그래프에서 특정 정점에서 목적지까지 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
대표적인 최단 경로 알고리즘중 하나가 다익스트라 알고리즘이다.
BFS,DFS 를 사용하는 경우(가중치가 같을경우)
그래프의 간선 가중치가 모두 같을 때 적합하다.
예를 들어 2차원배열에서 입력이 주어진 상태로 시작점에서 도착점까지의 최단경로 구할때 어떤 위치에서 다음위치까지 거리가 같기때문에 BFS,DFS 를 사용해서 최단경로를 구하는게 대부분이다.
가중치가 다를땐 어떤방식으로 해야할까요?
이번에 배워볼 다익스트라 알고리즘으로 가중치가 다를때 구하는게 적합하다.
다익스트라 알고리즘이란?
- Edsger Wybe Dijkstra가 고안한 최단경로 알고리즘.
- 우선순위 큐를 이용하려 만들 수 있다.
- 시간복잡도는 V가 정점의 수, E가 간선의 수일때 시간복잡도는 Elog V 가 된다.
다익스트라 알고리즘 순서
- 먼저 시작점을 제외한 나머지 정점을 다 무한값으로 초기화 해준다.
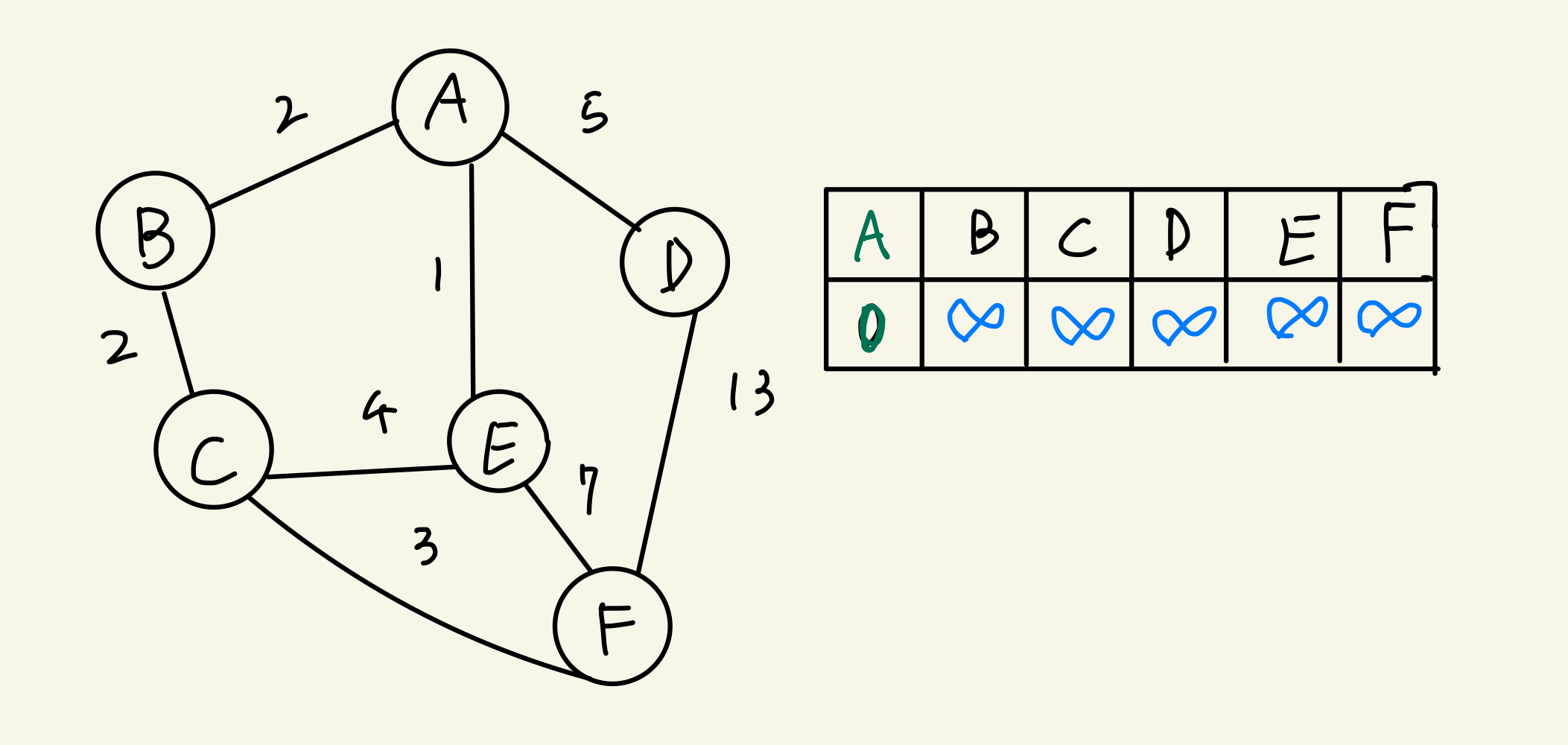
- 시작점 기준으로 시작점에서 갈 수 있는 정점을 찾고 값을 재할당 해 준다.
