프로그래밍 경력 5년차인 제가 실무에서 실제로 사용하고 있는 자동화 스크립트를 공개합니다! 단조로운 작업에 시간을 낭비하는 것은 아깝죠. 이 글에서는 데이터 분석부터 성능 모니터링까지, 실제로 유용한 Python 스크립트를 엄선했습니다.
신입 엔지니어였을 때, 같은 작업을 반복하며 답답했던 경험이 있습니다. 그때 선배에게 배운 것이 '자동화의 힘'이었습니다. 이번에는 그 경험을 바탕으로, 여러분의 작업 효율을 폭발적으로 높여줄 스크립트를 공유합니다!
데이터 처리 도구
1.1 데이터 클리닝
CSV 파일의 공백이나 중복을 한 번에 제거할 수 있는 스크립트입니다. 데이터 분석 전처리에 매번 사용하고 있습니다!
import pandas as pd
def clean_data(input_file, output_file):
df = pd.read_csv(input_file)
df.dropna(inplace=True) # 빈 값 제거
df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) # 중복 값 제거
df.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# 사용 예시
clean_data("data.csv", "cleaned_data.csv")1.2 데이터 비교
두 개의 CSV 파일 차이를 쉽게 찾을 수 있습니다. 버전 관리나 데이터 검증에 매우 유용합니다!
import pandas as pd
def compare_data(file1, file2):
df1 = pd.read_csv(file1)
df2 = pd.read_csv(file2)
diff = df1.compare(df2)
return diff
# 사용 예시
result = compare_data("file1.csv", "file2.csv")
print(result)네트워크 검사 도구
2.1 포트 개방 확인
서버의 포트가 열려 있는지 확인하는 스크립트입니다. 트러블슈팅의 첫 단계로 사용합니다!
import socket
def check_port(host, port):
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
result = sock.connect_ex((host, port))
sock.close()
return result == 0
# 사용 예시
if check_port("example.com", 80):
print("Port 80이 열려 있습니다")
else:
print("Port 80이 닫혀 있습니다")2.2 일괄 Ping 테스트
여러 호스트에 대해 한 번에 Ping 테스트를 할 수 있습니다. 네트워크 장애 분석에 최적입니다!
import os
def ping_hosts(hosts):
for host in hosts:
response = os.system(f"ping -c 1 {host}")
if response == 0:
print(f"{host} 응답 있음")
else:
print(f"{host} 응답 없음")
# 사용 예시
hosts = ["google.com", "example.com", "localhost"]
ping_hosts(hosts)시스템 작업 자동화 도구
3.1 디스크 용량 모니터링
디스크 용량이 부족해지면 경고해주는 스크립트입니다. 서버 관리자의 든든한 조력자입니다!
import shutil
def check_disk_space(path, threshold):
total, used, free = shutil.disk_usage(path)
free_gb = free // (2**30)
if free_gb < threshold:
print(f"경고: 여유 공간이 {threshold}GB 이하입니다.")
else:
print(f"여유 공간: {free_gb}GB")
# 사용 예시
check_disk_space('/', 10)테스트 자동화 도구
4.1 unittest를 사용한 단위 테스트
코드 품질을 유지하기 위한 단위 테스트입니다. 팀 개발에서는 필수 스킬입니다!
import unittest
def add(a, b):
return a + b
class TestMyFunction(unittest.TestCase):
def test_addition(self):
result = add(1, 2)
self.assertEqual(result, 3)
# 사용 예시
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()파일 관리 자동화 도구
5.1 확장자별 파일 정리
흩어진 폴더를 확장자별로 정리해주는 마법 같은 스크립트입니다. 데스크톱 정리에 최적입니다!
import os
from shutil import move
def sort_files(directory_path):
for filename in os.listdir(directory_path):
file_path = os.path.join(directory_path, filename)
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
file_extension = filename.split('.')[-1]
destination_directory = os.path.join(directory_path, file_extension)
if not os.path.exists(destination_directory):
os.makedirs(destination_directory)
move(file_path, os.path.join(destination_directory, filename))
# 사용 예시
sort_files('/path/to/directory')5.2 빈 폴더 삭제
불필요한 빈 폴더를 일괄 삭제할 수 있습니다. 시스템 정리 정돈에 도움이 됩니다!
