뷰를 사용한 Android Room - Kotlin
이 포스팅은 아래 구글 코드랩을 개인 학습용으로 정리한 글입니다.
1. 시작하기 전에
실행할 작업
- Android 아키텍처 구성요소를 사용하여 권장 아키텍처 구현
- 데이터를 가져오고 저장하며 샘플 단어로 데이터베이스를 미리 채우도록 데이터베이스 사용
- MainActivity 클래스의 RecyclerView에 있는 모든 단어 표시
- 사용자가 +버튼을 탭하면 두 번째 활동이 열림
사용자가 단어를 입력하면 입력한 단어가 데이터베이스에 추가되고 RecyclerView 목록에 표시
2. 아키텍처 구성요소 사용
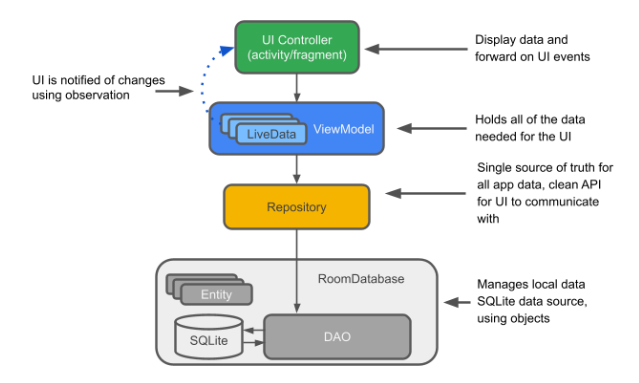
LiveData
-
관찰할 수 있는 데이터 홀더 클래스
-
항상 최신 버전의 데이터를 보유/캐시
-> 데이터가 변경된 경우 관찰자에게 알림 -
LiveData는 수명주기를 인식
-> 관찰하는 동안 관련 수명 주기 상태의 변경 인식 & 자동으로 관리
ViewModel:
-
저장소(데이터)와 UI간의 통신 센터 역할
-> UI에서 데이터의 출처에 관해 걱정하지 않아도 됨 -
ViewModel 인스턴스는 Activity/Fragment 재생성에도 유지됨
저장소
- 개발자가 만드는 클래스
- 여러 데이터 소스를 관리하는데 주로 사용
Entity
- Room 작업 시 데이터베이스 테이블을 설명하는 주석 처리된 클래스
Room 데이터베이스
-
기본 SQLite 데이터베이스의 엑세스 포인터 역할
-> 데이터베이스 작업 간소화 -
Room 데이터베이스는 DAO를 사용하여 SQLite 데이터베이스에 쿼리 실행
SQLite 데이터베이스
-
기기 내 저장소
-
Room 지속성 라이브러리에서 이 데이터베이스를 만들고 유지
DAO
-
데이터 액세스 객체
-
SQL 쿼리를 함수에 매핑
-
DAO를 사용할 때 메서드를 호출하면 Room에서 나머지 처리
RoomWordSample 아키텍처 개요
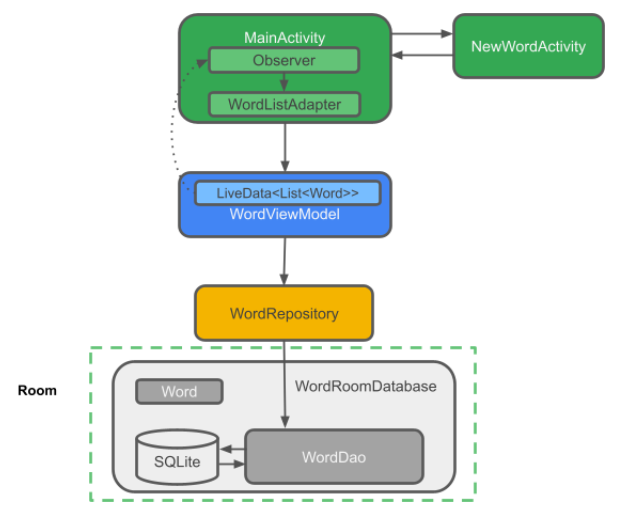
3. 앱 만들기
4. Gradle 파일 업데이트
build.gradle(Module:app)
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.android'
}
apply plugin: 'kotlin-kapt'
android {
...