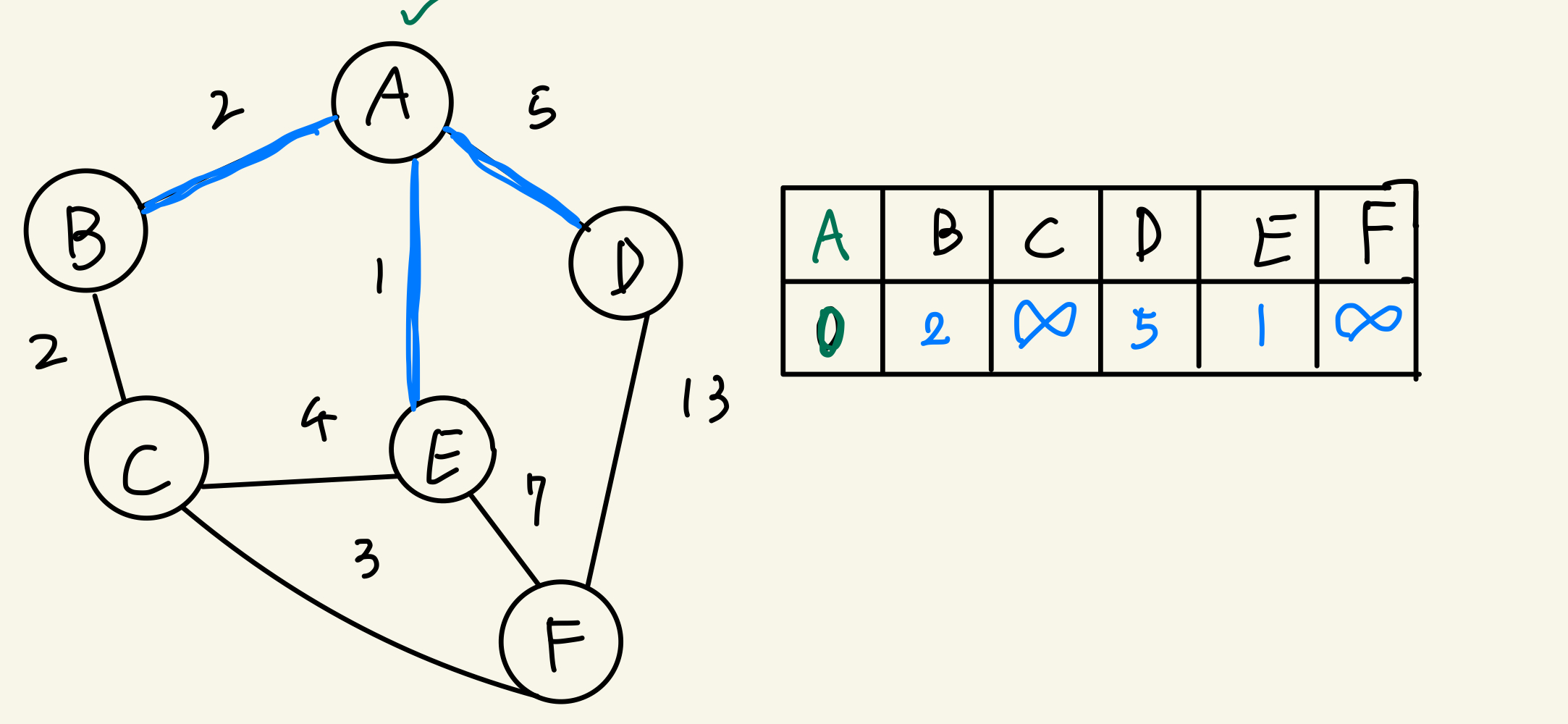
- 여기서 설정된 정점중에 최단거리가 제일 짧은 정점을 선택해 준다. 선택후 해당 정점(E)에서 또 뻗어나간 간선을 통해서 정점 값을 재할당 해 준다.
