
> 이전 글
- [PintOS project] 1. Part 1: Threds - Alarm Clock
https://velog.io/@takealittletime/PintOS-project-1.-Part-1-Threds-Alarm-Clock
00. Priority Scheduling
Main Goal
- 현재 우리의 PintOS는 FIFO(Fist-In-First-Out) 방식으로 스레드를 스케줄링 한다.
→ 이를 스레드의 우선 순위(Priority)를 기준으로 선점(Preemption) 방식을 이용 해 스케줄링 하도록 수정한다.
01. 목표 구현을 위해 코드 뜯어보기
-
스레드들을 우선 순위를 기준으로 스케줄링 하기 위해서는
thread.c파일에 대한 이해가 필요하다. 이는 이전 글에서 한 번 뜯어 보았다.- [PintOS project] 1. Part 1: Threds - Alarm Clock
https://velog.io/@takealittletime/PintOS-project-1.-Part-1-Threds-Alarm-Clock
- [PintOS project] 1. Part 1: Threds - Alarm Clock
-
thread.c코드를 열어보면,thread구조체 안에int priority;값이 이미 존재한다.
/* threads/thread.c */
struct thread {
/* Owned by thread.c. */
tid_t tid; /* Thread identifier. */
enum thread_status status; /* Thread state. */
char name[16]; /* Name (for debugging purposes). */
int priority; /* Priority. */
/* 이하 생략 */
...
};- 이
priority값은 0(PRI_MIN)부터 63(PRI_MAX)까지, 기본적으로 31로 지정된다.
값이 클수록 우선순위가 높은 것이다.
/* threads/thread.c */
/* Thread priorities. */
#define PRI_MIN 0 /* Lowest priority. */
#define PRI_DEFAULT 31 /* Default priority. */
#define PRI_MAX 63 /* Highest priority. */- 자, 그렇다면, 우선순위에 대한 어떠한 변수를 우리가 추가 해 줄 필요는 없다. (이미 존재 하니까!)
02. 스레드의 우선순위 기준 스케줄링 구현하기
- 그럼 이제 우리는 무엇을 해야할까?
💡 스레드들을 우선순위를 기준으로 스케줄링 한다?
ready_list를 우선 순위를 기준으로 정렬한다.- 우선 순위가 가장 큰 스레드로 실행 스레드를 선점한다.
-
우선, 1번부터 해결해보자.
ready_list는 항상 우선 순위를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬 상태를 유지해야 한다.
→ 그럼 어떻게 해야할까?
→ready_list에 삽입할 때마다priority를 비교하여 삽입 해 주면 될 것이다.
sleep_list를 구현 할 때 처럼,list_insert_ordered()를 사용 해 구현해주면 된다. 어려울 것 없다! :) -
그럼,
ready_list에 스레드를 삽입하는 경우는 언제 언제가 있었나?
→ ① 스레드를 생성할 때, ②sleep_list의 스레드를 깨울 때, ③thread_yield로
→ 그리고, ①, ②의 경우 모두thread_unblock()을 호출 해ready_list로 스레드를 삽입하고 있으므로,thread_unblock()함수를 먼저 수정해주면 되겠다.
/* threads/thread.c */
// sleep_list에 스레드 삽입 중 정렬 위해 priority을 비교하는 함수
bool
cmp_thread_priority(const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED){
struct thread *t_a = list_entry(a, struct thread, elem);
struct thread *t_b = list_entry(b, struct thread, elem);
return t_a->priority > t_b->priority;
}
void
thread_unblock (struct thread *t) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (is_thread (t));
old_level = intr_disable ();
ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED);
//list에 삽입 시 우선순위를 기준으로 삽입 하도록 수정
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, & t->elem, cmp_thread_priority, NULL);
t->status = THREAD_READY;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}-
list_push_back (&ready_list, &t->elem);문장을 지우고,list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, & t->elem, cmp_thread_priority, NULL);와 같이 수정 하였다. -
list_insert_ordered()함수에서 사용을 위해 두 스레드의 우선순위를 비교해 대소를 비교하는cmp_thread_priority()함수를 위와 같이 작성하였다. -
thread_yield()함수도 똑같이 수정할 수 있다.
