두 개 테이블 생성
create table TB_MGR
( MGR_ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY
, MGR_NAME VARCHAR2(100)
);
insert into TB_MGR values(1, '홍길동');
insert into TB_MGR values(2, '김길동');
insert into TB_MGR values(3, '이순신');
insert into TB_MGR values(4, '세종대왕');
select * from TB_MGR;
commit;
create sequence SQ_SAL start with 1 INCREMENT BY 1 MAXVALUE 9900 CACHE 100 NOCYCLE;
create table TB_SAL
( SAL_ID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY
, MGR_ID NUMBER
, SAL_ITEM VARCHAR2(100)
);
insert into TB_SAL values( sq_sal.nextval, 1, '활빈당');
insert into TB_SAL values( sq_sal.nextval, 3, '거북선');
insert into TB_SAL values( sq_sal.nextval, 3, '명량대첩');
insert into TB_SAL values( sq_sal.nextval, 4, '훈민정음');
insert into TB_SAL values( sq_sal.nextval, 4, '측우기');
insert into TB_SAL values( sq_sal.nextval, 5, '살수대첩');
select * from TB_SAL;
commit;
--update TB_SAL set MGR_ID = '3' where SAL_ID = 3;
--update TB_SAL set MGR_ID = '4' where SAL_ID = 7;
--update TB_SAL set MGR_ID = '5' where SAL_ID = 5;
--drop table TB_SAL;
--drop sequence sq_sal;Join
- 공통 컬럼 사용 시 모호성 제거 -> alias m, s
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID; -- Oracle std, ANSI std -> inner join
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID(+); -- left outer join
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID(+) = s.MGR_ID; -- right outer join
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m full outer join TB_SAL s on m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID; -- full outer join
-- oracle은 full 실행 안되서 left, right mix 후 union으로 처리
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID(+) -- left outer join
union -- distinct가 내부에 숨어있음
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID(+) = s.MGR_ID; -- right outer join
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID(+)
union all -- 모든 data 표시
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID(+) = s.MGR_ID;
select *
from -- Sub Query 처리(Inline View 이용)
(
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID(+)
union all
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID(+) = s.MGR_ID
)
order by 1,2,3;
select distinct * -- union all -> union
from
(
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID(+)
union all
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID(+) = s.MGR_ID
)
order by 1,2,3;View
- 복잡한 구조를 단순화시켜주지만 장기적으로 계속 사용하게되면 DB 성능 하락 있음
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID
and MGR_NAME = :입력값을넣으세요;
-- Bind List Value에 이순신 입력하고 다시 실행
create view vw_mgr_sal
as
select m.MGR_ID,
m.MGR_NAME,
s.SAL_ITEM
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID = s.MGR_ID;
select * from VW_MGR_SAL where MGR_NAME = :뷰에검색값입력
-- Bind List Value에 이순신 입력하고 다시 실행★★★ Cartesian Product
출처: https://gbs1995.tistory.com/59
조인 조건절을 적지 않게 되면 해당 테이블에 대한 모든 데이터를 전부 가져오는 현상
이를 카티션 곱이라고 부른다.
즉, 카티션 곱이란 join 쿼리 중에 WHERE 절에 기술하는 join 조건이 잘못 기술되었거나 아예 없을 경우 발생하는 현상입니다.
ANSI SQL에서는 CROSS JOIN 이라고도 부른다.
이런 경우는 Join 작업에 참조되는 테이블 행 수를 모두 곱한 값의 결과가 만들어진다.
다중컬럼 서브 쿼리
- || 연결 연산자
다중행 서브 쿼리
- IN, ANY, ALL 중에 IN 많이 사용
★★★ Exist 연산자
- 성능 향상에 큰 도움 가능, 튜닝에 많이 사용
Inline View
- Inline View를 Table로 사용해서 무궁무진하게 쿼리문 변환해서 활용 가능
outer join / scalar sub query
select * from TB_MGR;
select * from TB_SAL;
select m.MGR_ID as "MGR_ID" ,
m.MGR_NAME as "MGR_NAME" ,
s.SAL_ITEM as "SAL_ITEM"
from TB_MGR m,
TB_SAL s
where m.MGR_ID(+) = s.MGR_ID order by 1 desc; -- outer join ↔ scalar query
select s.mgr_id as "MGR_ID",
(select t.mgr_name
from tb_mgr t
where t.mgr_id = s.mgr_id) as "MGR_NAME",
s.sal_item as "SAL_ITEM"
from tb_sal s order by 1 desc; -- scalar sub query ↔ outer join
select mgr_id as "MGR_ID"
, mgr_name as "MGR_NAME"
,(select s.sal_item
from tb_sal s
where t.mgr_id = s.mgr_id) as "SAL_ITEM"
from tb_mgr t;
-- error, select 절의 s.sal_item 컬럼에 2개 이상 열이 반환될 때,
-- 위의 문장으로 변환시퀀스
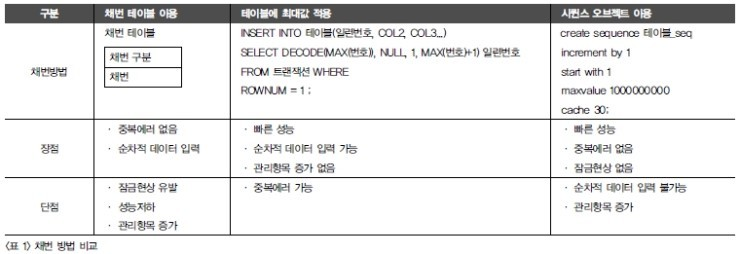
채번 : 새로운 번호를 부여
채번 방법 : 채번 테이블, 테이블에 최대값 적용, 시퀀스 오브젝트 이용
select * from tb_sal;
select * from user_sequences;
select sq_sal.currval from dual;
select sq_sal.nextval from dual; -- value increment occur
insert into tb_sal values (sq_sal.currval, 5, '수양제');
select * from TB_SAL;
delete from TB_SAL where sal_item = '수양제';
select * from TB_SAL;
insert into tb_sal values (sq_sal.nextval, 5, '수양제');
select * from TB_SAL;
commit;
create sequence sq_test start with 100 increment by 100 maxvalue 300 cache 100 nocycle;
select sq_test.nextval from dual; -- currval 먼저 하면 정의 아직 안되있어서 에러
select sq_test.currval from dual;
drop sequence sq_test;
create sequence sq_test start with 100 increment by 1 maxvalue 110 cache 100 cycle;
select sq_test.nextval from dual;
drop sequence sq_test;synonym
select * from dba_users where username = 'SCOTT';
select * from apa55353.tb_mgr;
select * from all_tables where table_name = 'TB_MGR';
select * from syn_mgr;
create public synonym syn_mgr for apa55353.TB_MGR;
grant select on apa55353.TB_MGR to scott;
revoke select on apa55353.TB_MGR from scott;