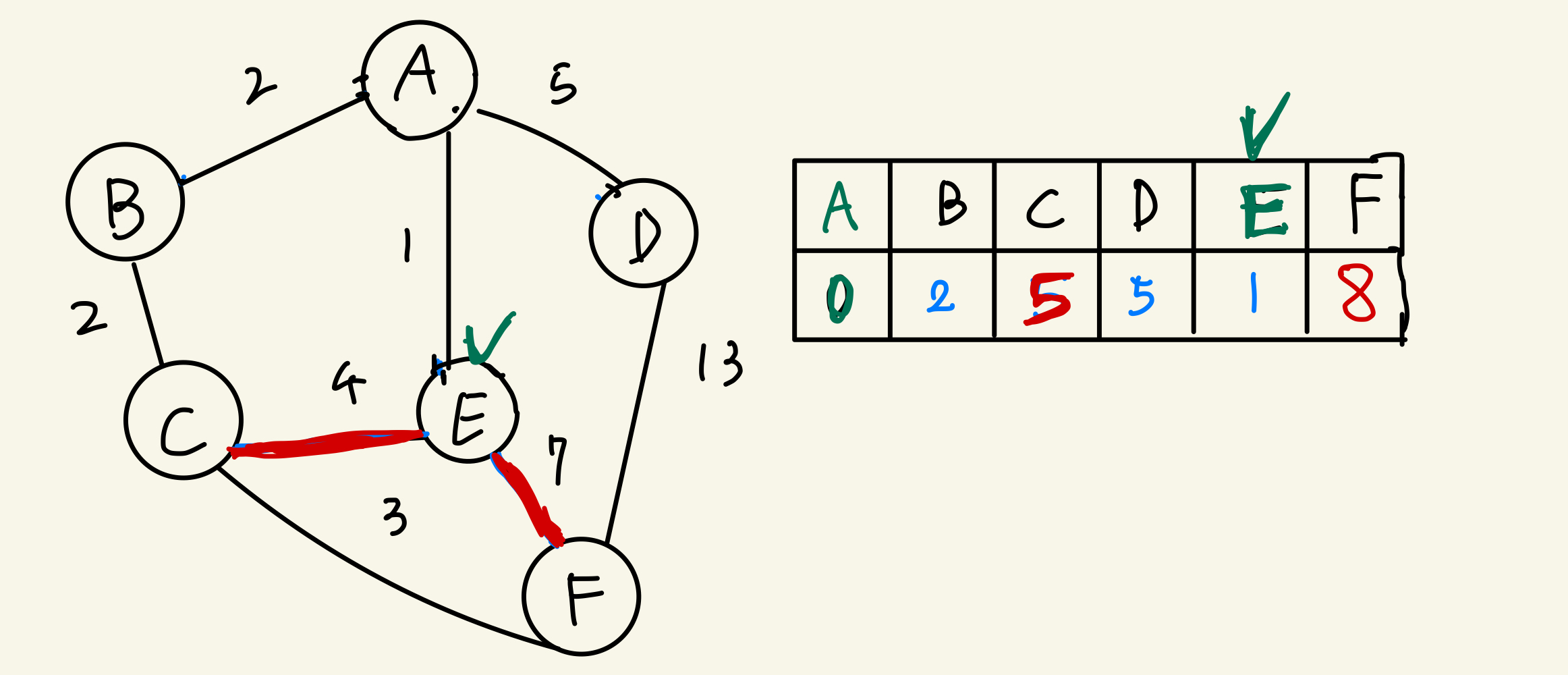
- 이제 현재정점(E)을 방문처리한 후 다음으로 최단거리인 정점(B)을 선택한후에 똑같은 방식으로 진행을 한다.
