

-
링크 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2zjoKjt97vQ&list=PLRx0vPvlEmdAghTr5mXQxGpHjWqSz0dgC&index=2&t=1008s
-
이런 문제는 DFS BFS에서도 나옴
[주의사항]
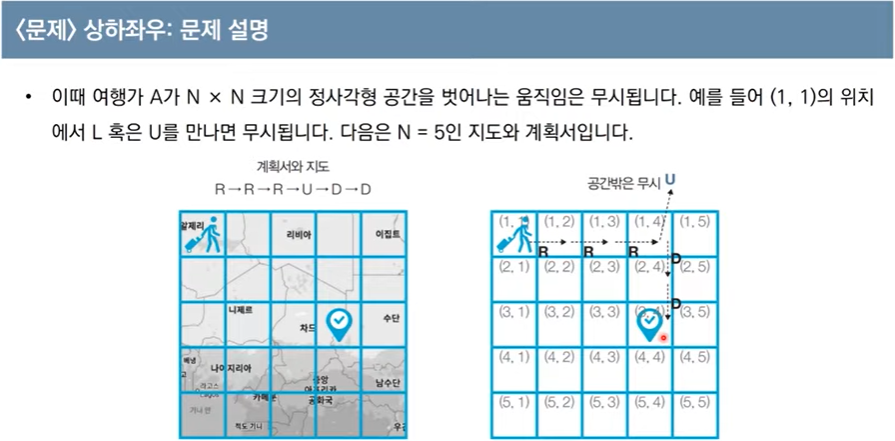
1. 가장 왼쪽 위 좌표 = (1,1)
2. 시작 좌표는 항상 (1,1)
3. 상 하 좌 우 로만 이동가능
- 코드 작성 시 (x,y)가 아니라 (y,x)임을 주의!!!
R R R U D D
''' 내가 1차적으로 푼 - 돌다리도 두드려보고 건너기 '''
def sol(n, direct):
# 좌, 하, 우, 상
da = ['L', 'D', 'R', 'U']
dy = [0, 1, 0, -1]
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
now = [1,1]
tmp = [1,1]
for i in direct:
for j in range(4):
# 이동하기 전 tmp로 두드려보고 가자
if i == da[j]:
tmp[0] += dy[j]
tmp[1] += dx[j]
# 이동한 위치가 범위 안에 있을 경우에만 수행 (중요) "and" 연산으로 묶어줘야 함
if 0<tmp[0] and tmp[0]<=n and 0<tmp[1] and tmp[1]<=n:
now[0] = tmp[0]
now[1] = tmp[1]
else: # 밖에 있는 경우 무시하기(=원래 자리로 돌아와)
tmp[0] -= dy[j]
tmp[1] -= dx[j]
return now
n = int(input())
direct = list(input().split())
print(sol(n, direct))
''' 내가 2차적으로 푼 - 일단 가보고 넘어가면 후진 '''
def sol(n, direct):
# 좌, 하, 우, 상
da = ['L', 'D', 'R', 'U']
dy = [0, 1, 0, -1]
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
now = [1,1]
for i in direct:
for j in range(4):
# 일단 이동한다
if i == da[j]:
now[0] += dy[j]
now[1] += dx[j]
# 이동한 위치가 범위 밖에 있을 경우 무시(=원래 자리로) (중요) "or" 연산으로 묶어줘야 함
if now[0] <= 0 or n < now[0] or now[1] <= 0 or n < now[1]:
now[0] -= dy[j]
now[1] -= dx[j]
return now
n = int(input())
direct = list(input().split())
print(sol(n, direct))
''' 동빈나 솔루션 스타일 - 내가 푼 첫 번째와 비슷(코드 더 간결, 변수 줄임) '''
def sol(n, direct):
# 좌, 하, 우, 상
da = ['L', 'D', 'R', 'U']
dy = [0, 1, 0, -1]
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
now = [1,1]
for i in direct:
for j in range(4):
# 일단 이동한다
if i == da[j]:
tmpy = now[0] + dy[j]
tmpx = now[1] + dx[j]
# 이동한 위치가 범위 밖에 있을 경우 변경 X (중요) "or" 연산으로 묶어줘야 함
if tmpx <= 0 or n < tmpx or tmpy <= 0 or n < tmpy:
continue
else:
now[0] = tmpy
now[1] = tmpx
return now
n = int(input())
direct = list(input().split())
print(sol(n, direct))
