Firebase Realtime Database
JavaScript SPA 프로젝트에서는 Could Firesotre를 이용했었다. 딱히 Realtime Database와 차이를 고려한 것은 아니었고, 좀 더 최근에 나왔다기에 막연히 더 좋을 것이라고 생각했던 것 같다.
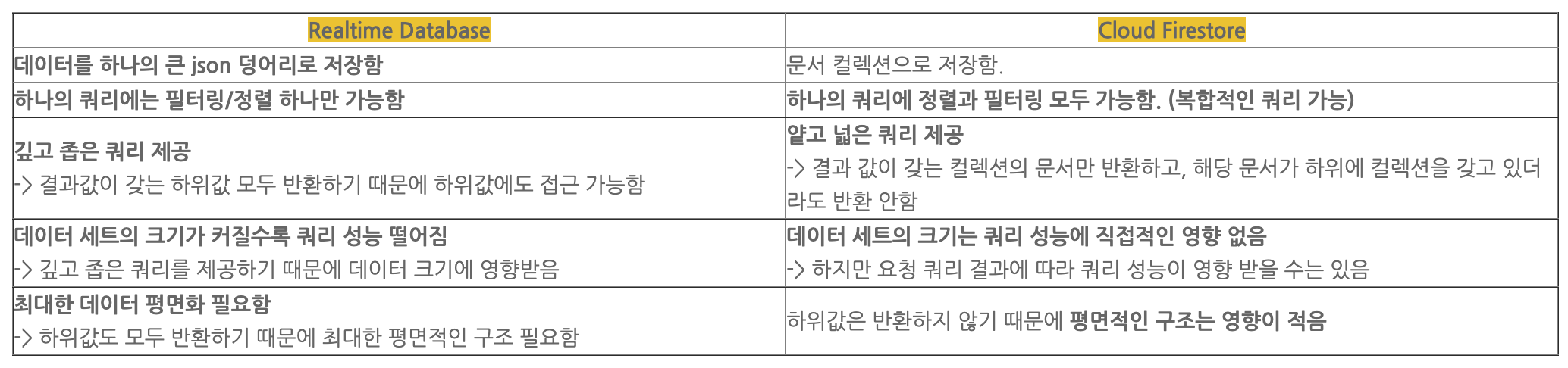
앞서 React Todo List 과제에서 json-server를 사용했었는데, Realtime도 데이터를 json 덩어리로 저장한다는 점이 비슷했다.
단점으로는 하나의 쿼리에서 필터링/정렬을 동시에 할 수 없고, json depth가 깊어질수록 당연히 성능이 떨어진다. 따라서 평면적인 데이터 설계가 요구된다.
이번 프로젝트에서 사용할 데이터는 depth가 2였고 고급 필터링/정렬이 필요하지 않았기에 Realtime Database를 쓰기에 적합하다고 생각했다.
Firebase Realtime, Cloud Firestore [의미, 공통점, 차이점, 앱 기능에 따라 데이터베이스 추천]

Read
Firebase/database에서 제공하는 onValue()는 특정한 경로에 있는 데이터의 스냅샷을 읽을 수 있다.
리스너가 연결될 때 한 번 실행되고, 하위 데이터가 변경될 때마다 다시 실행된다.
따라서 데이터를 추가, 삭제, 변경하는 함수 내에서 setTodos를 따로 해줄 필요가 없다.
// App.js
export default function App() {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]);
const [category, setCategory] = useState('');
useEffect(() => {
// Firebase에서 todos 값이 변경될 때마다 가져오기
const todoRef = query(ref(dbService, 'todos'), orderByChild('id'));
onValue(todoRef, (snapshot) => {
console.log('todos 받아오는 중');
const data = snapshot.val();
const todoArray = [];
for (const idx in data) {
todoArray.push(data[idx]);
}
setTodos(todoArray ?? []);
});
// Firebase에서 category 값이 변경될 때마다 가져오기
onValue(ref(dbService, 'category'), (snapshot) => {
const data = snapshot.val();
setCategory(data ?? 'JavaScript');
});
}, []);
}Create
Firebase의 set(), ref()를 사용한다.
set(데이터 위치, 데이터)ref(database 인스턴스, 경로)
// components/TodoInput.jsx
export default function Input({ category }) {
const [text, setText] = useState('');
const addTodo = () => {
const newTodo = {
id: Date.now(),
text,
isDone: false,
category,
};
// Firebase에 Todo 추가
set(ref(dbService, `todos/${newTodo.id}`), newTodo);
setText('');
};
return (
<TextInput
style={styles.input}
placeholder='할 일을 입력하세요.'
maxLength={20}
defaultValue={text}
onChangeText={setText}
onSubmitEditing={() => addTodo()}
/>
);
}Update
isDone 토글
Firebase의 update(), ref()를 사용한다.