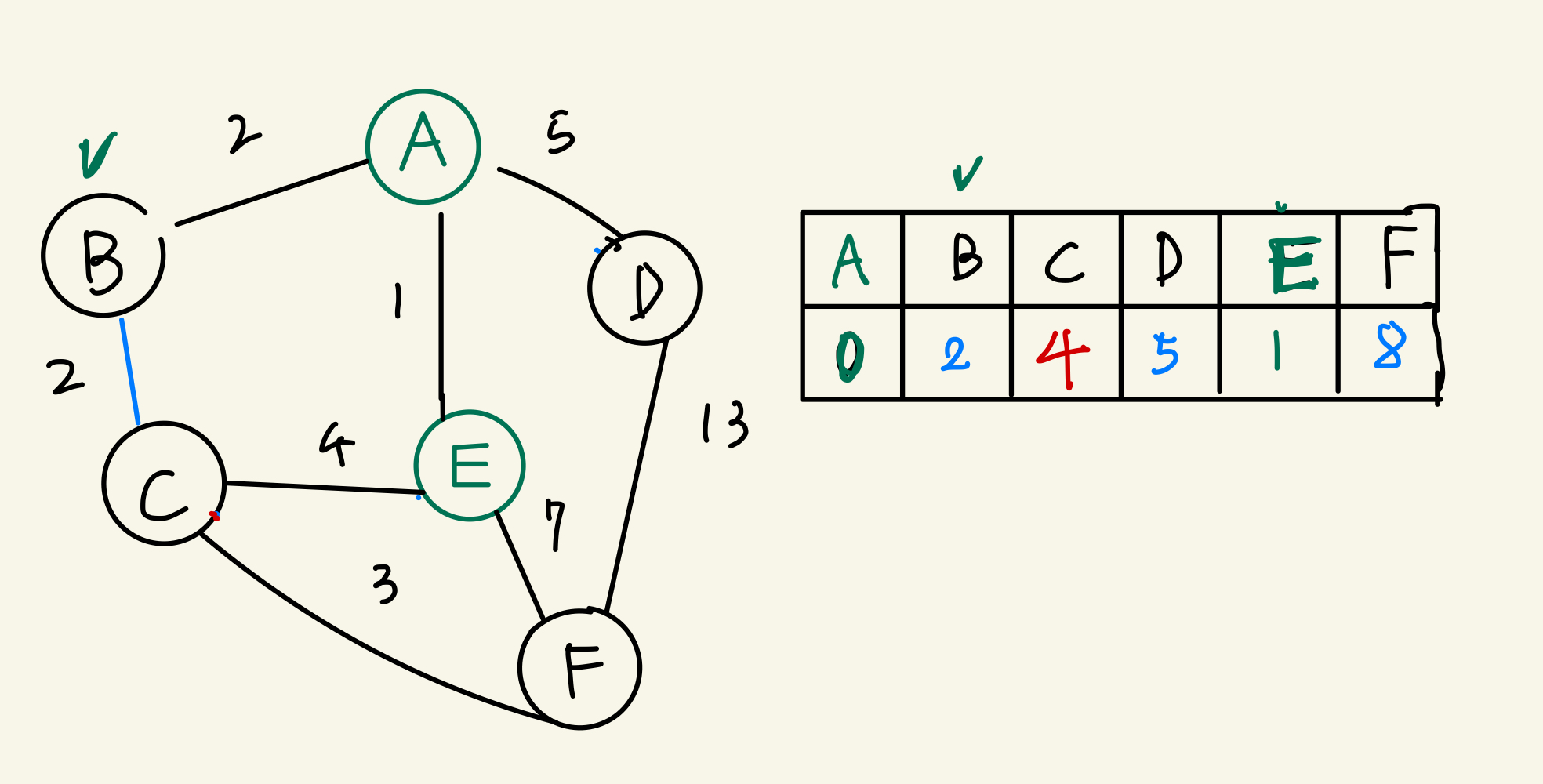
B정점에서 갈수 있는 정점은 C 바께 없음을 확인하실 수 있습니다. 여기서 기존에 C정점의 값이 5였는데 A→B→C 로 가는값이 4다. 즉 기존에 5보다 짧기때문에 다시 C정점에 값을 재할당 해 준다.