packagingOptions {
exclude 'META-INF/atomicfu.kotlin_module'
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = '1.8'
}
}
dependencies {
implementation "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:$rootProject.appCompatVersion"
implementation "androidx.activity:activity-ktx:$rootProject.activityVersion"
// Dependencies for working with Architecture components
// You'll probably have to update the version numbers in build.gradle (Project)
// Room components
implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:$rootProject.roomVersion"
kapt "androidx.room:room-compiler:$rootProject.roomVersion"
androidTestImplementation "androidx.room:room-testing:$rootProject.roomVersion"
// Lifecycle components
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:$rootProject.lifecycleVersion"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-livedata-ktx:$rootProject.lifecycleVersion"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-common-java8:$rootProject.lifecycleVersion"
// Kotlin components
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:1.7.10"
api "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:$rootProject.coroutines"
api "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:$rootProject.coroutines"
// UI
implementation "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:$rootProject.constraintLayoutVersion"
implementation "com.google.android.material:material:$rootProject.materialVersion"
// Testing
testImplementation "junit:junit:$rootProject.junitVersion"
androidTestImplementation "androidx.arch.core:core-testing:$rootProject.coreTestingVersion"
androidTestImplementation ("androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:$rootProject.espressoVersion", {
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-annotations'
})
androidTestImplementation "androidx.test.ext:junit:$rootProject.androidxJunitVersion"
}-
dependencies 블록의 $kotlin_version 사용 중인 코틀린 플러그인의 버전으로 수정
-
File -> Settings -> Languages & Frameworks -> Kotlin 에서 플러그인 버전 확인 가능
build.gradle(Project:RoomWordsSample)
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
plugins {
id 'com.android.application' version '7.3.0' apply false
id 'com.android.library' version '7.3.0' apply false
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.android' version '1.7.10' apply false
}
ext {
activityVersion = '1.1.0'
appCompatVersion = '1.2.0'
constraintLayoutVersion = '2.0.2'
coreTestingVersion = '2.1.0'
coroutines = '1.3.9'
lifecycleVersion = '2.2.0'
materialVersion = '1.2.1'
roomVersion = '2.2.5'
// testing
junitVersion = '4.13.1'
espressoVersion = '3.1.0'
androidxJunitVersion = '1.1.2'
}5. 항목 만들기
Word.kt
- 단어의 항목(SQLite 테이블)을 설명하는 데이터 클래스
- 클래스의 각 속성은 테이블의 열을 나타냄
- Room에서 이 속성들을 사용하여 테이블을 만들고, 데이터베이스 행에서 객체를 인스턴스화
data class Word (val word:String)- Word 클래스를 Room 데이터베이스에 의미있게 만들려면 Kotlin 주석을 사용하여 클래스와 데이터베이스 간의 연결 만들어야
package googlecodelabs.roomwordsample
import androidx.room.ColumnInfo
import androidx.room.Entity
import androidx.room.PrimaryKey
@Entity(tableName = "word_table")
data class Word (@PrimaryKey @ColumnInfo(name = "word") val word:String)-
@Entity(tableName = "word_table")
- 각 @Entity 클래스는 SQLite 테이블을 나타냄
- 테이블 이름을 클래스 이름과 다르게 하려면 테이블 이름 지정하면 됨 -
@PrimaryKey
-
@ColumnInfo(name = "word")
- 테이블의 열 이름을 멤버 변수 이름과 다르게 하려는 경우 열 이름 지정 -
데이터베이스에 저장된 모든 속성은 공개 가시성(Kotlin 기본값)이 있어야
➕
- 기본 키 자동 생성 가능
@Entity(tableName = "word_table")
data class Word (
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true) val id: Int,
@ColumnInfo(name = "word") val word:String
)6. DAO 만들기
DAO 란?
