사이트: HackerRank
난이도: 미디움
분류: Graph Theory
문제
무방향 가중치 그래프가 주어지고 노드 n개가 주어질 때, 1번 노드에서 n번 노드까지의 거리중 가장 적은 비용이 드는 값을 찾아서 반환하라.
각 노드간 가중치가 존재하며 다음 노드로 이동시 가중치 값을 다음과 같이 계산한다.
1->2->4로 이동한다고 했을 때,1->2의 가중치는20,2->3으로 이동하면30이다. 이후 값에서 이전 값을 뺀 나머지가 다음 비용으로 계산되며, 따라서 값은20 + (30 - 20) = 30이 되게 된다.
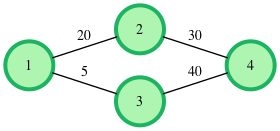
1. 나의 풀이
다익스트라 알고리즘으로 접근하는 것이 맞을지 고민하다가, 가중치 계산이 우선순위 큐와 맞지 않을 것 같아서 dfs로 해결하려고 했다. 그러나 생각만큼 잘 되지 않았고, 풀이를 찾아보게 되었다.
function getCost(gNodes, gFrom, gTo, gWeight) {
// Print your answer within the function and return nothing
const graph = Array.from(
new Array(gNodes + 1),
() => []
);
for (let i = 0; i < gFrom.length; i++) {
graph[gFrom[i]].push([gTo[i], gWeight[i]]);
}
const stack = [[1, 0]];
const visited = Array.from(new Array(gNodes + 1), () => false);
visited[1] = true;
let result = Infinity;
while(stack.length) {
const [current, cWeight] = stack.pop();
for (const [next, weight] of graph[current]) {
const nWeight = cWeight + Math.max(weight - cWeight, 0);
if (next === gNodes) {
result = Math.min(result, nWeight);
} else if (!visited[next]) {
stack.push([next, nWeight]);
}
}
}
console.log(result);
}2. 다른사람의 풀이
function getCost(gNodes, gFrom, gTo, gWeight) {
// Print your answer within the function and return nothing
const edges = [];
for (let i = 0; i < gWeight.length; i++) {
edges.push([gFrom[i], gTo[i], gWeight[i]]);
edges.push([gTo[i], gFrom[i], gWeight[i]]);
}
// cost를 계산할 변수를 생성한다.
// 0번째 인덱스를 통해 계산된 코스트가 있는지 확인한다.
// 1번째부터 시작이므로 1번째 노드의 가중치는 0이다.
const costs = [ true, 0, ...Array(gNodes - 1).fill(Infinity) ];
while (costs[0]) {
costs[0] = false;
for (const [u, v, w] of edges) {
if (costs[v] > costs[u] && costs[v] > w) {
// 다음 노드로의 가중치가 계산되었다면, 0번째 인덱스를 true로 변경한다.
costs[0] = !!(costs[v] = Math.max(costs[u], w))
}
}
}
// 마지막 노드까지의 가중치 값이 계산되었다면 Infinity가 아니므로 그 값을 반환하면 된다.
// 반대로 Infinity일 경우 NO PATH EXISTS를 반환한다.
console.log(
costs[gNodes] !== Infinity
? costs[gNodes]
: 'NO PATH EXISTS'
);
}