머리말
이글은 자바를 빠르게 끝내기 위해 내가 헷갈리는 부분만을 정리해논 글입니다. Do it! 자바 프로그래밍 입문을 정리하지만 내용을 많이 건너뜀

목차
Object 클래스
String 클래스
Wrapper 클래스
일급컬렉션
Class 클래스
Object 클래스
java.lang 패키지
우리는 프로그래밍하면서 String, Integer와 같은 클래스들을 사용하엿다.
이런 클래스들은 어디에 있는 것인가?
java.lang 패키지 안에서 존재한다.
String은 원래 java.lang.String인 것이다.
모든 클래스의 최상위 클래스 Object
Object 클래스는 모든 클래스의 최상위 클래스로 모든 클래스는 Object클래스에서 상속 받는다.
그렇기 때문에 모든 클래스는 Object 클래스의 메서드를 사용 가능하고 그 중 일부는 재정의하여 사용할 수 있다. 위치는 java.lang.Object 클래스이다.
Object 클래스의 메서드
1. toString()
기본동작 : 객체의 해시코드 출력
override 목적 : 객치의 정보를 문자열 형태로 표현하고자 할 때
package object;
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
public Book(String title, String author){
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book book = new Book("깊은 밤 부억에서", "모리스 샌닥");//object 클래스의 toString()메서드
System.out.println(book);
}
}
//결과
object.Book@119d7047
Process finished with exit code 0toString()의 원형
getClass.getName()+'@'+Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
package object;
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
public Book(String title, String author){
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return title +", " + author;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("Apple");//String 클래스의 toString()메서드
System.out.println(str);
Book book1 = new Book("정말 깊은 밤속", "신범철");//book클래스에서 toSting()메서드 직접 재정의
System.out.println(book1);
}
}
//결과
Apple
정말 깊은 밤속, 신범철결국
override를 통해 객체의 정보를 문자열 형태로 표현할 수 있다.
2. equals()
기본 동작 : '==' 연산 결과 반환
override 목적 : 물리적으로 다른 메모리에 위치하는 객체여도 논리적으로 동일함을 구현하기 위해
물리적 동일함 : 객체가 메모리에서 같은 주소를 갖는 것
논리적 동일함 : 물리적으로 다른 위치에 있지만 같은 저장되어 있는 정보가 같다면 논리적 동일함
package object;
public class EqualsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("abc");
System.out.println(str1==str2);//false
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true
}
}str1==str2에서 ==는 주소값이 동일한지(물리적 동일함)을 묻는 것이고
두 인스턴스는 다른 주소에 있기 때문에 false를 반환
str1.equals(str2)는 인스턴스의 값(논리적 동일함)을 묻는 것이기때문에 true를 반환
package object;
import exam.Subject;
class Student{
int studentNum;
String studentName;
public Student(int studentNum, String studentName){
this.studentNum = studentNum;
this.studentName = studentName;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj instanceof Student){
Student std = (Student)obj;//Object클래스로 업캐스팅 된것을 다운캐스팅해준다.
return (this.studentNum == std.studentNum);
}
return false;
}
}
public class EqualsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student Lee = new Student(100,"이순신");
Student Lee2 = Lee;
Student shin = new Student(100,"이순신");
System.out.println(Lee ==Lee2);//true
System.out.println(Lee == shin);//false
System.out.println(Lee.equals(shin));//재정의전//false
System.out.println(Lee.equals(shin));//재정의후//true
}
}- Lee와 Lee2는 물리적으로 같은 주소를 가지고 있기 때문에 Lee==Lee2는 true
- Leee와 shin은 물리적으로 다른 주소를 가지고 있기 때문에 false
- Lee.equals(shin) 재정의 전에는 그냥 == 개념이므로 false
- Lee.equals(shin) 재정의 후엔 값을 비교하므로 true
hashCode() 메서드
기본 동작 : JVM이 부여한 코드값. 인스턴스가 저장된 가장 머신의 주소를 10진수로 반환
override목적 : 두 개의 서로 다른 메모리에 위치한 객체가 동일성을 갖기 위해
해시코드란 JVM이 인스턴스를 생성할 때 메모리 주소를 변환해서 부여하는 코드이다.
실제 메모리 주소값과는 별개의 값이며 실제 메모리 주소는 System 클래스의 identityHashCode()로 확인 가능
자바에서는 동일성은 equals()의 반환값이 true, hashCode() 반환값이 동일함을 의미한다.
