Clarify the problem
Problem: Determine if the given linked list has a cycle.
Input: The head of linked list
Output: Return True if cycle exists. Otherwise return False
Example:
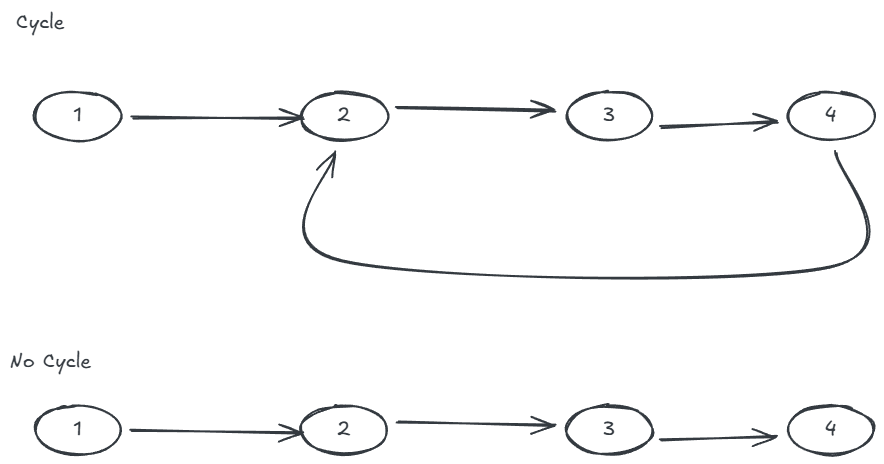
Design a solution
Idea
We can detect a cycle by traversing the linked list and finding a node that is visited more than once. We can determine that there is no cycle if the traversal ends at the last node.
Alternative approach:
Another efficient method is to use two cursors, commonly referred to as fast and slow. This approach runs in O(1) space complexity and is generally faster than the origianl solution since it doesn't require additional memory to store vistied nodes.
Algorithm
- Initialize the current node (cursor) and a visited set.
- Traverse the given linked list with
whileloop (loop until current node is None) - Operation at each node
-
Base operation:
- Check cycle: if a node has already been visited, returnTrue
- Add the current node to a visited set -
Cursor Maneuver:
- Move the cursor to the next node
- Return
Falseif the traversal completes without detecting a cycle
Implement the code
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head):
# Initialize
cur = head
visited = set()
# Traverse a linked list
while cur:
# base operation
if cur in visited:
return True
visited.add(cur)
# cursor maneuver
cur = cur.next
# Return False, if no cycle in a linked list
return FalseSelf Review (Eye Test)
This implementation correctly detects a cycle in a linked list. It also handles edge cases, such as when the linked list is empty.
Check Performance
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in a linked list. Each node is visited most once.
Space Complexity: O(n) because a set is used to store visited nodes.