-
DAO(Data Access Object, 데이터 엑세스 객체)
-
DAO는 인터페이스 또는 추상 클래스여야 함
➖
-
DAO는 SQL 쿼리를 지정하여 메서드 호출과 연결
-
컴파일러는 SQL을 확인하고 @Insert와 같은 일반 쿼리의 편의 주석으로 쿼리 생성
-
Room은 DAO를 사용하여 코드를 위한 깔끔한 API를 만든다
➖
-
기본적으로 모든 쿼리는 별도의 스레드에서 실행되어야
-
Room에서는 Kotlin 코루틴 지원
-> 쿼리를 suspend 수정자로 주석 처리
-> 코루틴이나 다른 정지 함수에서 호출 가능
DAO 구현
- 다음과 같은 쿼리를 제공하는 DAO 작성하기
- 모든 단어를 알파벳 순으로 정렬
- 단어 삽입
- 모든 단어 삭제
WordDao.kt
@Dao
interface WordDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM word_table ORDER BY word ASC")
fun getAlphabetizedWords(): List<Word>
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.IGNORE)
suspend fun insert(word: Word)
@Query("DELETE FROM word_table")
suspend fun deleteAll()
}-
@Dao
- Room의 DAO 클래스로 식별
-
suspend fun insert(word: Word)
- 한 단어를 삽입하는 정지 함수
-
@Insert
- SQL을 제공하지 않아도 되는 특수 DAO 메서드 (@Insert, @Delete, @Update) -
onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.IGNORE
- 선택된 onConflict 전략: 이미 목록에 있는 단어 삽입하는 경우, 새 단어 무시
-
suspend fun deleteAll()
- 모든 단어를 삭제하는 정지 함수
- 여러 항목을 삭제하는 편의 주석은 없으므로 일반적인 @Query로 주석처리
-
@Query("DELETE FROM word_table")
- 문자열 매개변수로 SQL 쿼리를 주석에 제공
- 복잡한 읽기 쿼리와 기타 작업 허용
-
fun getAlphabetizedWords(): ListWord
- 모든 단어를 가져와서 Words의 List를 반환하는 메서드
-
@Query("SELECT * FROM word_table ORDER BY word ASC")
- 오름차순으로 정렬된 단어 목록을 반환하는 쿼리
7. 데이터베이스 변경사항 관찰
-
데이터가 변경될 때 대응할 수 있도록 데이터 관찰해야
-> kotlinx-coroutines의 Flow 사용
(FLow는 값의 비동기 시퀸스) -
메서드 설명에 Flow 타입의 반환값 사용
-> Room이 데이터베이스가 업데이트될 때 Flow를 업데이트하는 데 필요한 모든 코드 생성
WordDao.kt
- getAlphabetizedWords()에서 반환된 ListWord가 Flow로 래핑되도록 변경
@Query("SELECT * FROM word_table ORDER BY word ASC")
fun getAlphabetizedWords(): Flow<List<Word>>8. Room 데이터베이스 추가
Room 데이터베이스 란?
-
Room은 SQLite 데이터베이스 위에 있는 데이터베이스 레이어
-
Room은 개발자가 SQLiteOpenHelper를 사용하여 처리하던 일반적인 작업을 처리
-
Room은 DAO를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 쿼리 실행
-
UI 성능 저하 방지를 위해 Room에서는 기본 스레드에서 쿼리 실행 불가능
-> Room 쿼리가 Flow를 반환하면 쿼리는 자동으로 백그라운드 스레드에서 비동기식으로 실행
Room 데이터베이스 구현
-
Room 데이터베이스 클래스는 추상 클래스
-> RoomDatabase 확장해야 -
일반적으로 전체 앱에 Romm 데이터베이스 인스턴스 하나만 있으면 됨
WordRoomDatabase.kt
@Database(entities = arrayOf(Word::class), version = 1, exportSchema = false)
public abstract class WordRoomDatabase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun wordDao(): WordDao
companion object {
@Volatile
private var INSTANCE: WordRoomDatabase? = null
fun getDatabase(context: Context): WordRoomDatabase {
return INSTANCE ?: synchronized(this) {
val instance = Room.databaseBuilder(
context.applicationContext,
WordRoomDatabase::class.java,
"word_database"
).build()
INSTANCE = instance
// return instance
instance
}
}
}
}-
클래스를 Room 데이터베이스가 되도록 @Database로 주석 처리
- 주석 매개변수로 데이터베이스에 속한 항목 선언, 버전 번호 설정
-
데이터베이스 이전은 이 Codelab의 범위를 벗어남
-> 빌드 경고를 피하기 위해 exportSchema = false로 설정
-> 실제 앱에서는 현재 스키마를 버전 제어 시스템으로 확인할 수 있도록 ⚡스키마를 내보내는 데 사용할 Room 디렉터리를 설정하는 것이 좋다 -
데이터베이스는 ⚡각 @Dao의 추상 getter메서드를 통해 DAO를 노출
-
WordRoomDatabase 싱글톤으로 정의
-
getDatabase는 싱글톤을 반환
- 처음 엑세스할 때 Room의 데이터베이스 빌더 사용
- WordRoodDatabase 클래스의 애플리케이션 컨텍스트에서 RoomDatabase 객체를 만듦
- 이름 "word_database"로 지정
9. 저장소 만들기
저장소 란?