/* threads/thread.c */
/* Yields the CPU. The current thread is not put to sleep and
may be scheduled again immediately at the scheduler's whim. */
void
thread_yield (void) {
struct thread *curr = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (curr != idle_thread)
//우선순위 기준으로 삽입
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, & curr->elem, cmp_thread_priority, NULL);
do_schedule (THREAD_READY);
intr_set_level (old_level);
}-
이제 2번, '선점' 문제를 해결 해 보자.
① '현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위'와 '
ready_list의 가장 앞의 스레드의 우선순위' (항상 우선순위 기준 내림차순 정렬이 되어있으므로)를 비교② 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 후자의 우선순위가 더 높다면, 실행 중인 스레드를
thread_yield()하고 후자를 run 하도록 한다.위의 내용을 그대로 함수로 작성하면 된다.
필자는 아래와 같이 작성했다.
/* threads/thread.c */
// 현재 실행 중인 스레드와 레디 리스트의 가장 앞 스레드의 우선 순위를 확인해 스케줄
void
schedule_by_priority () {
struct thread * curr = thread_current();
if (!list_empty(&ready_list)){
struct thread *highest_priority_thread = list_entry(list_front(&ready_list), struct thread, elem);
if (curr->priority < highest_priority_thread->priority)
thread_yield();
}
}thread_set_priority(),thread_create()함수에서 동작을 끝낼 때 위 함수를 호출해주도록 하자!
/* threads/thread.c */
