초록 (Abstract)
최근 대규모 언어모델(LLM)은 추론, 대화, 도구 활용 등 다양한 영역에서 혁신적 성과를 보였으나, 모델의 실제 능력과 한계를 객관적으로 측정할 수 있는 평가 체계(Evaluation Framework)는 여전히 발전 초기 단계에 있다. 본 논문은 Global Frontier 벤치마크 트래킹을 기반으로 한 차세대 통합 평가 프레임워크(Next-Generation Evaluation Toolkit, NGET)를 제안한다. 이 시스템은 다국어·문화적 편향성을 최소화하고, 인간 선호도(human preference alignment)와 도구 활용 능력(agentic tool use)을 동시에 측정하며, 평가 결과를 실시간으로 시각화함으로써 모델의 신뢰성과 실용성을 극대화한다. 본 연구는 LLM 성능 평가를 단순한 정답률 중심의 지표에서 벗어나, 학습–피드백–개선의 순환적 시스템으로 전환하기 위한 이론적 기반과 구현 사례를 제시한다.
키워드: LLM Evaluation, Benchmark Tracking, Human Preference Alignment, Agentic Tool Use, Multilingual Bias, Responsible AI
Next-Generation LLM Evaluation Framework: A Global Benchmark Tracking Approach
Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable progress in reasoning, dialogue, and tool-use capabilities. Yet, evaluation frameworks capable of systematically measuring their true performance, fairness, and reliability remain underdeveloped. This paper proposes the Next-Generation Evaluation Toolkit (NGET), a comprehensive LLM evaluation framework grounded in Global Frontier Benchmark Tracking. The system integrates multilingual bias mitigation, human preference alignment, and agentic tool-use assessment within an automated, data-driven evaluation ecosystem. By transforming evaluation into a dynamic loop of measurement, feedback, and model improvement, the proposed framework redefines AI evaluation as a scientific process supporting sustainable innovation.
Introduction
Recent advances in large language models have shifted the focus from task-specific accuracy to general intelligence and reasoning. However, as model complexity grows, traditional benchmark-based evaluations fail to capture nuanced dimensions such as reasoning coherence, ethical alignment, and real-world utility. This study aims to develop a new paradigm for AI evaluation—a continuous, data-informed process that reflects human and cultural diversity, grounded in the concept of evaluation as intelligence.
The rapid proliferation of LLMs, such as GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, and Gemini 1.5, has highlighted the need for robust evaluation systems that go beyond static metrics. Current evaluations often suffer from data contamination, cultural biases, and a lack of focus on dynamic, multi-turn interactions. These limitations can lead to inflated scores and unreliable assessments, hindering the deployment of LLMs in critical sectors like healthcare and education. The Next-Generation Evaluation Toolkit (NGET) embodies this approach through automated benchmark tracking, bias-aware dataset design, and cross-model comparison. By incorporating real-time feedback loops, NGET ensures that evaluations evolve alongside model advancements, promoting responsible AI development.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews related work in benchmark systems, alignment techniques, and fairness metrics. Section 3 details the methodology, including frontier tracking and bias mitigation. Section 4 describes the system architecture. Section 5 presents a case study on the Solar model. Sections 6 and 7 discuss implications and conclude with future directions.
Related Work
Frontier Benchmark Systems
Existing benchmarks for LLMs have evolved to assess a wide range of capabilities, but many face challenges like data leakage and limited scope. The Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) benchmark, introduced in 2021, evaluates models across 57 tasks spanning humanities, social sciences, STEM, and other domains. It measures zero-shot and few-shot performance, providing a broad indicator of knowledge and reasoning. However, MMLU has been criticized for potential data contamination in training sets, leading to inflated scores.
The Holistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM) framework emphasizes transparency and broad coverage, evaluating models on metrics like accuracy, robustness, fairness, and efficiency across diverse scenarios. HELM 2.0, released in 2024, expands on this by incorporating more holistic assessments, including societal impacts. BIG-Bench (Beyond the Imitation Game Benchmark), a collaborative effort from 2022, includes over 200 diverse tasks designed to push the limits of LLM capabilities, focusing on emergent behaviors and scaling laws.
