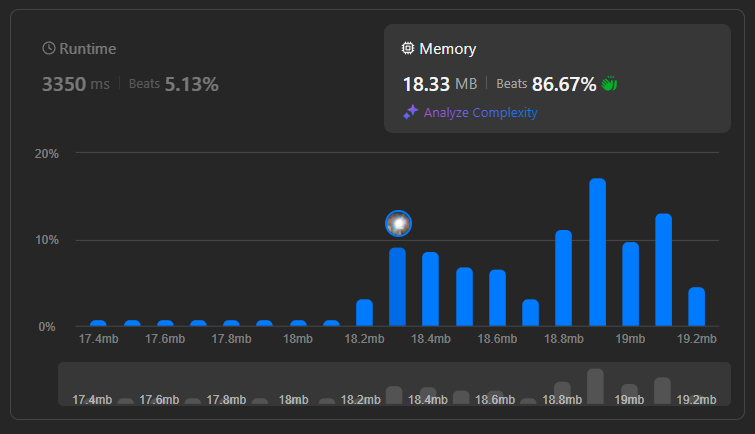
First try
- Insitnct: Simply check every possible pair of numeber in the list. I used two nested
forloops to accomplish this.
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
ans = []
for i, num1 in enumerate(nums):
for j, num2 in enumerate(nums):
if i < j and num1 + num2 == target:
ans.append(i)
ans.append(j)
return ans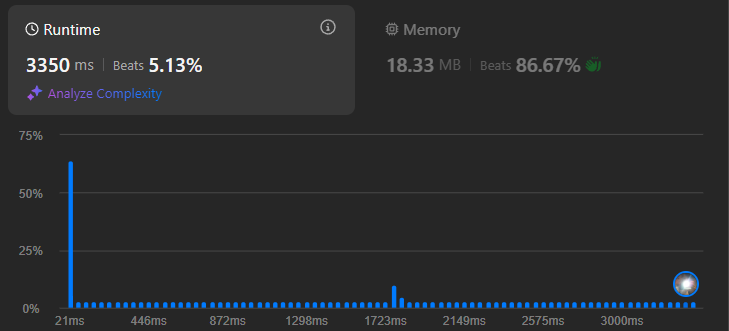
Problem: The two nested loops result in a time complexity of O(n^2). This is because for every element, the inner loop has to scan the entire list again, making it very slow for large inputs.
Second try
- Instinct: My next thought was to avoid the inner loop. For each number, I could calculate its complement (target - num) and then use Python's in and .index() to check if it exists in the list.
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
ans = []
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if ((target - num) in nums) and (nums.index(target-num) > i) :
ans.append(i)
ans.append(nums.index(target-num))
return ans
Problem: .index(value) always find the first occurrence of value in the list & still doesn't solve time complexity problem
Third try
- Instinct: Instead of a list, I used a
dictionaryto store the numbers I'd already seen.
Q. Why
dictionaryis better thanlistin terms oftime complexity?
A. There is difference between
dictionaryandlistabout how they store and retrieve data.
dictionary: Use a 'direct lookup' system using a key (Hashing, O(1)) (e.g. using a book's index to find a topic in a book)list: Use a 'search every item' system(Linear scan, O(n)) (e.g. reading a book page-by-page to do same thing)
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if num not in seen_numbers.keys():
seen_numbers[target-num] = i
elif num in seen_numbers.keys():
result.append(seen_numbers[num])
result.append(i)
return resultFinally it passed!
Problem: But it doesn't look clean and practical, and I finally realized I missed hint by reading the problem's description carefully:
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution,
Fourth try
- Instinct: I can return immediately after finding the first valid pair, which simplifies the logic.
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
seen_numbers = {}
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if num in seen_numbers:
return [seen_numbers[num], i]
else:
new_element = target - num
seen_numbers[new_element] = i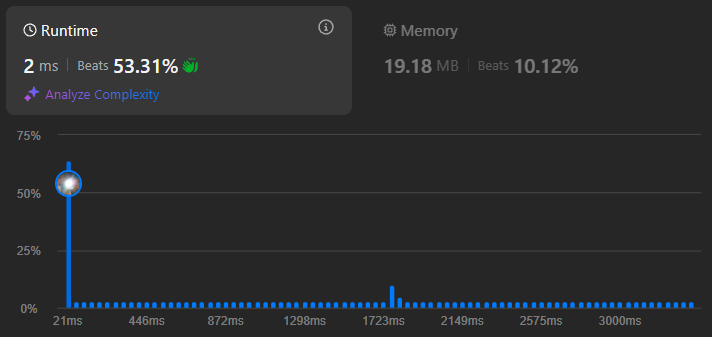
Conclusion:
This process taught me that I was initially a bit confused about the practical application of a dictionary and the importance of edge cases. It's crucial to consider edge cases, but first of all, it's essential to focus on the problem's definition and constraints.