import os
def remove_empty_folders(directory_path):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory_path, topdown=False):
for folder in dirs:
folder_path = os.path.join(root, folder)
if not os.listdir(folder_path):
os.rmdir(folder_path)
# 사용 예시
remove_empty_folders('/path/to/directory')5.3 파일 일괄 이름 변경
대량의 파일을 한 번에 이름 변경할 수 있습니다. 사진 정리나 자료 관리에 매우 유용합니다!
import os
def batch_rename(directory, prefix):
for count, filename in enumerate(os.listdir(directory)):
new_name = f"{prefix}_{count}.txt"
os.rename(os.path.join(directory, filename), os.path.join(directory, new_name))
# 사용 예시
batch_rename("/path/to/files", "file")5.4 큰 파일 검색
디스크 용량을 차지하는 큰 파일을 찾아냅니다. 스토리지 관리에 큰 도움이 됩니다!
import os
def find_large_files(directory, size_limit_mb):
size_limit = size_limit_mb * 1024 * 1024 # 바이트로 변환
large_files = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
if os.path.getsize(file_path) > size_limit:
large_files.append(file_path)
return large_files
# 사용 예시
large_files = find_large_files("/path/to/directory", 100) # 100MB 이상 파일 검색
print(large_files)성능 모니터링 도구
6.1 CPU와 메모리 사용 상황 모니터링
시스템 리소스 사용 상황을 실시간으로 모니터링할 수 있습니다. 성능 튜닝에 필수입니다!
import psutil
import time
def monitor_system(interval=1):
try:
while True:
cpu_usage = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=interval)
memory_usage = psutil.virtual_memory().percent
print(f"CPU 사용률: {cpu_usage}% | 메모리 사용률: {memory_usage}%")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("모니터링을 중지했습니다.")
# 사용 예시
monitor_system(interval=2)6.2 GPU 사용 상황 모니터링
머신러닝이나 게임 개발에서 중요한 GPU 사용 상황을 모니터링합니다. 리소스 최적화에 도움이 됩니다!
import pynvml
def monitor_gpu_usage():
pynvml.nvmlInit()
device_count = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetCount()
for i in range(device_count):
handle = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetHandleByIndex(i)
util = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetUtilizationRates(handle)
memory_info = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetMemoryInfo(handle)
print(f"GPU {i}: 사용률={util.gpu}%, 메모리 사용량={memory_info.used / 1024 ** 2} MB")
# 사용 예시
monitor_gpu_usage()6.3 네트워크 대역폭 모니터링
네트워크 사용 상황을 실시간으로 모니터링할 수 있습니다. 통신 문제 원인 파악에 도움이 됩니다!
import psutil
import time
def monitor_network_usage(interval=1):
old_value = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent + psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
try:
while True:
new_value = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent + psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
bandwidth = (new_value - old_value) / interval # 바이트/초
print(f"네트워크 대역폭: {bandwidth} B/s")
old_value = new_value
time.sleep(interval)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("모니터링을 중지했습니다.")
# 사용 예시
monitor_network_usage(interval=2)6.4 디스크 I/O 모니터링
디스크 읽기/쓰기 속도를 모니터링합니다. 스토리지 병목 현상 파악에 최적입니다!
import psutil
import time
def monitor_disk_io(interval=1):
old_read = psutil.disk_io_counters().read_bytes
old_write = psutil.disk_io_counters().write_bytes
try:
while True:
new_read = psutil.disk_io_counters().read_bytes
new_write = psutil.disk_io_counters().write_bytes
read_speed = (new_read - old_read) / interval
write_speed = (new_write - old_write) / interval
print(f"읽기 속도: {read_speed / 1024} KB/s | 쓰기 속도: {write_speed / 1024} KB/s")
old_read = new_read
old_write = new_write
time.sleep(interval)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("모니터링을 중지했습니다.")
# 사용 예시
monitor_disk_io(interval=2)6.5 프로세스 리소스 사용 상황 모니터링
특정 프로세스의 리소스 사용 상황을 모니터링합니다. 애플리케이션 성능 분석에 유용합니다!
import psutil
def monitor_process(pid):
process = psutil.Process(pid)
try:
while True:
cpu_usage = process.cpu_percent(interval=1)
memory_usage = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 ** 2 # MB로 변환
print(f"PID {pid}: CPU={cpu_usage}%, 메모리={memory_usage} MB")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("모니터링을 중지했습니다.")
