Dynamic Array
크기가 가변적인 배열, 필요에 따라 크기가 자동으로 조정되는 자료구조
Implementation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class DynamicArray {
private:
int* arr;
int capacity;
int size;
public:
DynamicArray(int initial_capacity = 2) {
capacity = initial_capacity;
size = 0;
arr = new int[capacity];
}
~DynamicArray() {
delete[] arr;
}
void push_back(int value) {
if (size == capacity) {
resize();
}
arr[size] = value;
size++;
}
int get(int index) const {
if (index >= 0 && index < size) {
return arr[index];
}
throw out_of_range("Index out of range");
}
int get_size() const {
return size;
}
int get_capacity() const {
return capacity;
}
void print() const {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
void resize() {
int new_capacity = capacity * 2;
int* new_arr = new int[new_capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
new_arr[i] = arr[i];
}
delete[] arr;
arr = new_arr;
capacity = new_capacity;
}
};
int main() {
DynamicArray darray;
darray.push_back(10);
darray.push_back(20);
darray.push_back(30);
darray.push_back(40);
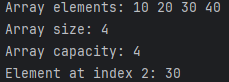
cout << "Array elements: ";
darray.print();
cout << "Array size: " << darray.get_size() << endl;
cout << "Array capacity: " << darray.get_capacity() << endl;
cout << "Element at index 2: " << darray.get(2) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Efficiency
| Time Complexity | Explaination |
|---|
| Search | O(1) | 연속된 메모리 공간을 사용하므로 특정 인덱스를 빠르게 접근 가능. |
| Insertion | O(1)(평균), O(n)(재할당시) | 끝에 요소를 추가할 때 평균적으로 O(1), 용량이 초과하면 크기를 두 배로 재할당하여 O(n). |
| Deletion | O(n) | z중간 요소를 삭제할 경우, 이후 요소들을 모두 이동해야 함. O(n) |
| 재할당 복사 | O(n) | 크기가 초과할 경우, 두 배 용량의 새로운 메모리를 할당하고 기존 데이터 복사하는 작업 발생. |
| Space Complexity | O(n) | n개의 요소를 저장하는 O(n)의 공간이 필요. |
Efficiency Summary
크기가 불확실하거나 자주 변하는 데이터를 저장할 때 유리
랜덤 접근이 빈번히 필요한 경우 - 배열처럼 특정 인덱스의 데이터에 상수 시간으로 빠르게 접근 가능
중간에서 빈번한 삽입/삭제가 필요한 경우 부적합
쓰레드 지원 안함
STL
std::vector
메모리 관리가 자동화된 형태로 구현 됨
크기 조절, 메모리 관리 수월