그래서 일반적으로 equals()와 hashCode()는 함께 override 한다.
System.out.println(Lee);//object.Student@776ec8df
System.out.println(Lee.hashCode());//2003749087
System.out.println(shin.hashCode());//1324119927-
기본 주소값이 16진수인 것과 다르게 hashCode()를 사용하면 10진수 주소를 반환해준다.
-
두개의 서로 다른 메모리의 위치한 인스턴스가 동일하다는 것은 equals()의 반환값이 true여서 '논리적 동일함'을 보여주고 또한 동일한 hashCode()값을 가져야한다.
-
위의 Lee와 shin은 equals()의 반환값은 true이지만 hashCode의 값은 다른 모습을 보여준다. 이유는 hashCode()는 재정의 하지 않았기 때문이다. 이러한 이유로 equals()를 재정의할 때 hashCode()를 같이 재정의 해주는 경우가 대부분이다.
-
참고로 hashCode가 같아지게 재정의 한다고 해서 실제 hashCode 주소값이 값다는 것은 아니다.
//book클래스
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj instanceof Student){
Student std = (Student)obj;//Object클래스로 업캐스팅 된것을 다운캐스팅해준다.
return (this.studentNum == std.studentNum);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode(){
return studentNum;
}
//main
System.out.println(Lee);//object.Student@64
System.out.println(Lee.hashCode());//100
System.out.println(shin.hashCode());//100
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(Lee));//2003749087
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(shin));//1324119927-
hashCode를 재정의하여 Lee와 shin의 hashCode()를 같게 만드려고 할 때 return값은 equals를 재정의 할때 썼던 멤버 변수를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
-
그래서 return을 equals에서 기준이 되었던 studentNum을 사용하면 Lee와 shin의 hashCode()값이 100으로 같아지는 것을 확인할 수있다.
clone() 메서드
-
clone() 메서드는 객체의 복사본을 만드는 메서드로 기본틀(prototype)이 되는 객체로부터 같은 속성 값을 가진 복사본을 생성할 수 있는 메서드이다.
-
객체지향 프로그래밍의 정보은닉에 위배되는 가능성이 있으므로 복제할 객체는 cloneable 인터페이스를 명시하여야한다.
그외
wrapper 클래스
정수를 사용할 때 기본형인 int를 사용했다. 하지만 정수를 객체형으로 사용하는 경우가 있다.
public void setValue(Integer i){ ...}
public Integer returnValue() { ...}
이러한 경우에 자바에서는 기본 자료형 처럼 사용할 수 있는 클래스를 제공한다. 그것이 wrapper 클래스이다.
- 자바 API 클래스중 하나이다.
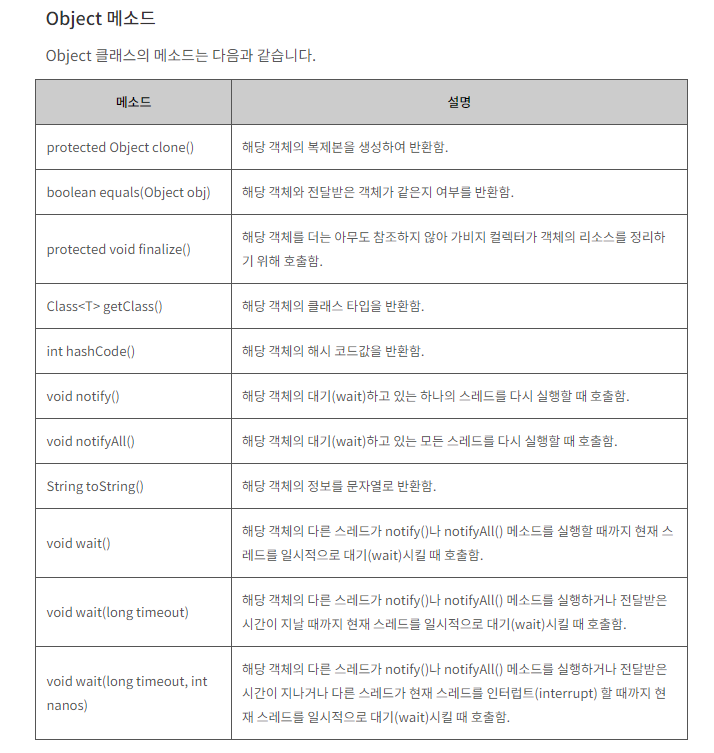
- 자바의 자료형은
primitive type(기본 타입)과reference type(참조 타입)으로 나누어진다.
