
List
순서가 있는 데이터의 집합으로, 데이터 중복을 허용하고, 형태가 배열과 유사하다. 종류로는 ArrayList, LinkedList이 있다.
1) ArrayList
ArrayList는 동적배열로 데이터를 추가 및 삭제할 때 메모리를 재할당하기 때문에 정적배열인 Array와 달리 크기가 가변적이다. Array는 초기화시 할당받은 메모리를 재할당하지 않는다.
1-1) 선언 및 생성
사이즈를 지정하지 않기 때문에 초기화를 하지 않아도 된다.
ArrayList<{참조 자료형}> {변수명} = new ArrayList<{참조 자료형}>(); ArrayList<Integer> intList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 1-2) 값 추가
{변수명}.add({value});intList.add(1);
intList.add(2);
intList.add(3);1-3) 값 호출
{변수명}.get({index});// 0번 index의 값을 호출
intList.get(0); // [결과: 1]
// 1번 index의 값을 호출
intList.get(1); // [결과: 2]
// 2번 index의 값을 호출
intList.get(2); // [결과: 3]1-4) 값 수정
{변수명}.set({index}, {value});// 1번 index의 값을 10으로 수정
intList.set(1, 10);1-5) 값 삭제
{변수명}.remonve({index});// 1번 index의 값을 삭제
intList.remove(1); 1-6) 값 전체 삭제
{변수명}.clear();intList.clear();1-7) 값 전체 출력
{변수명}.toString();intList.toString();2) LinkedList
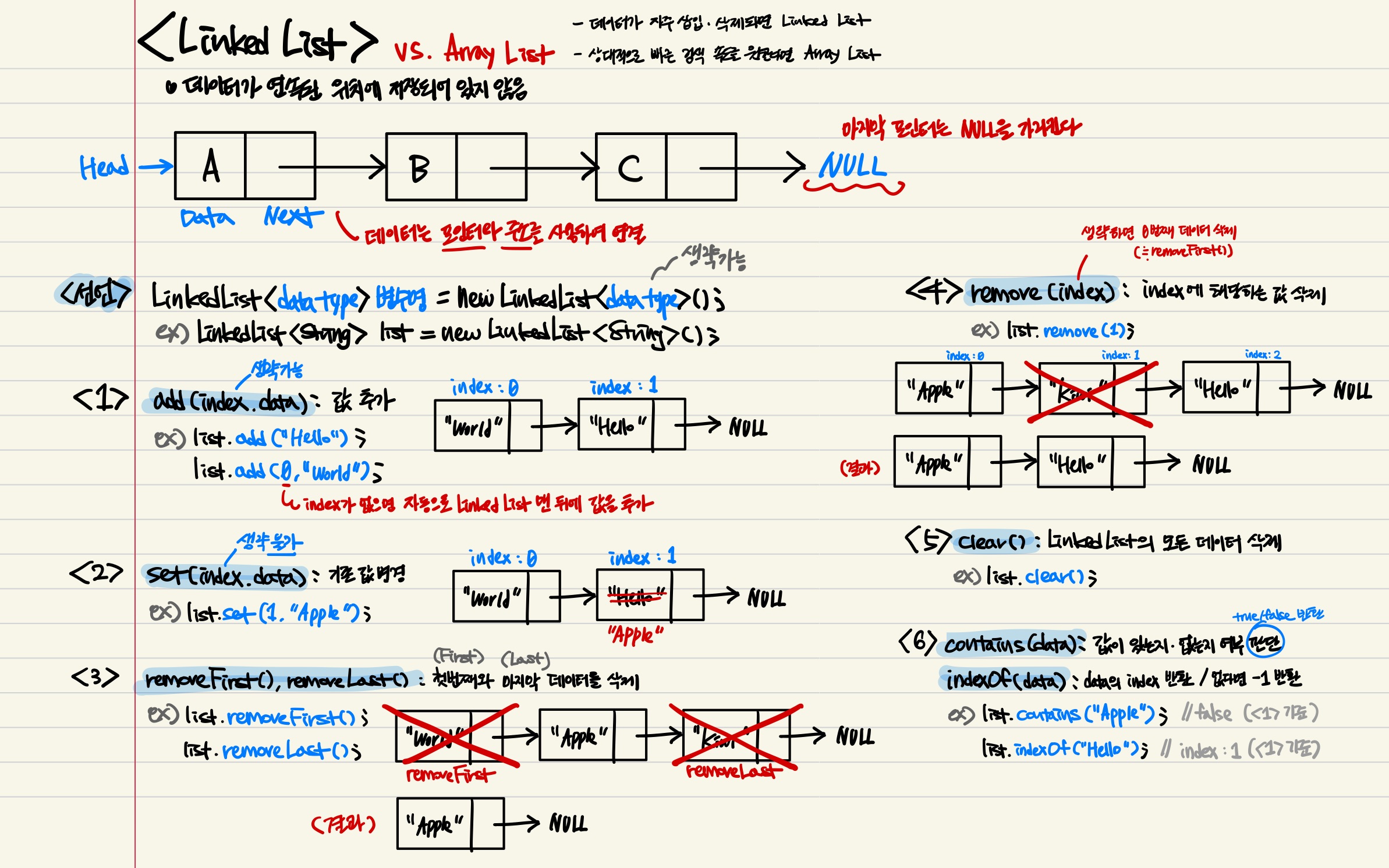
LinkedList는 메모리에 남는 공간을 요청해 실제 데이터를 나누어서 저장하고, 실제 데이터가 위치한 주소 값으로 List를 구성한다. 나누어서 저장하기 때문에 조회 속도가 ArrayList보다 느리다. 대신, 값을 추가하거나 삭제하는 속도가 빠르다.
2-1) 선언 및 생성
사이즈를 지정하지 않기 때문에 초기화를 하지 않아도 된다.
LinkedList<{참조 자료형}> {변수명} = new LinkedList<{참조 자료형}>(); LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>();2-2) 값 추가
{변수명}.add({value});linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);값을 도중에 추가하는 경우는 다음과 같다. (아래 1-2-4의 set과 유사하게 생겼다.)
{변수명}.add({index}, {value});// 2번 index에 7을 추가
linkedList.add(2, 7); 2-3) 값 호출
{변수명}.get({index});// 0번 index의 값을 호출
linkedList.get(0); // [결과: 1]
// 1번 index의 값을 호출
linkedList.get(1); // [결과: 2]
// 2번 index의 값을 호출
linkedList.get(2); // [결과: 4]
// 3번 index의 값을 호출
linkedList.get(3); // [결과: 3]2-4) 값 수정
{변수명}.set({index}, {value});// 1번 index의 값을 10으로 수정
linkedList.set(1, 10);2-5) 값 삭제
{변수명}.remonve({index});// 1번 index의 값을 삭제
linkedList.remove(1); 2-6) 값 전체 삭제
{변수명}.clear();linkedList.clear();2-7) 값 전체 출력
{변수명}.toString();linkedList.toString();