# 사용 예시
monitor_process(1234) # 대상 프로세스의 PID로 교체하세요로그 분석 도구
7.1 로그의 고빈도 오류 통계
로그 파일에서 자주 발생하는 오류를 추출하여 집계합니다. 문제의 근본 원인 파악에 도움이 됩니다!
from collections import Counter
import re
def top_n_errors(log_file, n=5):
error_pattern = re.compile(r"ERROR: (.+)")
errors = []
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
match = error_pattern.search(line)
if match:
errors.append(match.group(1))
return Counter(errors).most_common(n)
# 사용 예시
top_errors = top_n_errors("app.log", n=3)
print(top_errors)7.2 시간 범위로 로그 필터링
특정 시간대의 로그만 추출할 수 있습니다. 장애 발생 시 상황 분석에 최적입니다!
from datetime import datetime
def filter_logs_by_time(log_file, start_time, end_time, output_file):
start = datetime.strptime(start_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
end = datetime.strptime(end_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
logs = f.readlines()
filtered_logs = []
for log in logs:
log_time_str = log.split()[0] + " " + log.split()[1] # 타임스탬프는 로그의 처음 두 부분이라고 가정
log_time = datetime.strptime(log_time_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
if start <= log_time <= end:
filtered_logs.append(log)
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.writelines(filtered_logs)
# 사용 예시
filter_logs_by_time("app.log", "2025-02-26 12:00:00", "2025-02-26 14:00:00", "filtered_logs.log")7.3 로그에서 오류 정보 추출
로그 파일에서 오류 정보만 추출합니다. 문제 해결 시간을 단축시켜 줍니다!
def extract_errors(log_file, output_file):
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
errors = [line for line in lines if "ERROR" in line]
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.writelines(errors)
# 사용 예시
extract_errors("app.log", "errors.log")7.4 로그 파일 병합
여러 로그 파일을 하나로 합칩니다. 분산 시스템 분석에 유용합니다!
def merge_log_files(log_files, output_file):
with open(output_file, 'w') as outfile:
for log_file in log_files:
with open(log_file, 'r') as infile:
outfile.write(infile.read())
# 사용 예시
merge_log_files(["log1.log", "log2.log", "log3.log"], "merged_logs.log")7.5 로그 파일 실시간 모니터링
로그 파일의 업데이트를 실시간으로 모니터링합니다. 장애 발생 시 즉시 대응에 유용합니다!
import time
def tail_log_file(log_file):
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
f.seek(0, 2) # 파일의 끝으로 이동
try:
while True:
line = f.readline()
if line:
print(line.strip())
else:
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("모니터링을 중지했습니다.")
# 사용 예시
tail_log_file("app.log")이메일 자동화 도구
8.1 개인화된 이메일 전송 (보안 주의: 비밀번호를 하드코딩하지 마세요)
여러 수신자에게 개인화된 이메일을 보낼 수 있습니다. 고객 응대나 알림 자동화에 유용합니다!
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
def send_personalized_email(sender_email, sender_password, recipients, subject, body):
server = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.gmail.com', 587)
server.starttls()
server.login(sender_email, sender_password)
for recipient_email in recipients:
message = MIMEMultipart()
message['From'] = sender_email
message['To'] = recipient_email
message['Subject'] = subject
message.attach(MIMEText(body, 'plain'))
server.send_message(message)
server.quit()
# 사용 예시
sender_email = 'your_email@gmail.com'
sender_password = 'your_password' # 앱 비밀번호 사용 권장
recipients = ['recipient1@example.com', 'recipient2@example.com']
subject = '안녕하세요'
body = '이것은 테스트 이메일입니다.'
send_personalized_email(sender_email, sender_password, recipients, subject, body)데이터베이스 조작 도구
9.1 SQLite 데이터베이스 연결
SQLite 데이터베이스에 연결하여 쿼리를 실행합니다. 소규모 앱의 데이터 관리에 최적입니다!
