- 링크 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14888
- 브루트포스로 풀었으나, DFS로도 풀 수 있어서 여기에도 작성했음 (브루트포스 게시판에도 써둠)
메모
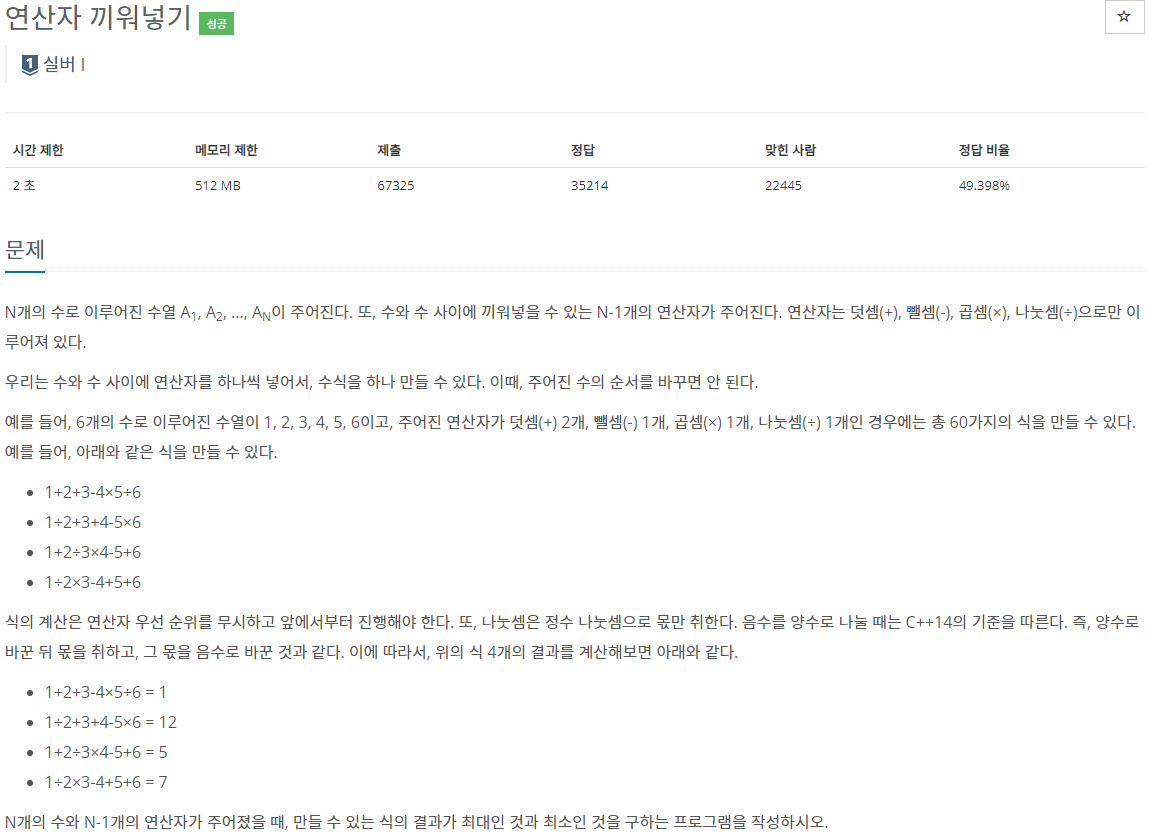
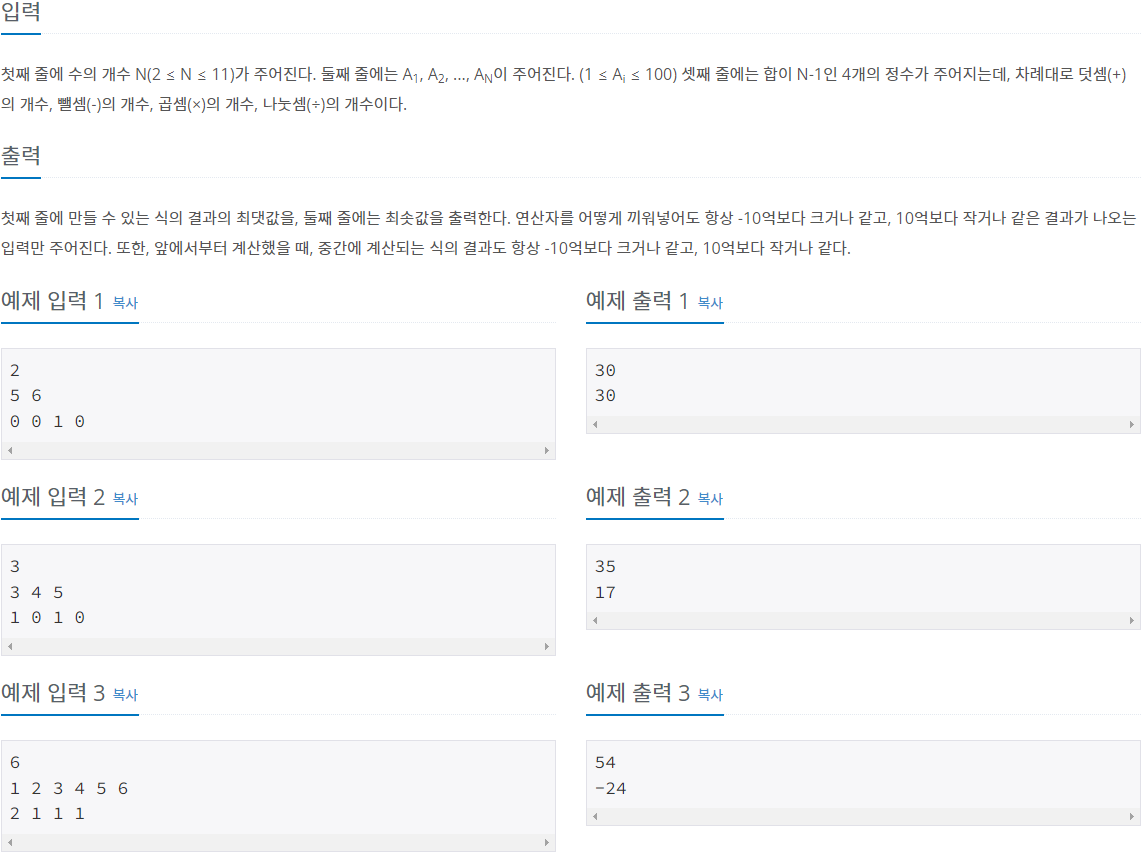
숫자 순서를 바구면 안된다
연산자 우선순위는 없다. 왼쪽부터 진행
나눗셈은 몫만 취하고, 수가 음수일 경우 양수로 바꾼 후 나누기한 다음 음수로?? -->파이썬 상관없을듯
입력 :
length,
숫자배열
+ - * // 개수 순서대로결론 : 만들 수 있는 식의 결과가 최대인 것과 최소인 것을 구하는
풀이!!
기호 수를 입력받았기 때문에, 각 기호에 해당하는 그 수만큼 operator 배열에 저장해둔다
operator의 개수만큼 저장했으면,
얘에 대해 모든 경우의 수(permutations)를 구한 다음에
그 모든 경우의수별로 끼워넣기를 진행한다
이때 끼워넣기는, 연산자 개수가 전체 숫자 개수-1개만큼 있으니까
for문 인덱스 진행할 때
배열은 [i]로
연산자는 [i-1]로 활용한다
이때, 주의점은 "나누기"연산에서 소수점 뒤에는 전부 버려줘야함
- "몫"으로 계산하니까 계속 틀린 답이 나와서 계산해보니, 0.3333이나 1.10342 이런거는 다 소숫점 뒤를 버려야함
솔루션 코드 - 내가 푼
- python3로 하면 시간초과
- pypy로 하면 통과
- 더 빠르게 할 수 있는 방법을 구글링해보자
from itertools import permutations
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
leng = int(input())
arr = list(map(int, input().split()))
tmp = list(map(int, input().split()))
operator = [] # max length = leng - 1
total_operator = []
# 연산자 각 개수만큼 변환해서 배열에 저장 (연산자 하나라도 있으면 해당 연산자를 append해줌)
for i in range(4):
if tmp[i] > 0:
for _ in range(1, tmp[i]+1):
if i == 0:
operator.append('+')
elif i == 1:
operator.append('-')
elif i == 2:
operator.append('*')
elif i == 3:
operator.append('//')
# 저장 후 모든 경우의 수를 구함(저장했다가 모든 경우에 수에 따라 계산하기위함)
for i in permutations(operator, leng-1):
