탐욕법이란?
탐욕법(그리디 알고리즘) 이라 불리우는 이 알고리즘은 동적 프로그래밍 사용 시 지나치게 많은 일을 한다는 것에서 착안하여 고안된 알고리즘입니다. 하지만 동적 프로그래밍을 대체하는 것은 아니고 같이 쓰이며 서로 보완하는 개념입니다.
그리디 알고리즘 조건
그리디 알고리즘을 사용하기 위해 필요한 조건은 2가지가 있다
- 탐욕스러운 선택 조건
- 최적 부분 구조 조건
문제 체육복

조건

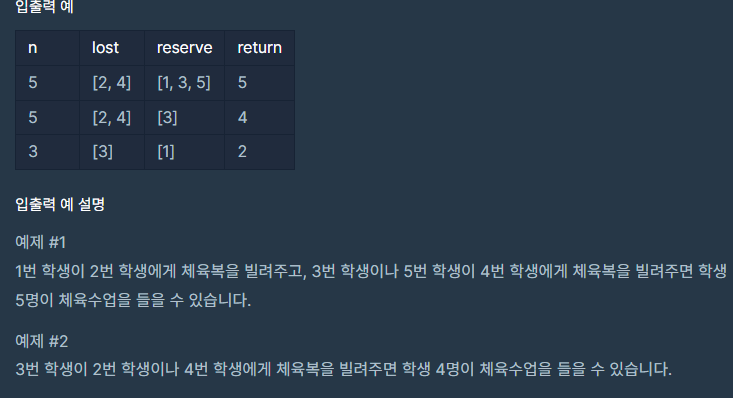
입출력 예
내가 생각한 방법
- 가져온 사람에 왼쪽 사람 한테만 빌려줄때 경우의 수 -- 실패
package 체육복;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[] lost, int[] reserve) {
int answer = 0;
// 전체 사람수 - 잃어버린 사람의 수
answer = n - lost.length;
// 만약 여벌있는 사람이 도둑맞으면 그 사람 번호 100로
for (int i = 0; i < reserve.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lost.length; j++) {
if (reserve[i] == lost[j]) {
reserve[i] = 100;
answer++;
}
}
}
// 그 왼쪽에 있는 사람에게만 빌려줌
for (int i = 0; i < reserve.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lost.length; j++) {
// 옆에 사람에게 빌려 줬다는 가정
if (reserve[i] != 100 && lost[j] != 100) {
if ((reserve[i] - 1) == lost[j]) {
reserve[i] = 100;
lost[j] = 100;
answer++;
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}- 총 사람 수에서 잃어 버린 사람 수 를 빼고 구하기 위에 방법 쓰기 --성공
package 체육복;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[] lost, int[] reserve) {
int answer = 0;
//모든 배열 정렬을 해준다
Arrays.parallelSort(lost);
Arrays.parallelSort(reserve);
// 전체 사람수 - 잃어버린 사람의 수
answer = n - lost.length;
// 만약 여벌있는 사람이 도둑맞으면 그 사람 번호 100으로
for (int i = 0; i < reserve.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lost.length; j++) {
if (reserve[i] == lost[j]) {
reserve[i] = 100;
lost[j] = 100;
answer++;
break;
}
}
}
// 그 왼쪽에 있는 사람에게만 빌려줌
for (int i = 0; i < reserve.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lost.length; j++) {
// 옆에 사람에게 빌려 줬다면 그 사람들을 모두 100으로 바꿈
if (reserve[i] != 100 && lost[j] != 100) {
if (Math.abs(reserve[i] - lost[j]) == 1) {
reserve[i] = 100;
lost[j] = 100;
answer++;
break;
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}단 이번 문제 같은 경우 배열을 정렬을 안했을시 테스트 13번과 18번에 오류 발생
예상하기로는 {5,2,3,1} 이런식으로 lost배열이 넘어 오는것 같습니다.
다른 사람 풀이
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[] lost, int[] reserve) {
int[] people = new int[n];
int answer = n;
for (int l : lost)
people[l-1]--;
for (int r : reserve)
people[r-1]++;
for (int i = 0; i < people.length; i++) {
if(people[i] == -1) {
if(i-1>=0 && people[i-1] == 1) {
people[i]++;
people[i-1]--;
}else if(i+1< people.length && people[i+1] == 1) {
people[i]++;
people[i+1]--;
}else
answer--;
}
}
return answer;
}
}