CSS의 position속성은 top, bottom, left, right 프로퍼티와 함께 사용하여 HTML요소를 배치할 때 사용한다.
position 속성값으로는 static, relative, absolute, fixed, sticky 5가지가 있다.
이 글에서는 그 중 static, relatvie, absolute 세 가지에 대해 다뤄보겠다.
<html>
<head>
<style>
div {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
color: white;
font-size: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
.div1 {
left: 100px;
background-color: #5d6a75;
}
.div2 {
position: relative;
left: 150px;
background-color: #5d8a50;
}
.div3 {
position: relative;
left: 300px;
background-color: #776e66;
}
.div3-inner {
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
background-color: #a2958a;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1">1</div>
<div class="div2">2</div>
<div class="div3">3
<div class="div3-inner">3-1</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>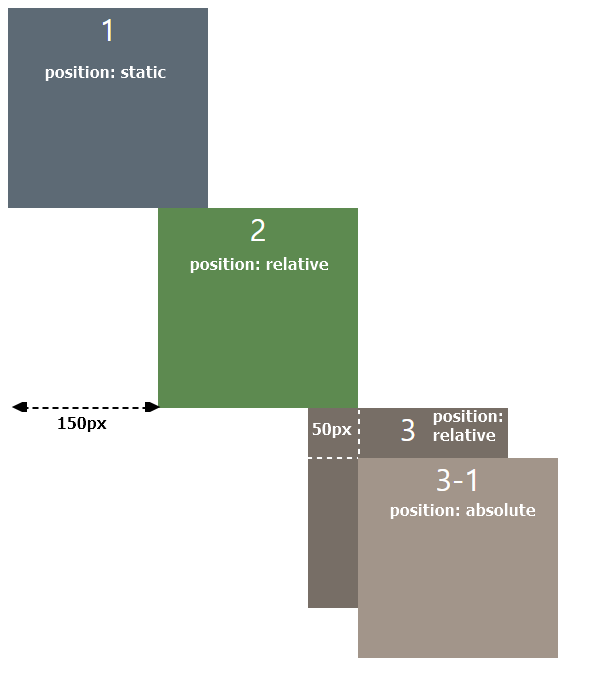
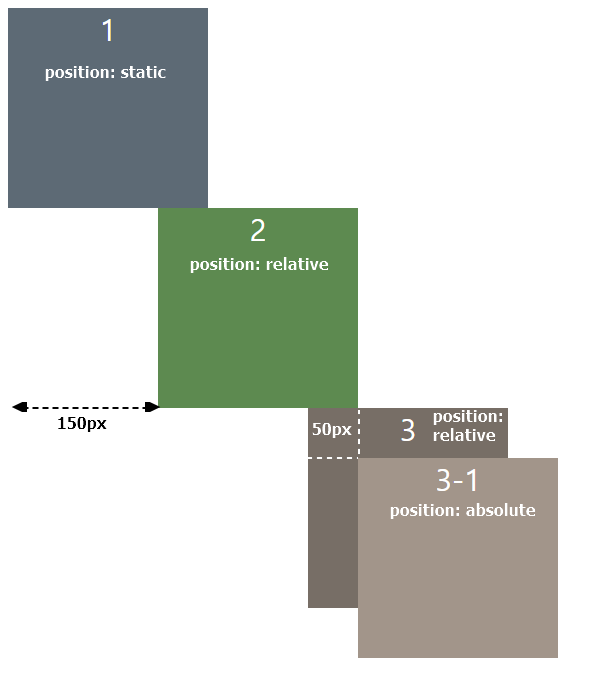
position: static
static요소는 top, right, bottom, left, z-index값을 주어도 적용되지 않는다.
position속성을 지정하지 않을시 default로 static이 설정된다.
position: relative
relative요소는 해당 요소가 static이었다면 당연히 와야할 위치 + top, right, bottom, left와 같은 위치 지정 속성이 적용되어 배치된다.
사진 속 요소들은 모두 div( block 엘리먼트 )이므로 1번 div아래에 2번 div가 자연히 와야(쌓여야)한다.
즉 자연히 와야할 위치 + left: 150px이 적용된 위치이다.
position: absolute
absolute요소도 top, right, bottom, left와 같은 위치 지정 속성이 적용된다.
relative와의 차이점은relative는 static일 때를 기준으로 이동하지만,
absolute는position: relative인 부모요소를 기준점으로 이동한다는 점이다
div4는 position: relative이므로 자신도 left: 300px만큼 이동하여 배치되어있다.
div4-inner는 position: absolute로, 가장 가까운 position: relative 부모요소를 먼저 찾고, div4를 기준으로 top: 50px, left: 50px만큼 이동하여 배치된 것을 볼 수 있다.
🛑 만약 relative인 부모요소가 없다면 body요소를 부모요소로 삼는다.