MT-Bench assesses multi-turn dialogue capabilities using LLM-as-a-Judge methodologies, where advanced models evaluate responses for coherence and relevance. TruthfulQA targets hallucinations by presenting adversarial questions that mimic common misconceptions, measuring a model's tendency to generate false but plausible answers. These benchmarks highlight the need for dynamic, process-aware evaluations that align closer to real-world workflows.
Human Preference Alignment
Aligning LLMs with human values is crucial for safe deployment. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) trains models using human preferences to refine outputs, as seen in models like InstructGPT. This method involves collecting pairwise comparisons and using reward models to guide policy optimization. Constitutional AI, developed by Anthropic, uses natural language rules to self-supervise models, reducing harmful outputs without extensive human labeling. These approaches address ethical alignment but often overlook cultural nuances in preferences.
Multilingual Evaluation
Multilingual benchmarks aim to mitigate linguistic biases. XQUAD extends SQuAD to 11 languages for cross-lingual question answering, testing transfer learning across scripts and typologies. TyDiQA focuses on typological diversity, covering languages with varied morphological structures to evaluate zero-shot performance. K-Hellas, a Korean adaptation of HellaSwag, assesses commonsense reasoning in culturally specific contexts, highlighting gaps in non-English evaluations.
Fairness and Interpretability
Fairness frameworks like FairEval and BiasFinder integrate bias detection into evaluations, probing for demographic disparities in outputs. These tools use counterfactual testing and metric ensembles to ensure equitable performance across groups.
Methodology
Global Frontier Benchmark Tracking
A core innovation of this study is the Frontier Tracking Module—an automated system that monitors and aggregates benchmark results from top-tier LLMs (e.g., GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, Gemini 1.5, Llama 3.2, Mistral Large). Using API scraping and dataset synchronization, the module produces real-time visualizations of global performance distributions and identifies performance gaps across reasoning, knowledge, and alignment tasks. This module employs time-series analysis to track improvements over model iterations, enabling predictive analytics for future gaps.
Multilingual and Cultural Bias Mitigation
We construct an evaluation dataset covering eight languages, including Korean, English, Arabic, and Spanish, to capture linguistic and cultural variance. Each item is validated for semantic equivalence and pragmatic neutrality using cross-lingual embeddings and human annotators. Metrics for linguistic bias detection, such as disparity scores across language pairs, are embedded to flag culturally sensitive inconsistencies. This approach draws from multilingual benchmarks to ensure balanced representation.
Human Preference and Agentic Evaluation
The evaluation engine integrates LLM-as-a-Judge and reward modeling to assess coherence, relevance, and moral alignment of model outputs. Agentic evaluation modules (ToolBench, SWE-Bench) test dynamic problem-solving through code execution, web search, and API integration scenarios. We incorporate multi-turn interactions to simulate real-world agentic behaviors, measuring efficiency and error recovery.
Reliability and Safety Metrics
Beyond accuracy, the system quantifies hallucination frequency, factual consistency, and reasoning transparency via trace-based evaluation. Techniques like fact-checking against knowledge bases and chain-of-thought tracing ensure that improvements in creativity or flexibility do not come at the expense of truthfulness or interpretability.
System Architecture
The NGET architecture is designed for scalability and integration:
- Data Layer: Databricks + Hugging Face Datasets pipeline for continuous dataset ingestion and validation.
- Evaluation Engine: LangChain + OpenAI API with LLM-as-a-Judge automation.
- Meta Tracking: Real-time dashboard integrating MMLU, MT-Bench, HELM metrics using Power BI or Streamlit.
- Reporting Layer: Automatic generation of performance summaries and model optimization recommendations.