-
저장소 클래스: 여러 데이터 소스 엑세스를 추상화
-
아키텍처 구성요소 라이브러리의 일부는 아니지만 코드 분리와 아키텍쳐를 위한 권장사항
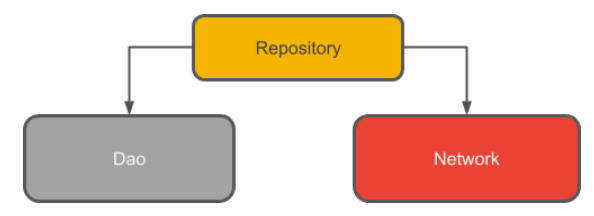
저장소를 사용하는 이유?
-
저장소는 쿼리 관리 & 여러 백엔드를 사용하도록 허용
-
가장 일반적인 저장소:
데이터를 네트워크에서 가져올지 or 로컬 데이터베이스에 캐시된 결과를 사용할 지 결정
저장소 구현
WordRepository.kt
class WordRepository(private val wordDao: WordDao) {
val allWords: Flow<List<Word>> = wordDao.getAlphabetizedWords()
@Suppress("RedundantSuspendModifier")
@WorkerThread
suspend fun insert(word: Word) {
wordDao.insert(word)
}
}-
저장소 생성자에 전체 데이터베이스가 아닌 DAO 전달
- DAO에 데이터베이스의 모든 읽기/쓰기 메소드 포함되어 있음
- 전체 데이터베이스를 저장소에 노출할 필요 X
-
단어 목록은 공개 속성
- Flow 목록을 가져와서 초기화됨
- Room은 별도의 스레드에서 모든 쿼리 실행
-
suspend
- 코루틴이나 다른 정지함수에서 호출되어야함을 컴파일러에 알림 -
Room은 기본 스레드 밖에서 정지 쿼리 실행
10. ViewModel 만들기
ViewModel이란?
- ViewModel: UI에 데이터 제공 & 구성 변경에도 유지됨
- 저장소와 UI간의 통신 센터 역할
- ViewModel을 사용하여 프래그먼트 간 데이터 공유도 가능
- ViewModel은 수명 주기 라이브러리의 일부
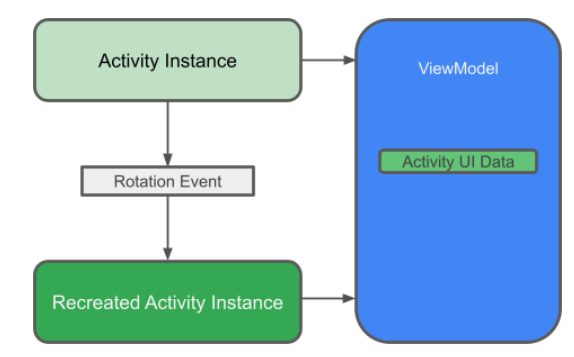
ViewModel을 사용하는 이유?
-
ViewModel은 수명주기를 고려하여 구성 변경에도 유지되는 앱의 UI 데이터 보유
-
앱의 UI 데이터를 Activity및 Fragment 클래스에서 분리하면 단일 책임 원칙을 더 잘 준수 가능
- Activity 및 Fragment 클래스: 화면에 데이터를 그리는 것 담당
- ViewModel: UI에 필요한 모든 데이터 보유, 처리
LiveData 및 ViewModel
-
LiveData: 관찰 가능한 데이터 홀더
-> 데이터가 변경될 때마다 알림을 받을 수 있음 -
FLow와 달리 LiveData는 수명주기 인식
-> 변경을 수신 대기하는 구성요소의 수명 주기에 따라 자동으로 관찰을 중지하거나 재 시작 -
ViewModel은 저장소의 데이터를 FLow에서 LiveData로 변환
-> 데이터베이스의 데이터가 변경될 때마다 UI가 자동으로 업데이트
viewModelScope
- Kotlin에서 모든 코루틴은 ⚡CoroutineScope 내에서 실행 됨
- ⚡범위는 전체 작업에 걸쳐 코루틴의 전체 기간을 제어
- ⚡범위의 작업을 취소하면 그 범위에서 시작된 코루틴 모두 취소됨
- AndroidX lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx 라이브러리
- viewModelScope를 ViewModel 클래스의 확장 함수로 추가
-> ⚡범위를 사용하여 작업 가능
ViewModel 구현
WordViewModel.kt
class WordViewModel(private val repository: WordRepository) : ViewModel() {
val allWords: LiveData<List<Word>> = repository.allWords.asLiveData()
/**
* Launching a new coroutine to insert the data in a non-blocking way
*/
fun insert(word: Word) = viewModelScope.launch {
repository.insert(word)
}
}
class WordViewModelFactory(private val repository: WordRepository) : ViewModelProvider.Factory {
override fun <T : ViewModel> create(modelClass: Class<T>): T {
if (modelClass.isAssignableFrom(WordViewModel::class.java)) {
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
return WordViewModel(repository) as T
}
throw IllegalArgumentException("Unknown ViewModel class")
}
}- WordViewModel 클래스
- WordRepository를 생성자 매개변수로 받음
- ViewModel 확장
- 단어 목록을 캐시하는 공개 LiveData 멤버 변수 추가
- 저장소의 allWords를 이용하여 LiveData 초기화
- asLiveData()를 호출하여 Flow를 LiveData로 변환
- 저장소의 insert() 메서드를 호출하는 래퍼 insert 메서드
- insert()의 구현이 UI에서 캡슐화됨
- 새 코루틴을 실행하고(launch) 정지 함수인 저장소의 insert 호출
- 수명 주기 기반의 코루틴 범위 viewModelScope 사용
- ⚡ViewModelProvider.Factory
- WordRepository를 매개변수로 가져오고 ViewModel을 만듦
➕
- ViewModel보다 수명 주기가 짧은 Context 참조를 유지하지 말 것
- ex. Activity, Fragment, View
- 참조를 유지하면 메모리 누수가 발생할 수 있음
- ViewModle은 OS에 더 많은 리소스가 필요할 때 앱 프로세스가 백그라운드에서 종료되면 유지되지 않음
11. XML 레이아웃 추가
values/themes.xml
<resources xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<!-- Base application theme. -->
