오늘은 터미널로 진행하는 up & down 게임을 만들면서 이용한 while 문에 대해 간단히 얘기해보고자 한다.
Contents
- while
1-1. "while True" construct - main() function
1. while
기본적으로 while 문은 특정 조건을 충족시키면 해당 statement 를 실행하고, 그렇지 않다면 else 로 넘어간다.
while (condition): --- statement --- else: --- statement ---
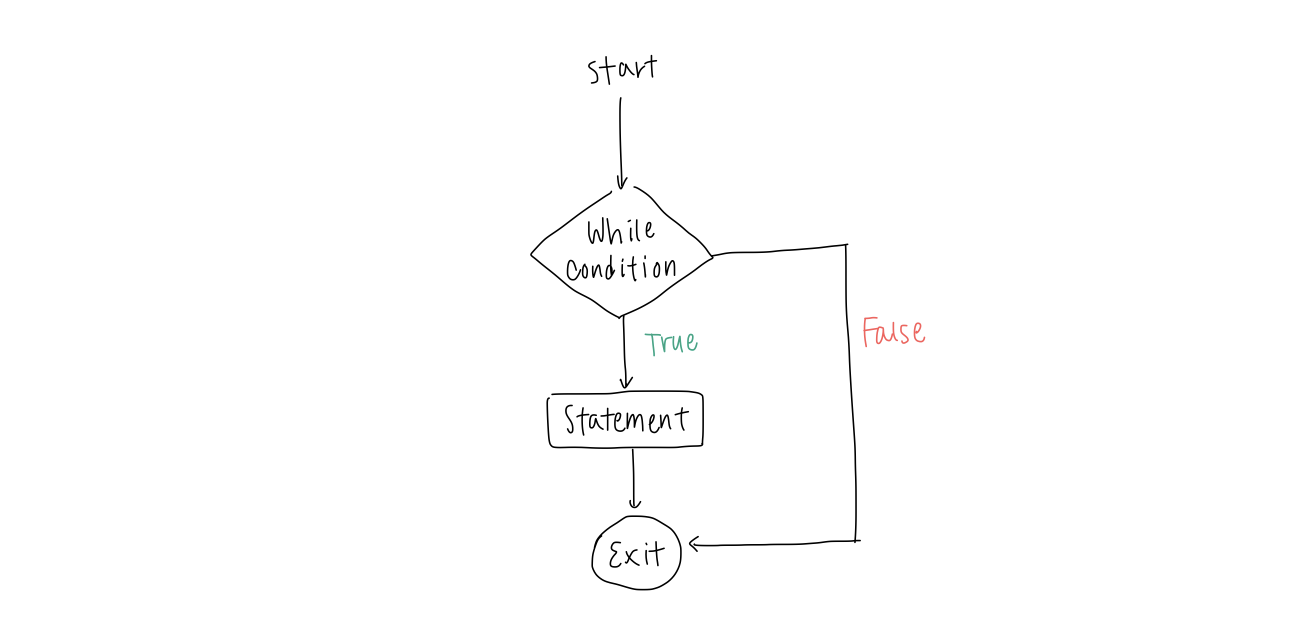
1-1. "while True" construct
이 때, loop condition 을 "while True" 로 적용한다면 코드를 더 효과적으로 작성할 수 있다. 조건을 True 로 두면 영영 while 문을 벗어나지 못할 것 같지만, return 을 통해 해결 가능하다. 다음의 예를 보자.
def get_user_input(): while True: try: num = int(input("Guess a number between 1 and 100: ")) if 1 <= num <= 100: return num else: print("The number should be between 1 and 100.") except ValueError: print("Invalid input. Please enter a number.")
위의 코드는 1 부터 100 사이의 숫자를 추측하는 게임에서 player 의 input 을 받는 함수이다. 만약 input 이 1 부터 100 사이라면 해당 숫자를 return 해주며 while loop 를 나가게 되고 그렇지 않다면 재입력을 요구한다.
즉, loop condition 이 "while True" 이더라도 코드가 "return" statement 를 가지고 있다면 특정 조건을 만족했을 때 loop 를 나갈 수 있다. 이는 "while True" construct 로 infinite loop 를 이용할 때 Python 에서 흔히 쓰이는 패턴 중 하나이다.
2. main() function
Up & Down 게임을 만들 때 게임 실행에 필요한 기능들을 담은 함수를 여러 개 만들어 사용하였다. 또한, 코드를 implement 하는 것 또한 따로 main() function 을 만들어 입력하였는데, 이를 통해 코드를 더욱 이해하기 쉽고 modular 하게 만들 수 있다. 참고로 알아 둘 것은, 첫 python 글에서 다루었던 _init_ 을 이용하여 main() function 을 실행시켜야 한다는 것이다.
... def main(): play = True round_num = 1 count = 0 while play: target_num = random.randint(1, 100) print(f"--- Round {round_num} ---") print(f"Previous max attempts: {count}") count = up_down(target_num) play = play_again() round_num += 1 if __name__ == "__main__": main()