update(database 인스턴스, 변경할 내용)
const doneTodo = () => {
// Firebase 업데이트
const updates = {};
updates[`todos/${id}`] = { ...todo, isDone: !isDone };
update(ref(dbService), updates);
};text 변경
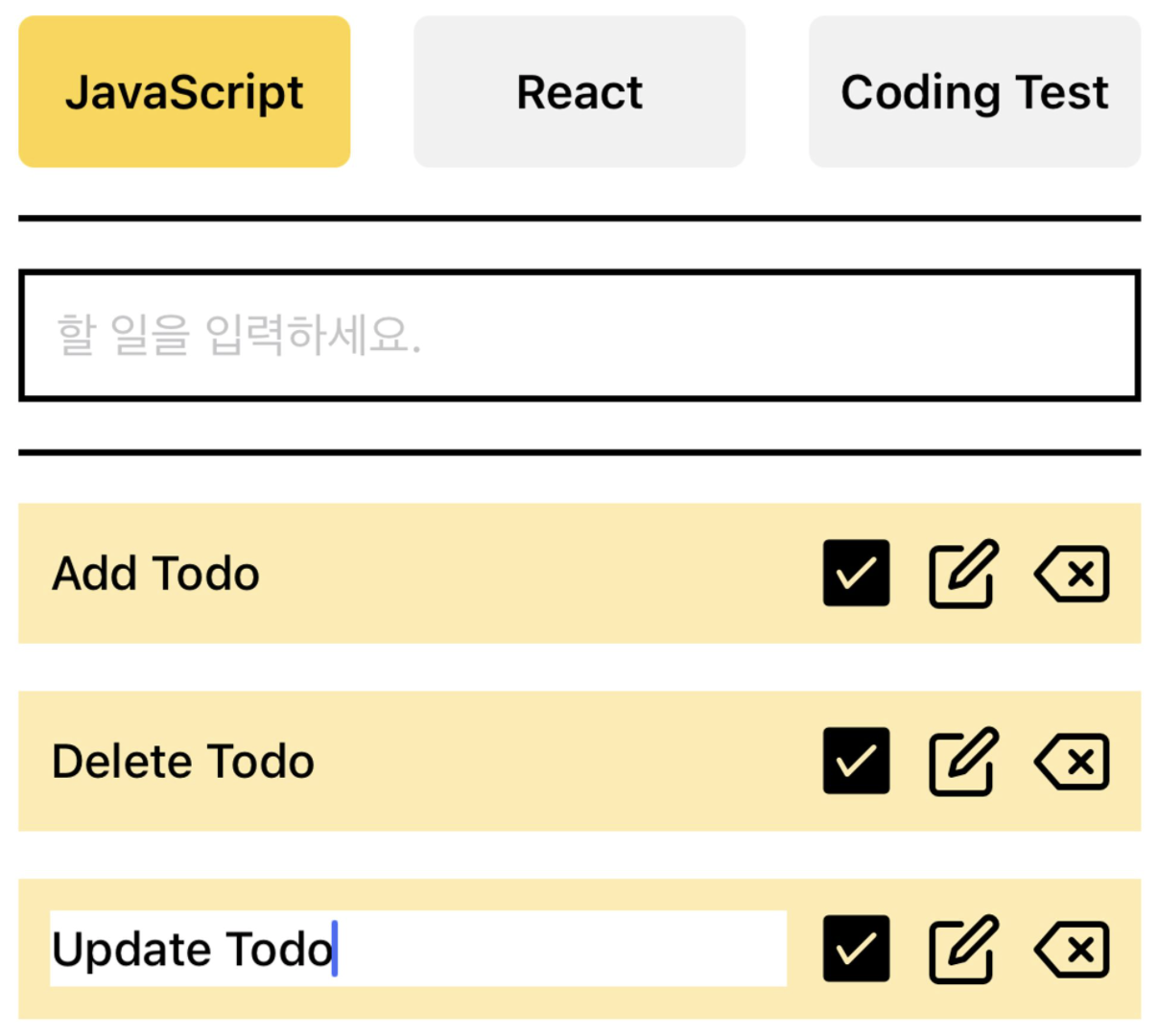
조건부 렌더링
// components/Todo.jsx
// isEditing state를 만들어서, true일 때 input을 보여준다.
// input이 submit 될 때 editTodo 함수가 실행된다.
{isEditing ? (
<TextInput
style={styles.textInput}
autoFocus={true}
maxLength={20}
defaultValue={editText}
onChangeText={setEditText}
onSubmitEditing={editTodo}
/>
) : (
<Text style={isDone ? styles.doneTodoText : styles.todoText}>
{text}
</Text>
)}수정 버튼
// components/Todo.jsx
<Feather
style={styles.todoButton}
name='edit'
size={24}
color='black'
onPress={() => {
if (!isEditing) {
// 수정 중이 아닐 경우, isEdit을 true로 토글해서 TextInput을 보여준다.
setIsEditing(true);
} else {
// 수정 중일 경우 (TextInput이 보이는 상태일 경우), 수정버튼 다시 누르면 수정 완료하기
editTodo();
}
}}
/>수정 함수
// components/Todo.jsx
const editTodo = () => {
// Firebase 수정
const updates = {};
updates[`todos/${id}`] = { ...todo, text: editText };
update(ref(dbService), updates);
// 수정 상태를 false로 변경 -> TextInput 숨기고 Text 보여주기
setIsEditing(false);
};Delete
Firebase의 remove() 또는 update()를 이용한다.
remove(ref(databse 인스턴스, 경로))update(): 변경할 내용을null로 지정하면 삭제가 가능하다.
// components/Todo.jsx
const alertDeleteTodo = () => {
Alert.alert('Todo 삭제', '정말 삭제하시겠습니까?', [
{
text: '취소',
style: 'cancel',
onPress: () => console.log('취소'),
},
{
text: '삭제',
style: 'default',
onPress: () => deleteTodo(),
},
]);
};
const deleteTodo = () => {
// Firebase 삭제
remove(ref(dbService, `todos/${id}`));
};Reference