import sqlite3
def connect_to_database(db_path):
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
return conn, cursor
def execute_query(cursor, query):
cursor.execute(query)
results = cursor.fetchall()
return results
# 사용 예시
conn, cursor = connect_to_database('/path/to/database.db')
query = 'SELECT * FROM table_name'
results = execute_query(cursor, query)
print(results)
conn.close()OCR 인식
10.1 이미지에서 텍스트 인식
이미지에서 텍스트를 추출합니다. 문서 디지털화나 정보 추출 자동화에 유용합니다!
import pytesseract
from PIL import Image
def recognize_text(image_path):
image = Image.open(image_path)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(image, lang='kor') # 한국어 사용
return text
# 사용 예시
text = recognize_text('/path/to/image.jpg')
print(text)PDF 조작 자동화
11.1 PDF에서 텍스트 추출
PDF 파일에서 텍스트를 추출합니다. 문서 처리 효율화에 도움이 됩니다!
import PyPDF2
def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):
with open(pdf_path, 'rb') as file:
reader = PyPDF2.PdfReader(file)
text = ''
for page in reader.pages:
text += page.extract_text() or ''
return text
# 사용 예시
text = extract_text_from_pdf('/path/to/document.pdf')
print(text)웹 스크래핑 자동화
12.1 웹사이트에서 데이터 추출
웹사이트에서 정보를 추출합니다. 시장 조사나 정보 수집 자동화에 유용합니다!
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def scrape_data(url):
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
return soup
# 사용 예시
url = 'https://example.com'
soup = scrape_data(url)
print(soup.title.string)12.2 이미지 일괄 다운로드
웹상의 이미지를 일괄적으로 다운로드합니다. 자료 수집 시간을 단축시켜 줍니다!
import requests
import os
def download_images(url, save_directory):
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
images = response.json() # API가 이미지 URL의 JSON 배열을 반환한다고 가정
for index, image_url in enumerate(images):
image_response = requests.get(image_url)
if image_response.status_code == 200:
with open(os.path.join(save_directory, f"image_{index}.jpg"), "wb") as f:
f.write(image_response.content)
# 사용 예시
download_images('https://api.example.com/images', '/path/to/save')Excel 자동화
13.1 Excel 읽기 및 쓰기
Excel 파일 읽기 및 쓰기를 자동화합니다. 사무 작업 효율화에 큰 도움이 됩니다!
import pandas as pd
def read_excel(file_path):
df = pd.read_excel(file_path)
return df
def write_to_excel(data, file_path):
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_excel(file_path, index=False)
# 사용 예시
data = {'열1': [1, 2, 3], '열2': [4, 5, 6]}
write_to_excel(data, '/path/to/output.xlsx')
df = read_excel('/path/to/output.xlsx')
print(df)이미지 편집 자동화
14.1 이미지 크기 변경
이미지 크기를 일괄 변경할 수 있습니다. 웹용 이미지 최적화에 유용합니다!
from PIL import Image
def resize_image(input_path, output_path, width, height):
image = Image.open(input_path)
resized_image = image.resize((width, height), Image.LANCZOS)
resized_image.save(output_path)
# 사용 예시
resize_image('/path/to/input.jpg', '/path/to/output.jpg', 800, 600)스크립트 다음은? 더 효율적으로 발전하는 방법
지금까지 소개한 14개의 Python 스크립트만으로도 일상 작업은 상당히 편해집니다.
하지만 실제 개발 현장에서는 "API를 지속적으로 테스트하고 싶다" "팀에서 사양을 공유하고 싶다"와 같은 요구사항도 생깁니다.
