📝 예외 처리
💡 프로그램 오류
- 프로그램 수행 시 치명적 상황이 발생하여 비정상 종료 상황이 발생한 것
- 프로그램 에러라고도 함
✏️ 오류의 종류
- 컴파일 에러
- 런타임 에러 : 프로그램 수행 중 발생하는 에러
- 시스템 에러
[예제]
package edu.kh.exception.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.print("정수 입력(0 입력 시 종료) : ");
int input = sc.nextInt();
int a = (int)99.9; // 자료형이 맞지 않아 연산을 못해서 "컴파일 에러"(코드 틀림)
// 코드로 수정 가능!
// 1) 변수 자료형을 double로 바꿈
// 2) (int)99.9로 강제 형변환
// 3) 99.9 -> 99 또는 100으로 변경
if(input == 0) {
break;
}
}
// 런타임 에러 예제
// 런타임 에러 : 프로그램 수행 중 발생하는 에러
// 주로 if문으로 처리 가능
int[] arr = new int[3]; // 인덱스는 2까지
arr[0] = 10;
arr[1] = 20;
arr[2] = 30;
arr[3] = 40;
if(arr.length >= 3) { // 배열 인덱스 범위 초과 시
System.out.println("배열의 범위를 초과했습니다.");
} else {
arr[3] = 40;
}
// java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException : 배열 범위 초과 예외
}
}💡 예외 (Exception)
소스 코드의 수정으로 해결 가능한 오류
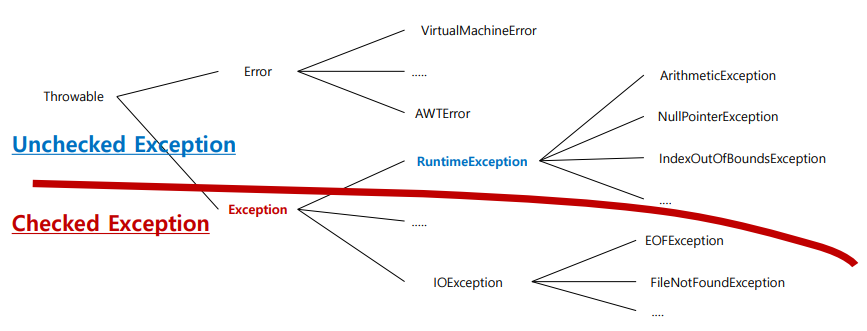
✏️ 예외 클래스 계층 구조
✏️ 예외의 종류
Checked Exception : 예외 처리 필수
- RuntimeException과 자식 예외를 제외한 나머지 예외
- if문과 같은 단순 코드로 해결이 불가능하여 반드시 예외 처리 구문을 작성해야 하는 예외
Unchecked Exception : 선택적으로 예외 처리
- RuntimeException과 자식 예외를 지칭함
- 프로그램 수행 중 개발자의 코딩 실수 또는 사용자의 잘못된 값 입력으로 흔하게 발생할 수 있는 예외
-> 예외 처리 구문이 아니라 if문 같은 단순 코드로 해결이 가능함
-> 예외 처리 구문을 반드시 작성할 필요가 없음
✏️ 예외 처리 방법
- try - catch 예외 처리
- try { } : 괄호 내부에 예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 코드를 작성한 후 시도
- catch(예외){ } : try 구문에서 발생한 예외를 잡아내서 처리하여 프로그램이 비정상 종료되지 않도록 함
[예제 1] 예외의 종류와 try - catch 예외 처리 알아보기
package edu.kh.exception.model.service;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExceptionService {
// 예외 (Exception) : 소스 코드의 수정으로 해결 가능한 오류
private Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public void ex1() {
// try - catch 예외 처리
System.out.println("두 정수를 입력 받아 나누기한 몫을 출력");
System.out.print("정수 1 입력 : ");
int input1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("정수 2 입력 : ");
int input2 = sc.nextInt();
/*
* try {
System.out.println("결과 : " + input1 / input2);
// java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
// 산술적 예외 : 0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.
} catch(ArithmeticException e) {
// try에서 던져진 예외를 catch문 매개변수로 잡음
System.out.println("infinity"); // 처리 코드
}
*/
if(input2 != 0) {
System.out.println("결과 : " + input1 / input2);
} else {
System.out.println("infinity");
}
// 발생하는 예외 중 일부 예외는 try-catch 구문을 사용하지 않아도
// 예외 상황을 방지할 수 있다!
