- 용감한 파이썬 링크 : https://covenant.tistory.com/141
(중요) 이상한 input 문자열 전처리하기
- 딕셔너리 모양으로 이상한 문자열 들어온거 리스트로 바꾸기
- eval( )함수 + replace( )함수
def solution(s):
answer = []
s = eval(s.replace("{", "[").replace("}", "]")) # <---------
print(s)
s.sort(key=lambda x: len(x))
for i in s:
for j in i:
if not int(j) in answer:
answer.append(int(j))
return answer
s = "{{2},{2,1},{2,1,3},{2,1,3,4}}"
print(solution(s))
1. 다양한 입력
# 1-1. 나누어 입력받기
# 백준 1000, 백준 15740
a, b = map(int,input().split())# 1-2. 입력 출력 가속 - 입력값이 많은 경우(반복문으로 여러 개 받을 경우)
# 백준 1927, 백준 10845, 백준 BOJ 15552
'''방법1'''
import sys
a = int(sys.stdin.readline().split(' '))
sys.stdout.write(a)# 1-2. 입력 출력 가속 - 입력값이 많은 경우(반복문으로 여러 개 받을 경우)
# 백준 1927, 백준 10845
'''방법2'''
from sys import stdin, stdout
input = stdin.readline
print = stdout.write2. 배열(리스트) 입력(Pythonic하게 입력받기)
# 2-1. Pythonic하게 입력받기 - 2차원 배열(중요)
'''
1. 첫 번째 줄에 입력되는 숫자들의 줄 수
2. 다음 줄부터 숫자들이 공백을 기준으로 입력
'''
''' Bad Code '''
MAP = []
for i in range(int(input())):
inputstr = input()
arr = list(inputstr)
MAP.append(arr)
''' Good Code -> 받을 내용들 반복 수행할 횟수 '''
aa = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(int(input()))]
print(MAP)
print(aa)
# 2-2. 정수와 배열이 같은 줄에 들어오는 경우
# 백준 9613
'''
1. 첫 번째는 숫자의 개수 n
2. 바로 다음(엔터없이) n개만큼의 수 입력받는 코드 작성
'''
N, *arr = map(int,input().split())
print(N, arr, end="\n----\n")
N, *arr = map(int,input().split())
print(N, arr, end="\n----\n")
N, *arr = map(int,input().split())
print(N, arr, end="\n----\n")
2-2-1. 유클리드 호제법을 활용한 최대공약수(GCD) 계산
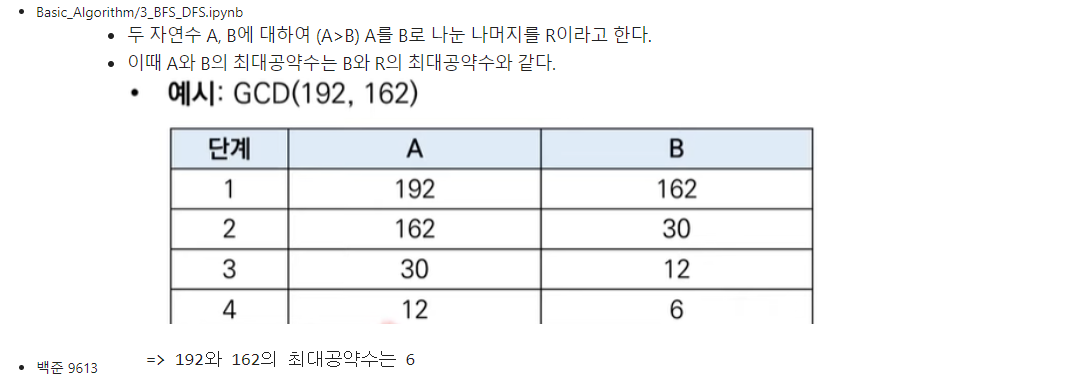
def gcd(a, b):
if a%b == 0:
return b
else:
return gcd(b, a%b)
print(gcd(5,12))# 2-3. 문자열을 한 글자씩 개별적으로 배열에 저장 - Graph input 받을 때 사용
'''
3
AAAA
ABCA
AAAA
'''
N = int(input()) # 노드의 수
arr = [list(input()) for _ in range(N)]
print(arr)
3. 배열(리스트) 출력
# 3-1. (중요) 배열을 연결해서 출력 1
arr = [1,2,3,4]
print("".join(map(str,arr))) # 숫자여도 map()에 str로 넣어줘야함!
print(" ".join(map(str,arr)))
# 3-2. (중요) 배열을 연결해서 출력 2
arr = [1,2,3,4]
print(*arr)
