이진탐색 핵심
- 이진탐색 적용해야되는 문제
- 데이터 범위가 10,000,000을 넘어가는 경우(천만 이상 초대량의 탐색 필요 시)
- 이진탐색 문제는 크게 두 가지 유형이 있음
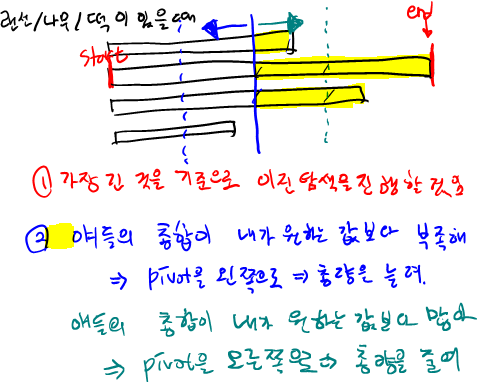
- 이진탐색을 해서 정해지지 않은 중앙값을 찾아내서 그 값에 따라 start end 조정
- 아래 문제처럼 bitsect라이브러리로 lower bound 사용해 특정 값 찾는 문제
- 이진탐색을 해서 정해지지 않은 중앙값을 찾아내서 그 값에 따라 start end 조정
메모
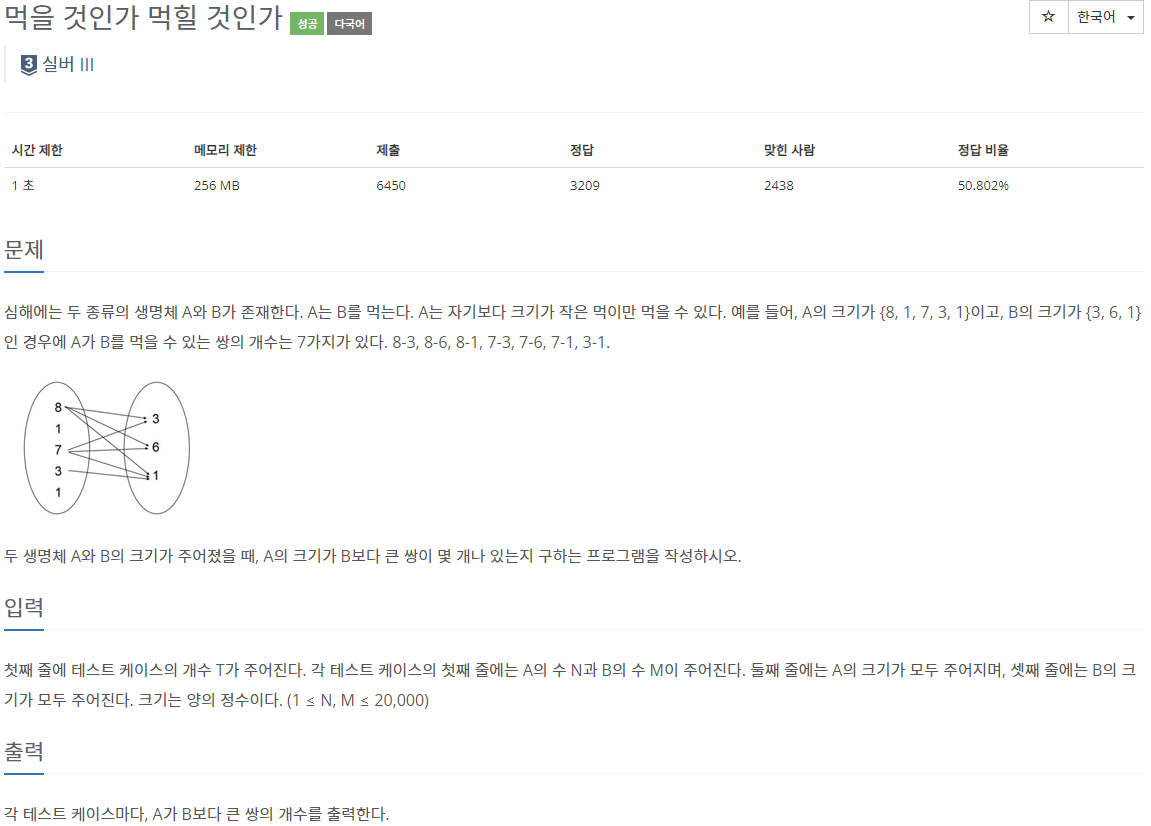
a랑 b가 있는데 a는 자기보다 작은 애들만 먹을 수 있음
브루트포스로 2중포문 돌리면 삽가능인데 보나마나 안되겠지..?