/* Sets the current thread's priority to NEW_PRIORITY. */
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority) {
struct thread *curr = thread_current();
curr->priority = new_priority;
schedule_by_priority();
}
tid_t
thread_create (const char *name, int priority,
thread_func *function, void *aux) {
struct thread *t;
tid_t tid;
/* ... 중략 ... */
/* Add to run queue. */
thread_unblock (t);
schedule_by_priority();
return tid;
}- 이렇게 작성하면, 우선 '스레드'의 우선 순위 기준 스케줄링은 일단 마무리 된다.
02-1. 실행 결과
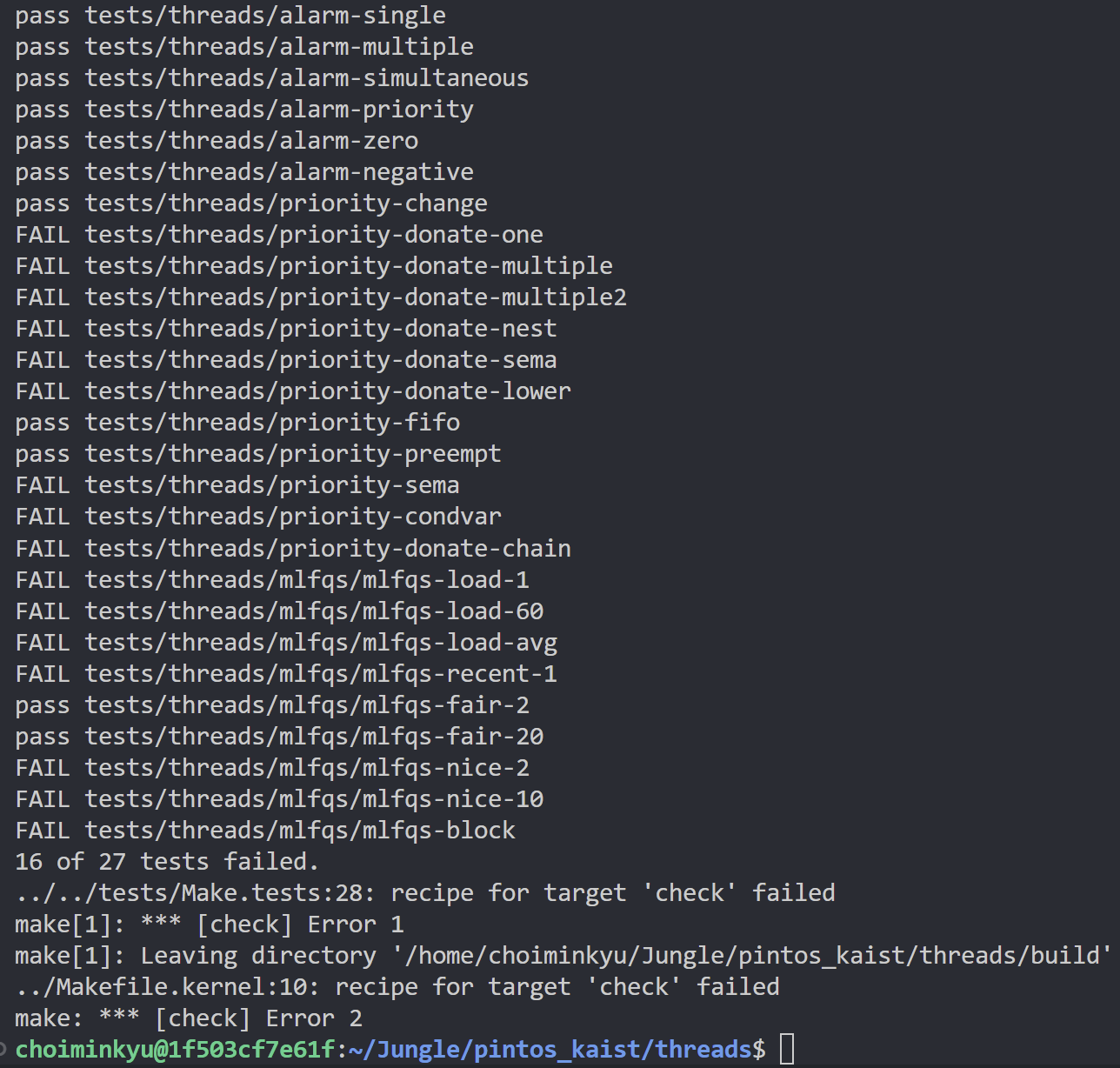
- 시작보다 네 개의 테스트 케이스가
pass되면서 결과가 좋아진 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
03. 동기화 도구들의 wait 리스트
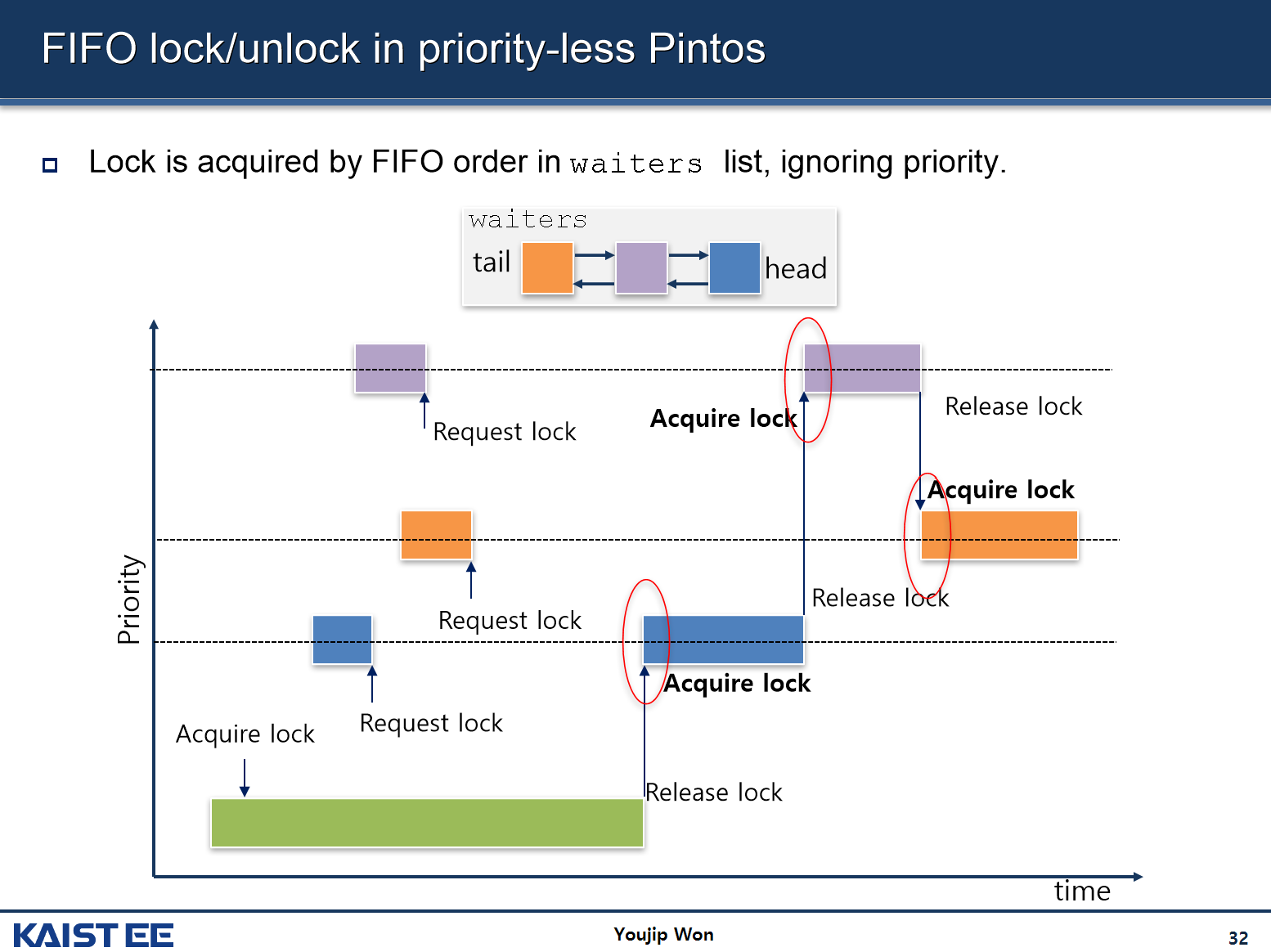
-
현재 제공받은 코드에서는 동기화 도구들이 우선순위를 기준으로 정렬되어 있지 않고, FIFO 방식으로 진행되고 있다.
-
이게 무슨 말인지 처음에는 이해가 잘 안갈 수 있지만, 어렵지 않다.
semaphore구조체를 확인 해보자.
/* threads/synch.h */
/* A counting semaphore. */
struct semaphore {
unsigned value; /* Current value. */
struct list waiters; /* List of waiting threads. */
};
/* Lock. */
struct lock {
struct thread *holder; /* Thread holding lock (for debugging). */
struct semaphore semaphore; /* Binary semaphore controlling access. */
};
/* Condition variable. */
struct condition {
struct list waiters; /* List of waiting threads. */
