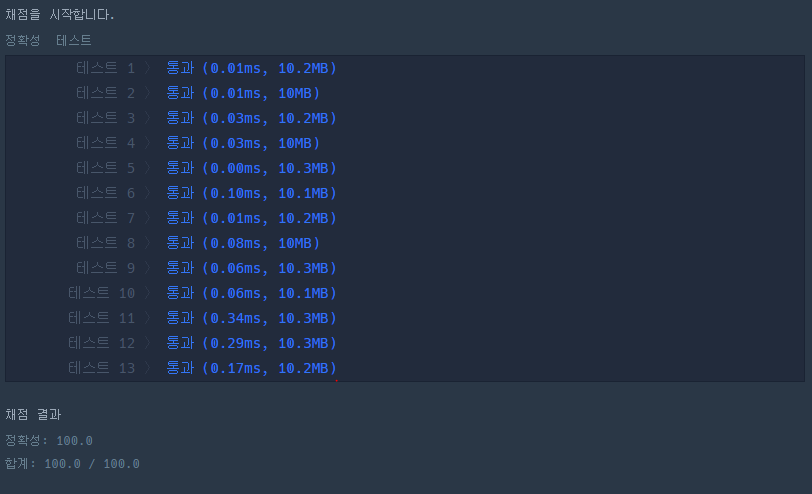

3 [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]] 2
3 [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1]] 1
-
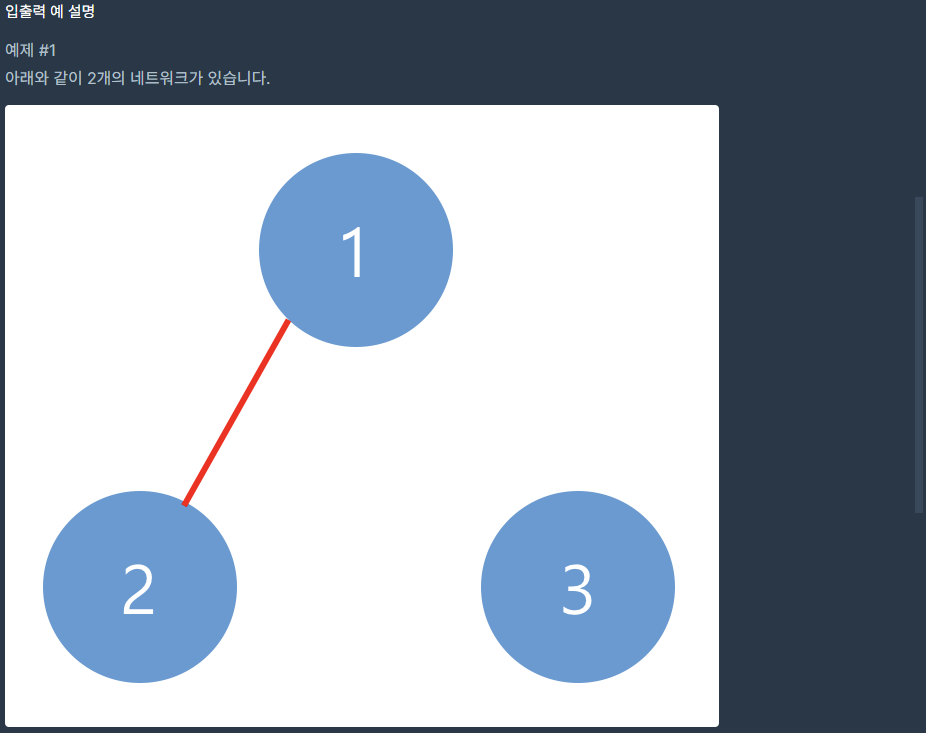
여기서 n=3일 때 2차원 배열 안에 있는 각각의 배열들이 하나의 노드임
-
그 노드가 A번 노드, B번 노드, C번 노드이고
-
A번 노드가 [1, 1, 0]일 경우 자기 자신과 B번 노드와 연결된 것 ([자기자신, B, 0])
-
B번 노드가 [1, 1, 0]일 경우 자기 자신과 A번 노드와 연결된 것 ([A, 자기자신, 0])
-
C번 노드의 경우 [1, 0, 0]이면 자기 자신만 연결되어있는것
- 풀이 생각한거
혹시 이건가 지금 그래프가 하나 주어졌잖아, DFS로 탐색하면서 방문한 노드는 visit = True로 체크해 => 이때 순회 하나 끝나면 answer += 1 (네트워크 1개)
다음 DFS로 탐색하면서 방문하지 않은 노드 찾아서 DFS 탐색해 => 위랑 마찬가지로 visit 체크하면서 순회 하나끝나면 또 answer += 1 이렇게
''' 블로그 (못풀었다...) '''
def solution(n, computers):
answer = 0
visited = [False] * n
# (중요) 여기서(main에서) DFS 기본틀 수행시킴
for node_idx in range(n): # node_idx = 그래프 순회의 시작노드
if visited[node_idx] == False: # 모든 노드 순서대로 방문하지 않은 노드 방문 시작
dfs(n, computers, visited, node_idx) # 방문하지 않은 노드의 인덱스도 넣어줌
answer += 1 # DFS 순회 하나 끝나면 그래프 1개
return answer
# 각 시작점에 대해서부터 dfs 수행(방문하지 않았던 노드만)
def dfs(n, computers, visited, node_idx): # node_idx = 그래프 순회의 시작노드
visited[node_idx] = True
for other_idx in range(n):
# 자기 자신 노드가 아니면서, 1인 경우(= 다른 노드와 연결된 경우)
if other_idx != node_idx and computers[node_idx][other_idx] == 1:
if visited[other_idx] == False:
dfs(n, computers, visited, other_idx) # 다른 노드로 이동
print(solution(3, [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]]), end="\n\n")
print(solution(3, [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1]]))
''' 몇일 후 내가 다시 푼 '''
def solution(n, computers):
answer = 0
visit = [False] * n
for i in range(n):
if not visit[i]:
visit[i] = True
dfs(computers, i, visit, n) # n은 range(len(n)) 안하려고 넣음(시간복잡도)
answer += 1 # dfs 1회 끝나면 네트워크 1개 파악된 것
return answer
def dfs(comp, i, visit, n):
for j in range(n):
if not visit[j]: # 방문하지 않은 노드에 대해서만
if i == j and i == 1: # 자기 자신으로 연결은 스킵
continue
elif comp[i][j] == 1: # 그 외에 연결된 경우 DFS
visit[j] = True
dfs(comp, j, visit,n)
print(solution(3, [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]]), end="\n\n")
print(solution(3, [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1]]))