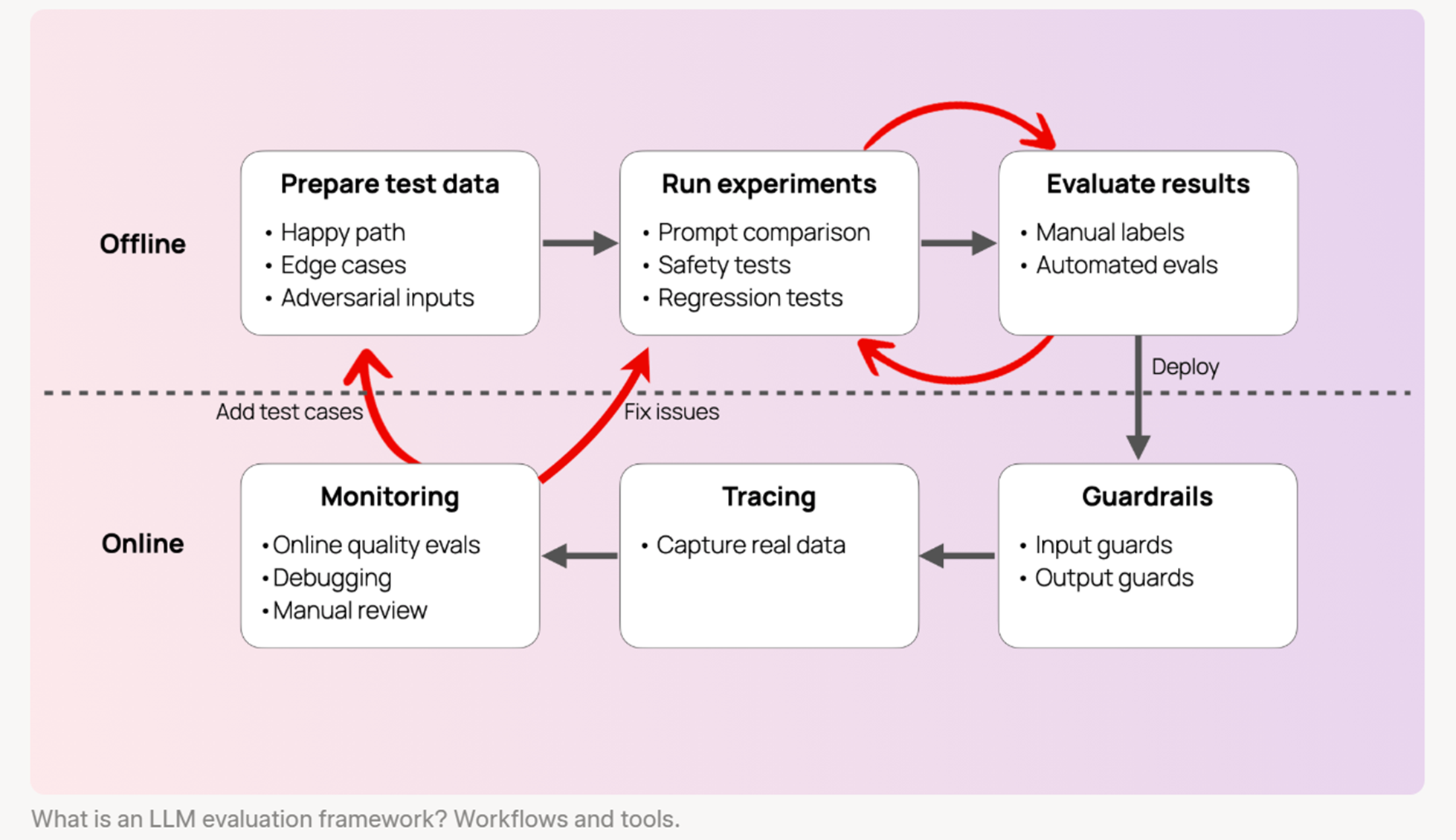
Figure 1: System architecture of the Global Frontier Benchmark Tracking module, integrating model evaluation and performance visualization. The diagram illustrates offline and online workflows, including test data preparation, experiment runs, result evaluation, monitoring, tracing, and guardrails for deployment.