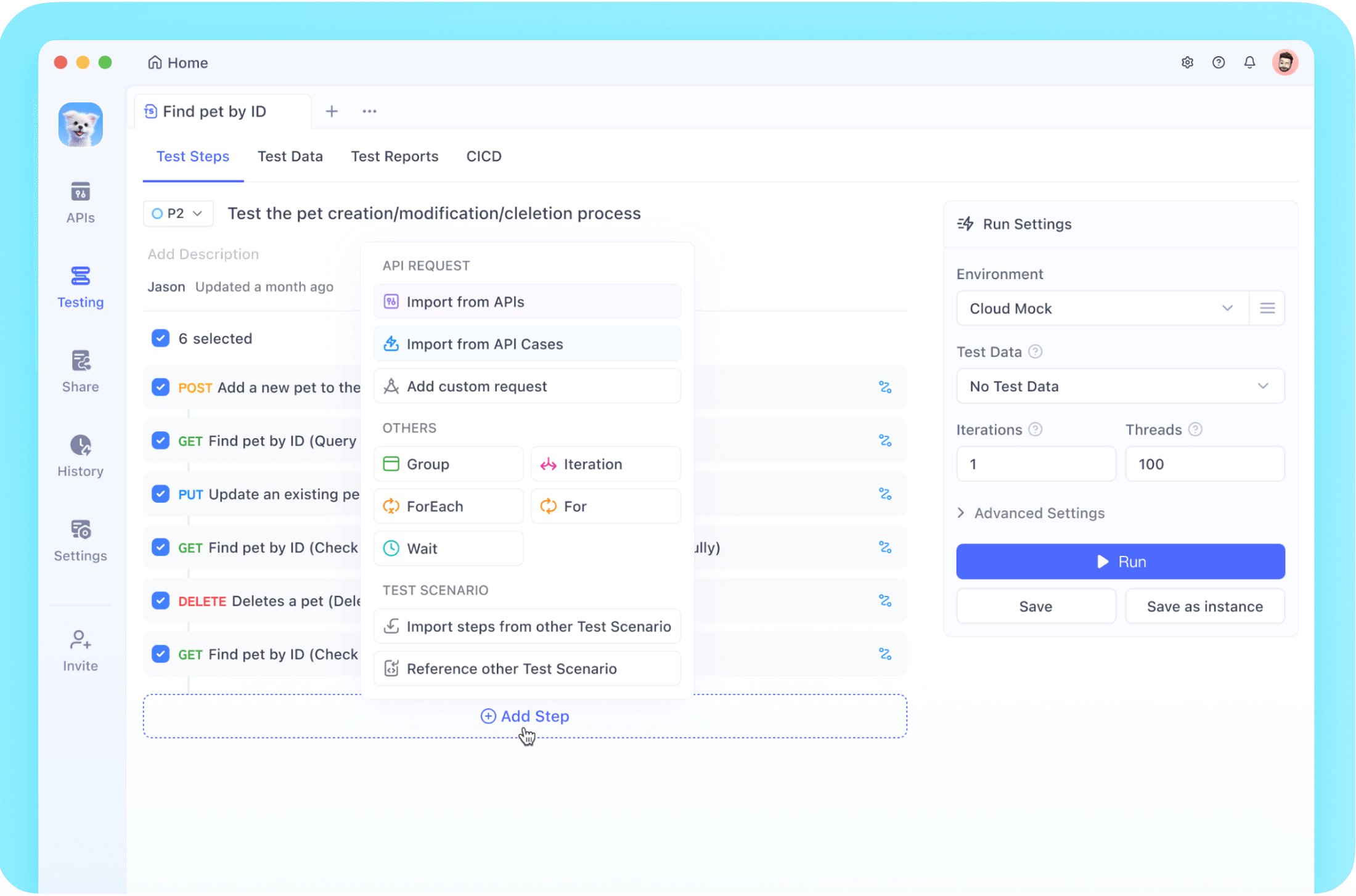
이런 경우에 추천하는 것이 Apidog입니다.
API 설계, 모킹, 테스트, 문서 관리까지 모두 하나의 플랫폼에서 완결할 수 있어 스크립트보다 더 효율적으로 작업할 수 있습니다.
Python 스크립트로 자동화를 첫 단계로 삼고, 다음 단계로 Apidog를 시도해 보는 것도 좋은 방법입니다.
요약
이번에 소개한 14개의 스크립트는 제가 실제로 일상 업무에서 사용하고 있는 것들입니다. 처음에는 작은 자동화부터 시작해서 점차 복잡한 작업도 자동화함으로써 정말 가치 있는 일에 집중할 수 있게 되었습니다.
여러분도 자신의 작업을 검토해보고 "이거, 매번 같은 일을 하고 있네"라고 생각되면 자동화를 고려해 보세요. 프로그래밍의 진정한 가치는 사람을 지루한 작업에서 해방시키는 데 있다고 생각합니다!
이 글이 여러분의 업무 효율화에 도움이 되길 바랍니다. 질문이나 자신만의 자동화 스크립트가 있다면 댓글로 알려주세요!