};-
semaphore는 세마포어 값value를 가지고, 해당 세마포어를 요청한 (즉, 대기 중인) 스레드들을waiters리스트에 할당한다.
이 때,waiters리스트에 스레드들이 우선 순위를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬 되도록 수정해주면 된다.
위에서 sleep_list를 구현할 때와 같다! -
위와 같이, 결국 동기화 도구의 개념론적인 부분은 잠깐 차치하고, 스레드의 우선 순위에 따라 리스트를 내림차순으로 정렬해주면 해결되는 문제다.
* 동기화 도구들의 개념론적인 부분은 다음 글에서 다룬다.
-
lock은 요소로semaphore를 가지기 때문에, 사실상 위의semaphore에서 우선 순위를 기준으로 정렬되게끔 수정해주면 알아서 해결 될 것이다. -
그나마
condition변수가 조금 복잡하다면 복잡할 수 있겠다.
구조체condition으로 나타낸condition variable은waiters라는 리스트를 가지고 있는데, 이 리스트는 사용되는 형식을 보면semaphore를 담는 리스트로 사용된다.
/* threads/synch.c */
/* One semaphore in a list. */
struct semaphore_elem {
struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */
struct semaphore semaphore; /* This semaphore. */
};
// ex) cond_wait()
// 다음 부분에서 list에 semaphore를 담고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock) {
struct semaphore_elem waiter;
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0);
list_push_back (&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem);
lock_release (lock);
sema_down (&waiter.semaphore);
lock_acquire (lock);
}03-1. Semaphore의 waiters 리스트를 우선 순위 기준 스케줄링
- 우선,
semaphore가 사용하는waiters리스트를 우선 순위를 기준으로 스케줄링 해 보도록 하자.
수정 전 코드는 아래와 같다.