- 기본 타입 : byte, short, char, int, long, float, double, boolean- 참조 타입 : class, interface ...
- 8개의 기본 타입에 해당하는 데이터를 객체로 표현하기 위해 포장해주는 클래스다 바로 wrapper 클래스이다.
- 예를 들어, 메소드의 파라미터로 객체 타입만이 요구될 경우
- 기본 타입의 데이터를 그대로 사용할 수 있지만 (AutoBoxing을 통해 가능해짐)
- 기본 타입의 데이터를 먼저 객체로 변환후 작업을 수행해야한다.- 기본 타입은 값을 갖는 객체인 포장 객체를 생성할 수 있다.(기본 타입의 값을 내부에 두고 포장하기 때문에
포장 객체라 칭함)- wrapper class는 각 타입에 해당하는 데이터를 파라미터로 전달받아, 해당 값을 가지는 객체로 마들어줌
- wrapper class로 감싸고 있는 기본 타입 값은 외부에서 변경이 불가능
- 변경하기 위해서는 새로운 포장객체를 만들어야 함
- 기본 타입은 값을 갖는 객체인 포장 객체를 생성할 수 있다.(기본 타입의 값을 내부에 두고 포장하기 때문에
wrapper class 사용 예
- Generic(제네릭)
정해진 형식에 의존하지 않고, 클래스 외부에서 접근할 때의 재사용성을 높이기 위해 사용하는 제네릭. 가령ArrayList<Integer> xx처럼 컬렉션 형태의 변수를 선엉할 때, 제네릭 타입의<Integer>가 자바의 int형과 매핑되는 래퍼클래스이다.
- Casting(형 변환)
String 형태인 정수 타입의 변수를 int 형태의 기본 타입으로 casting할 때, Interger 래퍼 클래스의 parseInt()라는 메서드를 사용하여 캐스팅을 진행한다.
String str = "2";
int strToInt = Integer.parseInt(str);
Wrapper Class 종류
Wrapper Class 구조
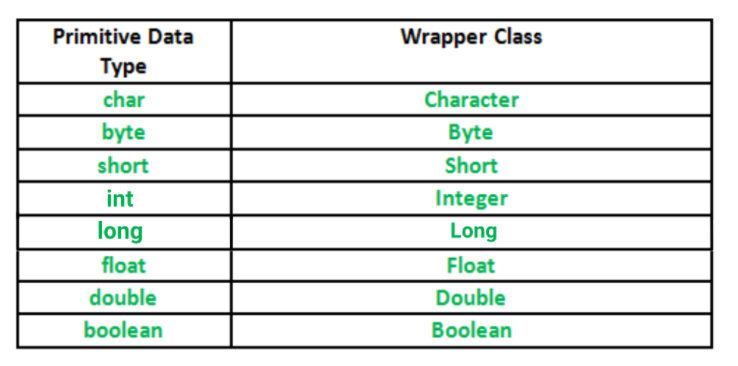
- wrapper class들은 모두 java.lang 패키지에 포함되어 제공된다.
- object 클래스 : 모든 wrapper class의 부모 클래스
- Number 클래스 : 내부적으로 숫자를 다루는 wrapper class들의 부모 클래스
Boxing과 UnBoxing
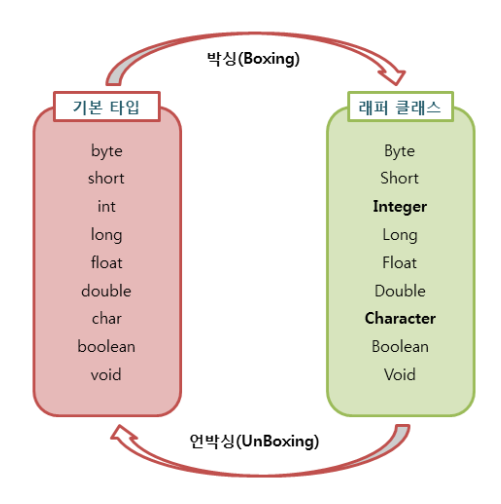
- boxing : 기본 타입에서 wrapper클래스로 전환
- unboxing : wrapper클래스 객체를 기본 타입으로 변환
public class Wrapper_Ex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer num = new Integer(17); // 박싱
int n = num.intValue(); //언박싱
System.out.println(n);
}
}AutoBoxing & AutoUnBoxing
- JDK 1.5부터 boxing , unboxing이 필요한 상황에서 자바 컴파일러가 이를 자동으로 처리해줌
- AutoBoxing : 자동화된 Boxing
- Integer num1 = 1; - AutoUnBoxing : 자동화된 UnBoxing
- int n1 = num1;
AutoBoxing & AutoUnBoxing 예시
Integer num = new Integer(17); // Boxing
int n = num.intValue(); // UnBoxing
Character ch = 'X'; // AutoBoxing : Character ch = new Character('X');
char c = ch; // AutoUnBoxing : char c = ch.charValue(); Wrapping의 장점
- 기본 자료형을 클래스화 하여 클래스의 장점을 활용할 수 있게 된다.
