1. 상속을 UML로 표시하면?

2. 부모 클래스와 자식 클래스의 다른 용어들은?
-
부모 클래스 : 상속의 대상이 되는 클래스 상위 클래스, 기초 클래스,
- ex) Man 클래스
-
자식 클래스: 상속을 하는 클래스 하위 클래스, 유도 클래스,
- ex) BusinessMan 클래스
3. this 키워드와 super 키워드의 차이는 무엇인가요?
super부모클래스를 참조한다.
this자기 자신(생성자)을 참조한다.
4. 단일 상속과 다중 상속 이란 무엇인가요? UML 로의 표기는?
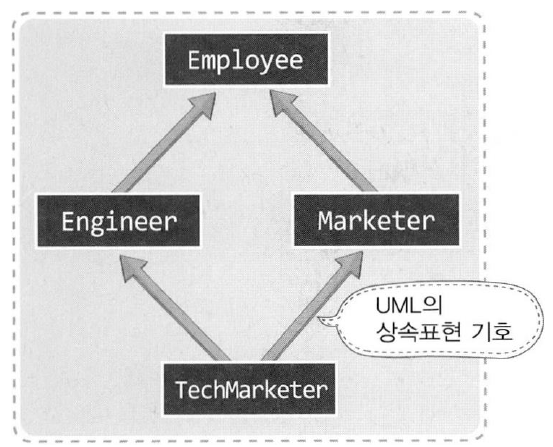
java는 클래스로부터의 다중 상속을 허용하지 않으며 지원하지 않는다. 클래스간에는 분류가 있을뿐 부모종속관계로 정의할 수 없기 때문이다. 다만 인터페이스에서는 지원이 된다.
5. 아래 문제를 구현하라.
다음은 2차원 상의 한 점을 표현하는 Point 클래스이다. Point를 상속받아 색을 가진 점을 나타내는 ColorPoint 클래스를 작성하라. 다음 main() 메소드를 포함하고 실행 결과와 같이 출력되게 하라.
class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
public int getX() { return x; }
public int getY() { return y; }
protected void move(int x, int y) { this.x =x; this.y = y; }
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5, 5, "YELLOW");
cp.setXY(10, 20);
cp.setColor("RED");
String str = cp.toString();
System.out.println(str+"입니다. ");
}
/*
RED색의 (10,20)의 점입니다.
*/
✅ 구현 해보기
class ColorPoint extends Point{
private String color;
public ColorPoint(int x,int y, String color) {
super(x,y);
this.color = color;
}
public void setXY(int x,int y) {
super.move(x, y);
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color ;
}
public String toString() {
return this.color+"색 ("+ super.getX() +","+ super.getY() +")의 점" ;
}
}6. 아래 문제를 구현하라.
다음 main() 메소드와 실행 결과를 참고하여 TV를 상속받은 ColorTV 클래스를 작성하라.
class TV{
private int size;
public TV(int size) { this.size = size; }
protected int getSize() { return size; }
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorTV myTV = new ColorTV(32, 1024);
myTV.printProperty();
}
/*
32인치 1024컬러
*/
✅ 구현 해보기
class ColorTV extends TV{
private int color;
public ColorTV(int inch,int color) {
super(inch);
this.color = color;
}
public void printProperty(){
System.out.println(super.getSize()+ "인치 "+color+"컬러");
}
}7. 아래 문제를 구현하라.
2차원 배열 4 * 3 을 선언하고, 각각의 방을 랜덤으로 값을 넣은뒤 모두 출력하시오.
✅ 구현 해보기
public class TwoDimenArrayTr2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arrTwo = new int[4][3];
// 배열의 구조대로 내용 출력
for(int i = 0; i < arrTwo.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < arrTwo[i].length; j++) {
arrTwo[i][j] = (int)((Math.random()*10)+1);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < arrTwo.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < arrTwo[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arrTwo[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