<style name="Theme.RoomWordSample" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light.DarkActionBar">
<!-- Primary brand color. -->
<item name="colorPrimary">@color/purple_500</item>
<item name="colorPrimaryVariant">@color/purple_700</item>
<item name="colorOnPrimary">@color/white</item>
<!-- Secondary brand color. -->
<item name="colorSecondary">@color/teal_200</item>
<item name="colorSecondaryVariant">@color/teal_700</item>
<item name="colorOnSecondary">@color/black</item>
<!-- Status bar color. -->
<item name="android:statusBarColor">?attr/colorPrimaryVariant</item>
<!-- Customize your theme here. -->
</style>
<!-- The default font for RecyclerView items is too small.
The margin is a simple delimiter between the words. -->
<style name="word_title">
<item name="android:layout_marginBottom">8dp</item>
<item name="android:paddingLeft">8dp</item>
<item name="android:background">@android:color/holo_orange_light</item>
<item name="android:textAppearance">@android:style/TextAppearance.Large</item>
</style>
</resources>⚡values/dimens.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<dimen name="big_padding">16dp</dimen>
</resources>layout/recyclerview_item.xml
- 새 벡터 애셋 추가:
File>New>Vector Asset>CLip Art 에서 원하는 애셋 선택>Next>Finish
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
style="@style/word_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_orange_light" />
</LinearLayout>layout/activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerview"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
tools:listitem="@layout/recyclerview_item"
android:padding="@dimen/big_padding"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:contentDescription="@string/add_word"
android:src="@drawable/ic_baseline_add_24"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>➕
- 플로팅 작업 버튼(Floating Action Button, FAB)
- 앱 UI의 기본 작업을 트리거하는 원형 버튼
- View.OnCliskListener를 적용하려 FAB 탭 처리 가능
12. RecyclerView 추가
MainActivity.kt
package googlecodelabs.roomwordsample
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.DiffUtil
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.ListAdapter
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val recyclerView = findViewById<RecyclerView>(R.id.recyclerview)
val adapter = WordListAdapter()
recyclerView.adapter = adapter
recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this)
}
}
class WordListAdapter : ListAdapter<Word, WordListAdapter.WordViewHolder>(WordsComparator()) {
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): WordViewHolder {
return WordViewHolder.create(parent)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: WordViewHolder, position: Int) {
val current = getItem(position)
holder.bind(current.word)
}
class WordViewHolder(itemView: View) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(itemView) {
private val wordItemView: TextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.textView)
fun bind(text: String?) {
wordItemView.text = text
}
companion object {