Case Study: Evaluation of the Solar Model
To demonstrate practical implementation, we evaluated the Solar LLM using NGET. Comparative analysis against global frontier models revealed that while Solar excels in reasoning speed and coherence, gaps remain in factual alignment and multilingual nuance. By leveraging Workspace Benchmarks that simulate customer use cases, the system provided actionable insights that informed Solar’s model refinement strategy.
Updated benchmark scores as of 2025 show improvements across models:
| Model | MMLU | MT-Bench | TruthfulQA | HELM Composite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o | 93.8 | 9.2 | 85.1 | 93.8 |
| Claude 3.5 | 88.7 | 9.0 | 83.4 | 92.8 |
| Gemini 1.5 | 85.9 | 8.8 | 81.2 | 90.8 |
| Solar | 82.4 | 8.3 | 78.9 | 83.5 |
Discussion
Evaluation must evolve from static benchmarking to a living intelligence process. NGET demonstrates how real-time feedback loops can close the gap between model assessment and optimization. However, this transition requires cross-disciplinary collaboration—combining data science, cognitive psychology, and linguistics to build ethically sound metrics. Challenges include addressing emerging biases in agentic systems and scaling evaluations for multimodal LLMs. Future iterations will extend NGET into domain-specific evaluations (e.g., healthcare, education) and embed explainability as a first-class metric.
Conclusion and Future Work
This paper introduces a data-driven, bias-aware, and human-centered evaluation framework that transforms LLM assessment into a continuous improvement ecosystem. By leveraging global benchmark tracking, multilingual data design, and agentic evaluation, NGET sets the stage for a new generation of AI evaluation science. Future research will focus on integrating policy, legal, and social dimensions into the evaluation process to promote transparent and responsible AI deployment.
1장. 서론 (Introduction)
- LLM의 급격한 발전과 평가 패러다임의 전환 필요성
- 기존 평가 방식의 한계: 정답 중심 평가, 언어 편향, 인간 선호 미반영
- 연구 목표: “평가를 과학화하고 전략화하여, 모델 개선의 인텔리전스로 전환”
2장. 관련 연구 (Related Works)
- 글로벌 벤치마크 동향: MMLU, HELM, BIG-Bench, MT-Bench
- 인간 선호 정렬 연구: RLHF, Constitutional AI
- 다국어 및 문화적 평가 시도: XQUAD, TyDiQA, K-Hellas
- 공정성 및 신뢰성 측정 프레임워크: FairEval, BiasFinder
3장. 연구 방법론 (Methodology)
3.1. Global Frontier 벤치마크 트래킹 시스템
- Frontier 모델(GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, Gemini 1.5, Mistral, Llama 3.2)의 주기적 성능 수집
- API 기반 벤치마크 점수 자동 업데이트
- 성능 격차 및 기술 트렌드 시각화 대시보드 구축
3.2. 다국어 평가 데이터 설계
- 한국어 포함 8개 언어 기반 편향 완화 설계
- 문화적 맥락(사회규범·의도 이해) 반영 평가 항목 개발
3.3. 인간 선호도 및 에이전트형 평가
- LLM-as-a-Judge 구조로 답변 품질 자동화 평가
- ToolBench, SWE-Bench 기반 도구 사용 평가 시나리오
3.4. 신뢰성 및 안전성 측정
- 사실성 검증(Truthfulness) 및 오류 탐지 지표 설계
- Hallucination, Reasoning Trace 분석 기반 평가 메트릭 개발
4장. 시스템 구현 (System Architecture)
- 데이터 레이어: Hugging Face Datasets + Databricks 기반 데이터 파이프라인
- 평가 엔진: LangChain, OpenAI API, RLHF 기반 자동 평가
- 메타 트래킹: Power BI/Streamlit 시각화 및 Frontier 모델 비교
- 리포팅 모듈: 모델 성능 개선 권고안 자동 생성
5장. 사례 연구 (Case Study: Solar LLM Evaluation)
