[JS]Asynchronous 비동기 실행 : callback, promise, async의 사용법
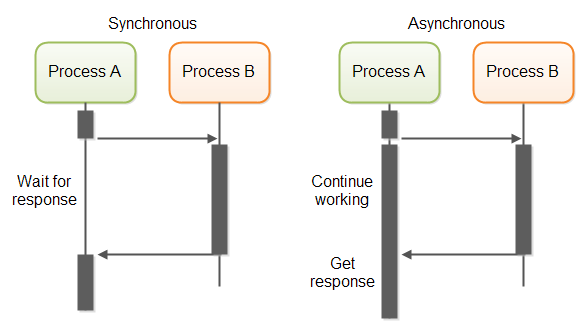
Asynchronous 비동기 실행
Synchronous 와의 차이
만약 유튜브에서 동기적인 처리를 한다면 동영상을 불러오는 동안 사용자는 화면 상에서 아무 동작도 할 수 없게 된다.
하지만 비동기 처리를 한다면 동영상이 불러와지는 동안 스크롤을 내려 댓글을 보는 등의 다른 작업을 진행할 수 있다.
이제 비동기로 작업을 실행하는 것이 좋다는 것을 알게 됬으니, 이 비동기 처리를 어떻게 내 마음대로 조작할 수 있을지 다음부터 알아보겠다.
1. Callback
1-1. 비동기를 다룰 수 있는 방법 중 하나, Callback
Callback error handling Design
const somethingGonnaHappen = callback => {
waitingUntilSomethingHappens()
if(isSomethingGood) {
callback(null, something)
}
if(isSomethingBad) {
callback(something, null)
}
}Usage
somethingGonnaHappen((err, data) => {
if(err) {
console.log('ERR');
return;
}
return data;
})err와 data의 자리가 정해진 것은 아니나, 통상적으로 위와 같이 쓰이고 있다.
1-2. Callback 의 단점
Callback hell의 발생 -> 가독성이 매우 떨어진다.
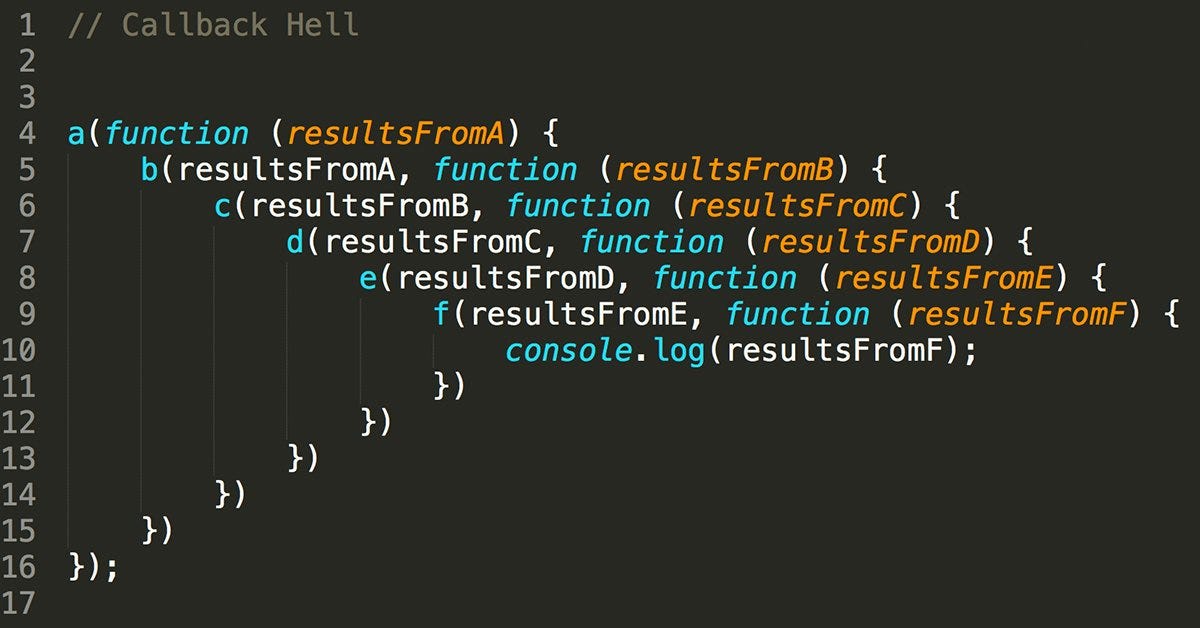
중첩된 Callback이 발생하는 사례
네트워크 요청, 파일 읽기, setTimeout 등..
이러한 callback 의 단점을 보완하기 위해서 나온 것이 있으니...바로 Promise!
