정(정해진) 동작에 콜백함수를 등록하여, 개발자와의 상호작용을 말한다.
오늘도 물리치료 받으러 간당...