- 메서드 사용
일급 컬렉션
- 컬렉션을 wrapping 할 때, 그 외의 다른 멤버 변수가 없는 상태를
일급 컬랙션이라고 한다. 다시 말해, Collection들을 한번 Wrapping 한 컬렉션이다.
예시
- Car라는 객체가 있다.
public class Car {
private int position;
public void move(MovingStrategy movingStrategy) {
if (movingStrategy.isMove()) {
position++;
}
}
public int getPosition() {
return position;
}
}- 이 Car라는 객체의 인스턴스를 3개 생성하는 경우
- 이 인스턴스들을 모두 함께 관리해야할 때, 일급 컬렉션인 Cars 클래스를 만들면 용이하다.public Cars(List<Car> car)
Car aCar = new Car() // Car 인스턴스 1
Car bCar = new Car() // Car 인스턴스 2
Car cCar = new Car() // Car 인스턴스 3public class Cars {
private List<Car> cars;
public Cars(List<Car> cars) {
this.cars = this.cars;
}
public List<Car> getCars() {
return cars;
}
}컬렉션을 Wrapping할 때 가지는 이점
- 하나의 인스턴스에서 비지니스 로직을 관리 할 수있다.
- Collection의 불변성 보장
- 상태와 행위를 한 곳에서 관리
- 이름이 있는 컬렉션
자세한 내용은 추후에 정리하자ㅏㅏㅏㅏ
Class 클래스
- 자바의 모든 클래스와 인터페이스는 컴파일 후 class 파일로 생성됩니다. class 파일에는 멤버변수, 메서드, 생성자 등 객체의 정보가 포함되어 있는데 class 클래스는 이 class 파일에서 객체의 정보를 가져올 수 있습니다.
Class c1 = String.class;
String str = new String();
Class c2 = str.getClass();
Class c3 = Class.forName("java.lang.String");- Class 클래스는 위와 같은 방법으로 불러올 수 있고 그중에 forName을 통해 가져오는 방법이 많이 사용되고 이를 동적 로딩이라고 부른다.
- 동적 로딩이라고 부르는 이유는 보통 다른 클래스 파일을 불러올 때는 컴파일 시 스태틱에 그 클래스 파일이 가이 바인딩이 되지만 forName으로 class 파일을 불러올 때는 컴파일에 바인딩되지 않고 런타임때 불러오게 되기 때문이다.
- 즉 실행시에 불러서 사용할 수 있기 때문에 동적 로딩이라고 부르게 된다.
- 단점은 클래스파일명을 직접 적게 되어 있어 만약 파일명에 오타가 나면 에러가 발생할 수 있기 때문에 주의해야한다.
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class c1 = String.class;
String str = new String();
Class c2 = str.getClass();
Class c3 = Class.forName("java.lang.String");//클래스 이름으로 가져오기
Constructor[] cons = c3.getConstructors();//모든 생성장 가져오기
for(Constructor con: cons) {
System.out.println(con);
}
System.out.println();
Method[] methods = c3.getMethods();//모든 메서드 가져오기
for(Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}-
Constructor과 Method를 모를 때 위와 같은 방식으로 모든 생성자와 메서드를 출력할 수 잇따.
-
하지만 보통 .을 누르면 어떤 것들이 사용가능한지 알 수 있기 때문에 사용하는 일은 많이 없다.