2. Promise 사용 패턴과 언어적인 특징
클래스의 한 종류로서 new Promise를 통해 인스턴스를 생성한다.
인스턴스를 생성할 때, 인자로 콜백함수를 받는데, 콜백함수의 인자로 resolve 와 reject를 받는다.
아래에서 callback으로 작성된 코드를 promise를 사용해 재작성해보면서 둘의 차이점을 확인해보겠다.
Callback으로 작성된 코드
const printString = (string, callback) => {
setTimeout (
() => {
console.log(string);
callback();
},
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
)
}
const printAll = () => {
printString('A', () => {
printString('B', () => {
printString('C' () => {})
})
})
}
printAll(); //실행Promise 변환해 작성된 코드
const printString = (string) => { //printString 함수에서 promise 인스턴스 생성
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(
() => {
console.log(string);
resolve(); //callback과 같은 역할
},
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
)
})
}
const printAll = () => {
printString('A')
.then(() => { //resolve의 return 값으로 들어감
return printString('B')
})
.then(() => {
return printString('C')
})
}
printAll() // 실행이제 Promise에서 사용되는 용어(문법)에 대해 아래에서 알아보겠다.
2-1. Producer : resolve, reject
** 새로운 인스턴스가 생성될 때, 자동으로 실행이 되므로 주의가 필요하다
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('doing something');
setTimeout(() => {
// resolve('ellie'); //callback의 역할과 같음
reject(new Error('no network'); //error handling
}, 2000);
});2-2. Consumer : then, catch, finally
promise
.then(value => {
console.log(value);
})
.catch(error => { //error handling, then chaining 가장 마지막에 사용한다.
console.log(error);
})
.finally(() => {
console.log('finally') //앞의 내용이 실패하든 성공하든 무조건 실행된다.
})2-3. Promise에서 인자를 넘기는 방법
Promise에서는 resolve의 인자를 then chaining을 사용해 넘길 수 있다.
2-4. Promise의 세가지 상태
State : pending(대기) -> fulfilled(완료) or rejected(에러)
2-5. Promise.all
callback hell을 보완하기 위해 고안된 promise 였지만....이 또한 hell 이 존재하였으니....
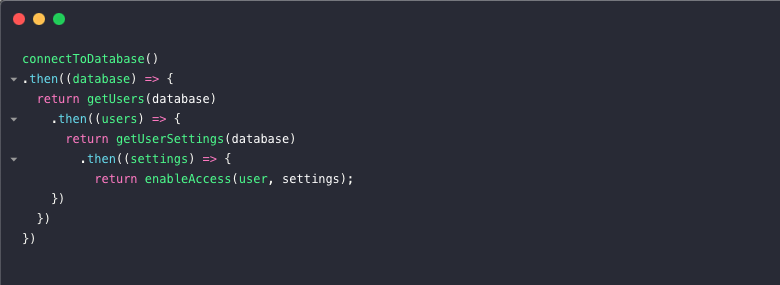
그리하여 나온 것이 async, await 문법입니다. 아래에서 살펴보겠습니다.
3. async, await
프로미스를 간결,간편하게 사용하도록 하고 동기적으로 실행되는 것처럼 보이게 만들어주는 친구.
프로미스는 여러가지 체이닝 가능한데(then), 이 체이닝이 계속되면 코드가 복잡해질 수 있다.
이걸 해결하기 위해 나온 것이 async, await
새로운 것이 추가 된 것이 아닌 기존에 존재하던 promise 위에 조금 더 간편한 api를 제공한 것이다.
이러한 것을 syntactic sugar라고도 한다. (= class, prototype 위에 그럴듯하게 씌워진 것)
프로미스를 사용할 때 반드시 async, await 을 사용하라는 것은 아니고, 상황에 맞게 적절하게 사용하면 된다.
async, await 코드 참고
function gotoCodestates() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('1. go to codestates')}, 100)
})
}
function sitAndCode() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('2. sit and code')}, 500)
})
}
function eatLunch() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('3. eat lunch')}, 300)
})
}
function goToBed() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('4. go to bed')}, 400)
})
}
const result = async () => {
const one = await gotoCodestates();
console.log(one);
const two = await sitAndCode();
console.log(two);
const three = await eatLunch();
console.log(three);
const four = await goToBed();
console.log(four);
}
result(); //실행blocking vs non blocking
포토샵 응답없음. -> blocking , 동기적인 작업에서 일어남
progress bar -> non - blocking , 비동기
v8엔진을 사용하는 시스템에서는 블라킹 = 동기, 논블라킹 = 비동기
그러낭 다른 엔진을 사용하는 곳에선 아닐 수 있음.
참고
- Codestates Software Engineer Immersive Course
- 드림코딩 by 엘리 자바스크립트 강의
읽을거리