fun create(parent: ViewGroup): WordViewHolder {
val view: View = LayoutInflater.from(parent.context)
.inflate(R.layout.recyclerview_item, parent, false)
return WordViewHolder(view)
}
}
}
class WordsComparator : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Word>() {
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: Word, newItem: Word): Boolean {
return oldItem === newItem
}
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: Word, newItem: Word): Boolean {
return oldItem.word == newItem.word
}
}
}-
WordViewHolder
- 텍스트를 TextView에 바인딩
- 레이아웃 확장을 처리하는 정적 create() 함수 노출
-
WordsComparator
- 두 단어가 동일한 경우/콘텐츠가 동일한 경우 계산하는 방법 정의 -
WordListAdapter
- onCreateViewHolder에서 WordViewHolder를 만들어 onVBindViewHolder에서 바인딩
13. 저장소 및 데이터베이스 인스턴스화
-
앱에 데이터베이스 인스턴스와 저장소 인스턴스를 하나씩만 사용하려고 함
-
쉬운 방법: 인스턴스를 Application 클래스의 멤버로 생성
-> 매번 구성하지 않고 필요할 때마다 Application에서 가져올 수 있음
WordsApplication.kt
- Application을 확장하는 새 클래스
class WordsApplication : Application() {
// Using by lazy so the database and the repository are only created when they're needed
// rather than when the application starts
val database by lazy { WordRoomDatabase.getDatabase(this) }
val repository by lazy { WordRepository(database.wordDao()) }
}-
데이터베이스 인스턴스를 만듦
-
저장소 인스턴스를 만듦
- 데이터베이스 DAO에 기반함
-
이러한 객체는 앱을 시작할 때가 아니라 처음 필요할 때만 만들어져야
-> 코틀린의 속성 위임 by lazy 사용
AndroidManifest.xml
<application
android:name=".WordsApplication"
...>14. 데이터베이스 채우기
-
현재 데이터베이스에 데이터가 없음
-
데이터를 추가하는 두 가지 방법:
- 데이터베이스를 만들 때 데이터를 추가
- 단어를 추가하는 Activity 추가 -
앱을 만들 때마다 모든 콘텐츠를 삭제하고 데이터베이스를 다시 채우려면 RoomDatabase.Callback을 만들고 onCreate() 재정의
-> Room 데이터베이스 작업 UI 스레드에서 할 수 없음
-> onCreate()는 I/O Dispatcher에서 코루틴 실행 -
코투린을 실행하려면 CoroutineScope 필요
-> 코루틴의 범위로 매개변수로 가져오도록 WordRoomDatabase 클래스의 getDatabase 메서드 업데이트
WordRoomDatabase.kt
fun getDatabase(
context: Context,
scope: CoroutineScope
): WordRoomDatabase {
...
}➖
- 데이터베이스를 채우는 작업은 UI 생명주기와 관련 X 앱의 수명주기와 관련 O
-> viewModelScope와 같은 coroutineScope를 사용해서는 안됨
-> applicationScope를 포함하도록 WordsApplication 업데이트
-> WordRoomDatabase.getDatabase로 전달
WordsApplication.kt
class WordsApplication : Application() {
// No need to cancel this scope as it'll be torn down with the process
val applicationScope = CoroutineScope(SupervisorJob())
val database by lazy { WordRoomDatabase.getDatabase(this, applicationScope) }
val repository by lazy { WordRepository(database.wordDao()) }
}➖
- WordDatabase에서 RoomDatabase.Callback() 구현
- CoroutineScope를 생성자 매개변수로 가져옴
- onOpen 메서드 재정의
✍...
📌참고자료
-
OnConflictStrategy
https://developer.android.com/reference/androidx/room/OnConflictStrategy.html
https://androidx.de/androidx/room/OnConflictStrategy.html
Set of conflict handling strategies for various Dao methods
- ABORT : abort the transaction
- FAIL : fail the transaction
- IGNORE : ignore the conflict
- REPLACE : replace the old data and continue the transaction
- ROLLBACK : rollback the transaction
- @Volatile
- 변수 선언 시 volatile을 지정하면 메인 메모리에만 적재하게 됨- volatile 변수를 사용하지 않는 일반적인 경우:
- 내부적으로 성능 향상을 위해 메인 메모리로부터 읽어온 값을 CPU 캐시에 저장