/* threads/synch.c */
void
sema_down (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
while (sema->value == 0) {
// 이 부분에서 list에 현재 스레드를 할당하고 있다.
list_push_back (&sema->waiters, &thread_current ()->elem);
thread_block ();
}
sema->value--;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
// list에서 가장 앞의 값을 꺼내고 unblock()
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters))
thread_unblock (list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters),
struct thread, elem));
sema->value++;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}-
위의 주석으로 표시한 것처럼 list에 순서대로
push_back()하고,pop()하는 것을 볼 수 있다. -
위의 sleep_list에서 했던 것처럼, 우리는
list_insert_ordered()함수를 이용해 아래와 같이 코드를 수정해주면 된다.
/* threads/synch.c */
void
sema_down (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
// sema->value가 0이라면 wait 리스트에 넣고 스레드 block함.
while (sema->value == 0) {
// 우선순위를 기준으로 waiters 리스트에 삽입.
list_insert_ordered(&sema->waiters,&thread_current ()->elem,cmp_thread_priority, NULL);
thread_block ();
}
// sema->value != 0이면 sema->value 1 감소
sema->value--;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
// sema->waiters 리스트에 대기 중인 스레드가 있다면
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters))
{
// 혹시 모르니 unblock 하기 전에 리스트 한 번 더 정렬
list_sort(&sema->waiters,cmp_thread_priority,NULL);
// waiters 리스트에서 가장 앞에 있는 스레드를 unblock하는 함수
thread_unblock (list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters),
struct thread, elem));
}
sema->value++;
schedule_by_priority();
intr_set_level (old_level);
}- 이렇게 수정하면,
semaphore와lock까지 우선 순위 스케줄링 변경도 끝이다.
03-2. Condition Variable의 waiters 리스트를 우선 순위 스케줄링
- 우선 변경 전의 Condition Variable에 대한 함수들을 살펴보자.
/* threads/synch.c */
void
cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock) {
struct semaphore_elem waiter;
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0);
// 이 부분에서 list에 값 추가
list_push_back (&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem);
lock_release (lock);
sema_down (&waiter.semaphore);
lock_acquire (lock);
}
void
cond_signal (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock UNUSED) {
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (!list_empty (&cond->waiters))
// 리스트에서 값을 꺼내 sema_up 연산
sema_up (&list_entry (list_pop_front (&cond->waiters),
struct semaphore_elem, elem)->semaphore);
}- condition variable 에서도 우선 모양새는 같아 보인다.
그렇다.list_insert_ordered()함수를 이용 해 이도 똑같이 우선 순위 기준 내림차순으로 정렬되도록 만들어주면 된다.
/* threads/synch.c */
void
cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock) {
struct semaphore_elem waiter;
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0);
list_insert_ordered(&cond->waiters,&waiter.elem,cmp_sema_priority,NULL);
lock_release (lock);
sema_down (&waiter.semaphore);
lock_acquire (lock);
}
void
cond_signal (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock UNUSED) {
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (!list_empty (&cond->waiters))
{
list_sort(&cond->waiters, cmp_sema_priority, NULL);
sema_up (&list_entry (list_pop_front (&cond->waiters),
struct semaphore_elem, elem)->semaphore);
}
}-
단, 이번에는 다음과 같이 스레드의 우선 순위를 기준으로 대소 비교를 하는 함수를 새로 작성해주어야 한다.
-
sema_elem→semaphore→waiters→list_begin()순서로 각 세마포어를 wait하고 있는 스레드, 그 중에서도 가장 앞의 스레드의 우선순위를 가져와 비교한다.
// cond 변수에서 waiters 리스트 정렬을 위한 비교 함수
bool
cmp_sema_priority(const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED){
struct semaphore_elem *a_sema = list_entry (a, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct semaphore_elem *b_sema = list_entry (b, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct list *waiter_a_sema = &(a_sema->semaphore.waiters);
struct list *waiter_b_sema = &(b_sema->semaphore.waiters);
return list_entry (list_begin(waiter_a_sema), struct thread, elem)->priority > list_entry(list_begin(waiter_b_sema),struct thread, elem)->priority;
}list_insert_ordered()함수의 사용을 위해cmp_sema_priority()함수를 위와 같이 작성 해 주었다.
이를 다음과 같이synch.h헤더 파일에 포함 해 주어야 한다.
/* threads/synch.h */
bool cmp_sema_priority(const struct list_elem *, const struct list_elem *, void *);- 이렇게 하면 Priority Scheduling도 끝이난다.