문제를 보니까 순서가 중요하진 않고, 작은거만 찾으면 되니까 일단 a랑 b 둘 다 정렬먼저 시키자
=> 자기보다 크거나 같으면 두 번째 for문 break해서 쓸데없는 탐색 줄이기
=> 응 안돼~
바이너리 서치를 사용해야한다
알고리즘
일단 a, b 둘 다 정렬해줘야함 => 이진탐색 수행을 위해! 그리고 각 번호의 인덱스가 그보다 작은 값들의 수를 저장한거나 다름없기 때문
a배열에 있는 값 하나씩 꺼내 target으로 지정
a의 각 원소에 대해 b배열에서 이진 탐색 수행
이때, res라는 변수에 찾은 인덱스값을 기록해줌 => (중요)정렬됐기 때문에 그 인덱스 자체가 그보다 작은 값들의 수가 되는거!
-
근데 bisect 를 사용하면 다 해결된다
- binary second이 걸리는 tree라고 외울까
- bisect_left()는 찾고자 하는 값의 lower_bound() "인덱스"를 구하는 함수
- 위에서 말한대로 lower_bound구하고 그 인덱스 더해주면 그보다 작은 값들을 한방에 더해주는게 됨(브루트포스가 아니고 인덱스값을 더함)
-
bisect 라이브러리 설명 : https://velog.io/@taehyeon96/이진-탐색-핵심-설명-중요
솔루션 - 브루트포스 - 시간초과!
- 브루트포스 -> 시간복잡도 : O(n^2)
# 브루트포스 버전 - 시간초과
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
for _ in range(int(input())):
n, m = map(int, input().split())
arr_a = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
arr_b = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
cnt = 0
for a in arr_a:
for b in arr_b:
if a <= b:
break
elif a > b:
cnt += 1
print(cnt)

솔루션 - 이진탐색 - 직접 구현 (라이브러리x)
- 이진탐색 -> 시간복잡도 : O(log n)
- 이 코드에서 시간복잡도 : O(nlog n)
- 이유 : a배열을 전부 탐색 O(n) * 이진탐색 O(log n)
# 방법 1 : 바이너리 서치 직접 구현
for _ in range(int(input())):
n, m = map(int, input().split())
arr_a = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
arr_b = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
cnt = 0
for target in arr_a:
start = 0
end = m - 1 # 인덱스 0부터임
res = -1 # 인덱스 0부터임
while start <= end:
pivot = (start + end) // 2
if target <= b[pivot]:
end = pivot - 1
elif target > b[pivot]:
res = pivot # (중요)
start = pivot + 1
cnt += (res+1) # res = -1이라서 pivot=0일경우 -1 더해주게되므로
print(cnt) 
(중요) 솔루션 - 이진탐색 - bisect 라이브러리
-
시간복잡도는 위와 동일
-
bisect() 사용
# 방법 2 : bisect를 사용하고, 찾고자 하는 값의 앞에 데이터를 넣어줌
from bisect import bisect
for _ in range(int(input())):
N, M = map(int, input().split())
A = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
B = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
cnt = 0
for a in A:
cnt += (bisect(B, a-1)) # a보다 하나 작은 값의 인덱스를 찾아서 그 인덱스를++
print(cnt)- bisect_left() 사용
- lower_bound를 찾는다
# 방법 3 : bisect_left를 사용해서, 찾고자 하는 값의 lower_bound를 검색
from bisect import bisect_left
for _ in range(int(input())):
N, M = map(int, input().split())
A = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
B = sorted(list(map(int, input().split())))
cnt = 0
for a in A:
cnt += (bisect_left(B, a)) # a보다 하나 작은 값의 인덱스를 찾아서 그 인덱스를++
print(cnt)
(중요) cpp의 lower bound, upper bound
- cpp
- vector는 lower_bound(), upper_bound() 함수를 제공
- 파라미터 : bound(v.begin(), v.end(), rightValue);
- 사용법 : vector<>::iterator a = ~~bound();
- vector는 lower_bound(), upper_bound() 함수를 제공
- 관련 문제 : https://velog.io/@taehyeon96/이코테이진탐색-기본-부품-찾기정렬된-배열에서-특정-수의-개수-구하기bisect라이브러리
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// 값이 [left_value, right_value]인 데이터의 개수를 반환하는 함수
int countByRange(vector<int>& v, int leftValue, int rightValue) {
vector<int>::iterator rightIndex = upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), rightValue);
vector<int>::iterator leftIndex = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), leftValue);
return rightIndex - leftIndex;
}
int n, x;
vector<int> v;
int main() {
// 데이터의 개수 N, 찾고자 하는 값 x 입력받기
cin >> n >> x;
// 전체 데이터 입력 받기
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int temp;
cin >> temp;
v.push_back(temp);
}
// 값이 [x, x] 범위에 있는 데이터의 개수 계산
int cnt = countByRange(v, x, x);
// 값이 x인 원소가 존재하지 않는다면
if (cnt == 0) {
cout << -1 << '\n';
}
// 값이 x인 원소가 존재한다면
else {
cout << cnt << '\n';
}
}