total_operator.append(list(i))
answers = []
# 끼워넣기 -> 첫 번째 값 미리 넣어놓고, 숫자는 1번인덱스부터, 연산자는 0번 인덱스(i-1)부터
for op in range(len(total_operator)):
ans = arr[0]
for i in range(1, leng):
if total_operator[op][i-1] == '+':
ans += arr[i]
elif total_operator[op][i-1] == '-':
ans -= arr[i]
elif total_operator[op][i-1] == '*':
ans *= arr[i]
elif total_operator[op][i-1] == '//':
ans = int(ans / arr[i]) # 소수일 경우, 소수점 뒤에 내용은 다 없애줘야함
answers.append(ans)
print(max(answers))
print(min(answers))
솔루션 코드 - 블로그
- 링크 : https://velog.io/@kimdukbae/BOJ-14888-연산자-끼워넣기-Python
- 내 솔루션에서 입력받은 숫자배열을 연산자로 변환하기 아래와 같이 변환하면 편함
op_num = list(map(int, input().split())) # +, -, *, /
op_list = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
op = []
for k in range(len(op_num)):
for i in range(op_num[k]):
op.append(op_list[k])- 순열을 사용한 방식
- pypy만 통과 가능
import sys
from itertools import permutations
input = sys.stdin.readline
N = int(input())
num = list(map(int, input().split()))
op_num = list(map(int, input().split())) # +, -, *, /
op_list = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
op = []
for k in range(len(op_num)):
for i in range(op_num[k]):
op.append(op_list[k])
maximum = -1e9
minimum = 1e9
def solve():
global maximum, minimum
for case in permutations(op, N - 1):
total = num[0]
for r in range(1, N):
if case[r - 1] == '+':
total += num[r]
elif case[r - 1] == '-':