- 계속 이런 절차를 통해서 진행해서 모든 정점이 다 방문처리되면
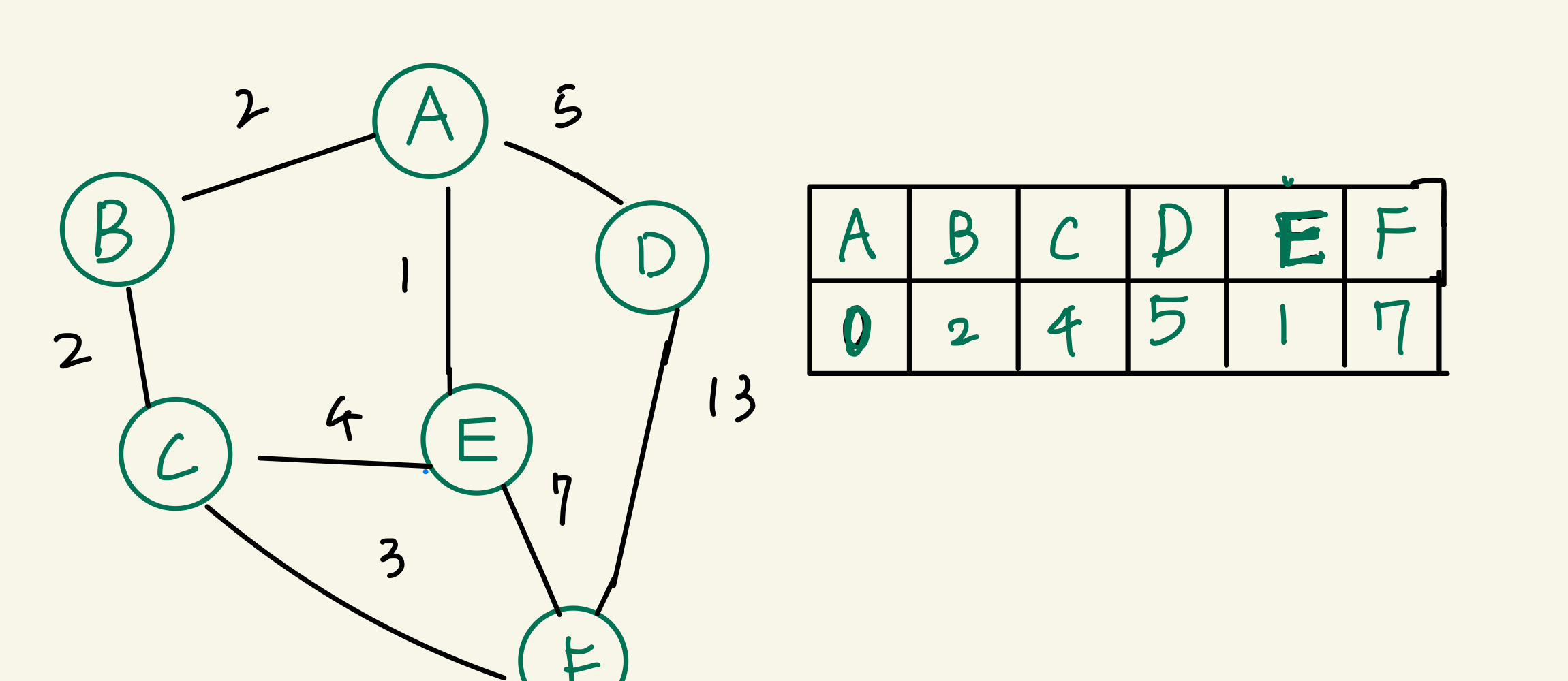
이런식으로 모드 값이 할당된게 보인다.