// (일부 예외 == 대부분의 UncheckedException)
}
public int inputNumber() {
int num = 0;
while(true) {
try {
System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : ");
num = sc.nextInt(); // java.util.InputMismatchException
sc.nextLine(); // 입력 버퍼 개행 문자 제거
break;
} catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("<잘못 입력하셨습니다. 정수만 입력해 주세요.>");
sc.nextLine(); // 버퍼에 남아 있는 잘못 입력된 문자열을 제거
}
}
return num;
}
public void ex2() {
// 정수 3개를 입력받아 3개의 합계 구하기
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) { // i=0, 1, 2
sum += inputNumber();
}
System.out.println("합계 : " + sum);
}[예제 2] 여러 가지 예외에 대한 처리 방법
public void ex3() {
// 여러 가지 예외에 대한 처리 방법
try {
System.out.print("입력 1 : ");
int num1 = sc.nextInt(); // InputMismatchException
System.out.print("입력 2 : ");
int num2 = sc.nextInt(); // InputMismatchException
System.out.println("나누기 결과 : " + num1 / num2);
// ArithmeticException
// ************************************************
// 강제로 NullPointerException 발생
// * NullPointerException : 참조하지 않는 참조변수를 이용해서 코드를 수행할 때 발생
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));
// NullPointerException에 대한 예외 처리가 없으면 오류 발생 후 종료
// ************************************************
// 관계 없는 예외는 순서 관계 없이 catch문에 작성하면 된다.
} catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("정수가 아닌 문자열이 입력되었습니다.");
} catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
} catch(Exception e /*부모 타입 참조 변수*/) {
// 예외 처리 + 다형성
// Exception 클래스 : 모든 예외의 최상위 부모
// 다형성 - 업캐스팅 : 부모 타입의 참조 변수로 자식 객체를 참조
System.out.println("뭔지 모르겠지만 예외가 발생해서 처리함.");
// ** 상위 타입의 예외 클래스를 catch문에 작성하면
// 다형성 업캐스팅에 의해서 모두 잡아서 처리! **
}
// * catch문 연속 작성 시 Exception 상속 구조를 주의하자!(다형성)
}[예제 3] try - catch - finally 예외 처리
public void ex4() {
// 1) try - catch - finally
// finally : try 구문에서 예외가 발생하든 말든 무조건 마지막에 수행
try {
System.out.println( 4 / 0 ); // ArithmeticException 발생
} catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("예외 처리됨");
// 2) catch문 매개변수 활용
// 매개변수 e : 예외 관련 정보 + 예외 관련 기능
System.out.println( e.getClass() ); // 어떤 예외 클래스인가?
System.out.println( e.getMessage() ); // 예외 발생 시 출력된 내용
// / by zero
System.out.println( e ); // e.toString();
// java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
e.printStackTrace(); // 예외가 발생하기까지의 모든 메소드 흐름을 출력
// 어디서 어떤 에러가 발생했는지 정확히 파악하는 용도
} finally {
System.out.println("무조건 수행됨");
}
}[예제 4] throws와 throw
public void ex5() {
// throws : 호출한 메소드에게 예외를 던짐
// -> 호출한 메소드에게 예외를 처리하라고 위임하는 행위
// throw : 예외 강제 발생 구문 (현재 메소드에 예외를 던짐)
try {
methodA();
} catch(Exception e) {
// Exception : 모든 예외의 최상위 부모
// -> Exception이 catch 매개 변수로 작성되었다 == 예외 종류 상관없이 모두 처리
System.out.println("예외 처리됨");
e.printStackTrace();
// 발생한 예외가 메소드와 위치에 대한 모든 내용을 출력
// - 예외 발생 지점 추척 가능
}
}
public void methodA() throws IOException {
methodB();
}
public void methodB() throws IOException {
methodC();
}
public void methodC() throws IOException {
// methodC() 메소드는 IOException을 발생시킬 가능성이 있으므로
// 호출하는 곳에서 예외 처리를 반드시 해야 한다!
// 단, UnCheckedException은 선택적으로 예외 처리할 수 있음
// IOException 예외 강제 발생
throw new IOException();
// 발생한 예외를 처리하는 방법
// 1) try - catch로 감싸서 현재 위치에서 처리
// 2) throws로 호출한 메소드로 예외를 위임하여 처리
}
public void methodD() {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
✏️ 오버라이딩 시 예외 처리
오버라이딩 시 예외는 같거나 더 좁은 범위
(* 좁은 범위 == 구체적인 예외)
package edu.kh.exception.model.vo;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Child extends Parent {
@Override
public void method() throws FileNotFoundException {
System.out.println("오버라이딩된 자식 메소드");
// 오버라이딩 시
// 예외는 같거나 더 좁은 범위
// * 좁은 범위 == 구체적인 예외
// FileNotFoundException은
// IOException의 자식 예외이므로 오버라이딩 가능
// Exception(모든 예외의 부모)은
// IOException의 부모 예외이므로 오버라이딩 불가
}
}