total -= num[r]
elif case[r - 1] == '*':
total *= num[r]
elif case[r - 1] == '/':
total = int(total / num[r])
if total > maximum:
maximum = total
if total < minimum:
minimum = total
solve()
print(maximum)
print(minimum)- 백트래킹(DFS)사용한 방식
- python3통과 가능
- 이때, 재귀함수 쓴 이유가 DFS 진행이므로, 각 연산 끝까지 트리 내려가고(DFS그림 생각해) 인터널 한칸 올라와서 다음 리프노드 계산하고 이런식
- (중요) 그 당시에 파라미터를 기억하고있어서 첨에 plus 쭉 타고 들어가다가 숫자 개수만큼 계산 끝나면 max, min 업데이트(=리턴)해주고, 옆에 리프노드 연산자 계산하고 이런식, 리프 끝났으면 다시 루트로 올라오는데 루트시점에서의 파라미터(연산자들)을 기억해서 걔네로 다음 인터널로 DFS
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
N = int(input())
num = list(map(int, input().split()))
op = list(map(int, input().split())) # +, -, *, //
maximum = -1e9
minimum = 1e9
# depth는 숫자 개수이고, N까지 갔다면 계산 다 끝난것으로, max, min 리턴
def dfs(depth, total, plus, minus, multiply, divide):
global maximum, minimum
if depth == N:
maximum = max(total, maximum)
minimum = min(total, minimum)
return
# 다음 숫자로 이동, += -= *= //= 계산해줌, 각 연산 수행했다면 해당 횟수에 -1
if plus:
dfs(depth + 1, total + num[depth], plus - 1, minus, multiply, divide)
if minus:
dfs(depth + 1, total - num[depth], plus, minus - 1, multiply, divide)
if multiply:
dfs(depth + 1, total * num[depth], plus, minus, multiply - 1, divide)
if divide:
dfs(depth + 1, int(total / num[depth]), plus, minus, multiply, divide - 1)
dfs(1, num[0], op[0], op[1], op[2], op[3])
print(maximum)
print(minimum)