
오늘의 학습 키워드 및 문제
#Heap #Array #PriorityQueue
LeetCode 506. Relative Ranks
크기가 n인 정수 배열 score가 주어지며, 여기서 score[i]는 경기에서 i번째 선수의 점수입니다. 모든 점수는 고유합니다.
선수들은 점수에 따라 순위가 정해지는데, 1위 선수가 가장 높은 점수를 받은 사람, 2위 선수가 두 번째로 높은 점수를 받은 사람 등이 이에 해당합니다. 각 선수의 순위는 다음과 같이 결정됩니다.
- 1위 선수의 등급은 "Gold Medal"입니다.
- 2위 선수의 등급은 "Silver Medal"입니다.
- 3위 선수의 등급은 "Bronze Medal"입니다.
- 4위부터 n위까지의 선수의 경우, 순위는 배치 번호입니다. (즉, x위 선수의 순위는 "x"입니다.)
answer[i]가 i번째 선수의 순위인 n 크기의 배열 answer를 반환합니다.
[예시1]
Input: score = [5,4,3,2,1]
Output: ["Gold Medal","Silver Medal","Bronze Medal","4","5"]
Explanation: The placements are [1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th].
[예시2]
Input: score = [10,3,8,9,4]
Output: ["Gold Medal","5","Bronze Medal","Silver Medal","4"]
Explanation: The placements are [1st, 5th, 3rd, 2nd, 4th].
문제풀이
영어 울렁증이.. 어찌저찌 해석하여 풀어냈다..
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String[] findRelativeRanks(int[] score) {
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
String[] answer = new String[score.length];
// score를 q에 담기
for(int i : score) {
q.add(i);
}
// q가 비어있을 때 까지 반복.
// 그 안에 score 반복문을 통해 q의 top값과 score의 요소가 같으면 answer에 String으로 변환하여 순위 저장
int th = 1;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int e = q.poll();
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) {
if (e == score[i]) {
answer[i] = String.valueOf(th);
th++;
}
}
}
// 1, 2, 3위 설정
for(int i=0; i<answer.length; i++) {
boolean first = false;
boolean second = false;
boolean third = false;
if (answer[i].equals("1")) {
answer[i] = "Gold Medal";
} else if (answer[i].equals("2")) {
answer[i] = "Silver Medal";
} else if (answer[i].equals("3")) {
answer[i] = "Bronze Medal";
} else if (first && second && third) {
break;
}
}
return answer;
}
}이 문제를 풀었긴 했지만 내 코드의 성능은 그다지 좋은 것 같지 않다..
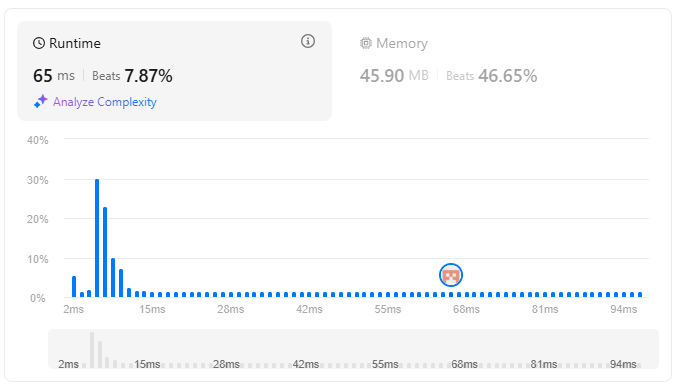
다른방법
문제의 Editorial을 참고하여 코드를 작성했다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String[] findRelativeRanks(int[] score) {
int n = score.length;
int[] sCopy = new int[n];
// score의 요소들을 sCopy배열에 복사
System.arraycopy(score, 0, sCopy, 0, n);
// 각 요소에 대한 인덱스를 map으로 저장
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
map.put(sCopy[i], i);
}
// sCopy 변수 오름차순 정렬
Arrays.sort(sCopy);
// 순위 매기기
String[] answer = new String[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
answer[map.get(sCopy[n-i-1])] = "Gold Medal";
} else if (i == 1) {
answer[map.get(sCopy[n-i-1])] = "Silver Medal";
} else if (i == 2) {
answer[map.get(sCopy[n-i-1])] = "Bronze Medal";
} else {
answer[map.get(sCopy[n-i-1])] = Integer.toString(i+1);
}
}
return answer;
}
}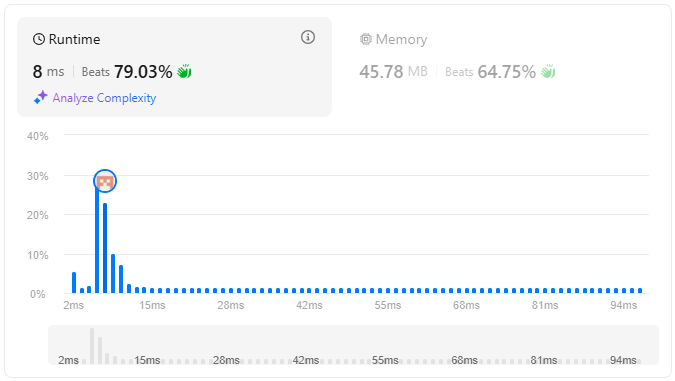
공부한 내용정리
- System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length) : 더 빠름
- 배열을 복사하여 다른 배열변수에 저장
- Object src : 복사할 객체, 원본 배열
- int srcPos : 복사 시작할 index
- Object dest : 복사된 배열
- int destPos : 원본으로부터 가져온 데이터를 복사된 배열의 몇번째 index부터 추가
- int length : 카피되는 배열 요소 개수
- Arrays.copyOf(원본배열, 복사할길이) / Arrays.copyOfRange(A, from_index, to_index) : 더 느림
- int[] A : 복사할 배열
- int from_index : 복사할 배열의 시작 index
- int to_index : 복사할 배열의 끝 index (복사할 끝 index값은 포함 안됨)
- 새로운 배열을 return