다익스트라 알고리즘을 보면 계속해서 가장 값이 낮은 정점을 선택하여 진행이되는 것 을 볼 수 있습니다. 따라서 해당 절차를 구현하기 위해서는 우선순위 큐 통해서 구현을 해야합니다. 이를 효율적으로 구현하기 위해서는 힙을 사용하실 수 있습니다.
다익스트라 정리
- 시작점을 제외한 모든 정점의 거리를 무한으로 설정한다. 시작점은 0으로 설정한뒤 시작한다.
- 선택한 정점에서 갈 수 있는 정점의 거리를 정점(해당 정점까지의 최단 거리)값 + 간선(거리)값 으로 갱신한다.
- 선택한 정점을 방문 처리한다.
- 이미 방문한 정점과 무한인 정점을 제외하고 가장 최단 거리인 정점을 선택한다.
- 더 이상 방문할 수 있는 정점이 없을 때 까지3~5를 반복.
- 바지막에 도착의 값을 확인한다.
예제
// 최소힙
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
push(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
let currentIndex = this.heap.length - 1;
let parentIndex = Math.floor(currentIndex / 2);
while (
parentIndex !== 0 &&
this.heap[parentIndex].cost > this.heap[currentIndex].cost
) {
this._swap(parentIndex, currentIndex);
currentIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = Math.floor(currentIndex / 2);
}
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return;
if (this.heap.length === 2) return this.heap.pop();
const returnValue = this.heap[1];
this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
let currentIndex = 1;
let leftIndex = 2;
let rightIndex = 3;
while (
(this.heap[leftIndex] &&
this.heap[currentIndex].cost > this.heap[leftIndex].cost) ||
(this.heap[rightIndex] &&
this.heap[currentIndex].cost > this.heap[rightIndex].cost)
) {
if (this.heap[leftIndex] === undefined) {
this._swap(currentIndex, rightIndex);
} else if (this.heap[rightIndex] === undefined) {
this._swap(currentIndex, leftIndex);
} else if (this.heap[leftIndex].cost < this.heap[rightIndex]) {
this._swap(currentIndex, leftIndex);
} else {
this._swap(currentIndex, rightIndex);
}
leftIndex = currentIndex * 2;
rightIndex = currentIndex * 2 + 1;
}
return returnValue;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.heap.length === 1;
}
_swap(a, b) {
[this.heap[a], this.heap[b]] = [this.heap[b], this.heap[a]];
}
}
// 다익스트라 알고리즘
function dijkstra(road, N) {
const heap = new MinHeap();
heap.push({ node: 1, cost: 0 });
const dist = [...Array(N + 1)].map(() => Infinity);
dist[1] = 0;
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
const { node: current, cost: currentCost } = heap.pop();
for (const [src, dest, cost] of road) {
const nextCost = cost + currentCost;
//양방향 고려하여 작성
if (src === current && nextCost < dist[dest]) {
// src가 현재 선택된 정점이면서 목적지까지 더 저렴할 경우
dist[dest] = nextCost; // 거리를 갱신한다.
heap.push({ node: dest, cost: nextCost });
} else if (dest === current && nextCost < dist[src]) {
dist[src] = nextCost;
heap.push({ node: src, cost: nextCost });
}
}
return dist;
}
}
function solution(N, road, K) {
const dist = dijkstra(road, N);
return dist.filter((x) => x <= K).length;
}