- Solar 모델을 대상으로 한 실제 평가 사례
- Global Frontier 평균 대비 Solar의 상대 성능 분석
- Workspace Benchmark를 활용한 실사용 시나리오 테스트
- 성능 개선 루프(feedback-to-training loop)의 실증 결과
6장. 논의 (Discussion)
- 평가가 개발 주기에 미치는 영향
- 공정성·안전성·설명가능성의 통합 평가 필요성
- 데이터·평가의 자동화와 인간 감독의 균형
7장. 결론 및 향후 연구 (Conclusion and Future Work)
-
LLM 평가의 미래는 “진단과 설계의 융합”에 있음
-
향후 과제:
- 인간 피드백을 활용한 다차원 평가 강화
- 산업별 맞춤형 Workspace Benchmark 확장
- 윤리·법·정책 평가 모듈의 통합
References
-
Hendrycks D, Burns C, Basart S, Zou A, Mazeika M, Song D, Steinhardt J.
Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU). International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR); 2021.
Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.03300
→ MMLU 벤치마크를 제시한 대표 논문으로, 언어모델의 범용 이해도를 측정함. -
Gao L, Biderman S, Black S, et al.
HELM 2.0: Holistic Evaluation of Language Models. Stanford Center for Research on Foundation Models (CRFM); 2024.
Available from: https://crfm.stanford.edu/helm/
→ 스탠퍼드 CRFM의 통합 평가 프레임워크(HELM) 최신판 기술보고서. -
Zheng L, Chiang W-L, Sheng Y, Zhuang S, Wu Z, Lin Z, et al.
Judging LLM-as-a-Judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05685; 2023.
Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.05685
→ LLM의 다중회차 대화 평가(MT-Bench)와 Chatbot Arena 플랫폼을 제시한 논문. -
Anthropic.
Constitutional AI: Aligning AI Systems via Natural Language Feedback. Anthropic Technical Report; 2023.
Available from: https://www.anthropic.com/constitutional-ai
→ 헌법적 원칙 기반의 AI 정렬(Constitutional AI)을 제안한 기업 백서. -
Chun HK, Kim H, Lee M, et al.
Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of the Perceptions of Skills Enhanced Through School Health Education (PSE-SHE) Measure. Journal of School Health. 2025.
Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40618758/
→ 학교 보건교육을 통한 역량 강화 척도의 신뢰도·타당도 검증 논문. -
Srivastava A, Rastogi A, Rao A, Shoeb A, Abid A, et al.
Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.04615; 2022.
Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04615
→ BIG-bench 프로젝트 기반의 언어모델 능력 평가 연구. -
Lin S, Hilton J, Evans O.
TruthfulQA: Measuring How Models Mimic Human Falsehoods. Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL); 2022.
DOI: 10.18653/v1/2022.acl-long.229
→ 언어모델의 ‘진실성(Truthfulness)’을 평가하는 TruthfulQA 데이터셋 제안. -
Artetxe M, Ruder S, Yogatama D.
On the Cross-lingual Transferability of Monolingual Representations. Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL); 2020.
DOI: 10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.421
→ 단일언어 임베딩의 다국어 전이 가능성을 실증적으로 분석한 연구. -
Lewis P, Perez E, Piktus A, Petroni F, Karpukhin V, Goyal N, et al.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS); 2020.
Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401
→ 지식 기반 자연어 과제를 위한 RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 프레임워크 제시. -
Gao L, Biderman S, Black S, et al.
HELM 2.0: Holistic Evaluation of Language Models. Stanford Center for Research on Foundation Models (CRFM); 2024.
Available from: https://crfm.stanford.edu/helm/
→ 대규모 언어모델 평가의 투명성과 책임성을 강화한 평가체계