03-3. 실행 결과
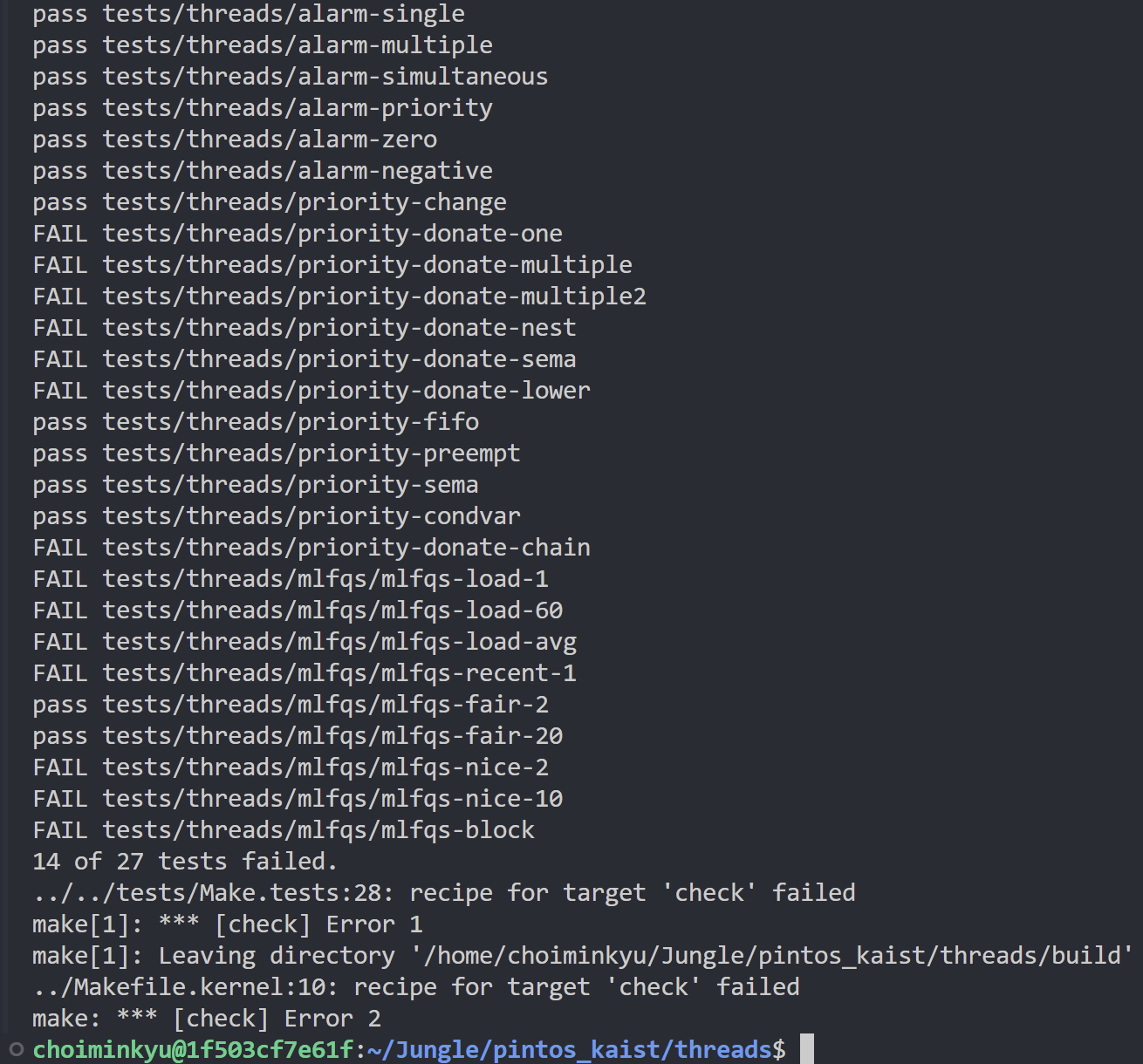
- 위에서 구현했던 것보다 2개의 테스트 케이스를 더 통과했다!
* 참고 자료 / 이미지 출처
- KAIST:OSLAB:Pintos Slides
https://oslab.kaist.ac.kr/pintosslides/
