Position
css position속성은 문서 상에 요소를 배치하는 방법을 지정한다. top, right, bottom, left속성이 요소를 배치할 최종 위치를 결정한다
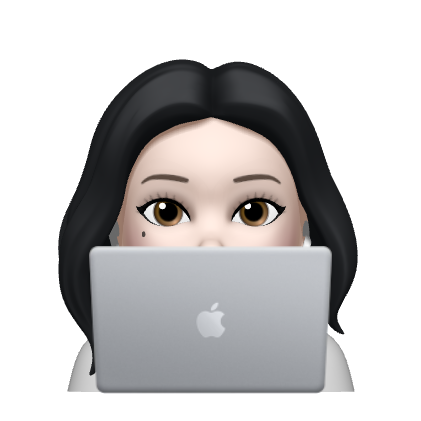
- static(default) : 요소를 일반적인 문서 흐름에 따라 배치한다.
- relative : 요소를 일반적인 문서 흐름에 따라 배치하지만, 자신의 static위치에서
top,right,bottom,left와 같은 속성에 의해 상대적인 위치에 배치된다. - absolute : 지정 부모 요소에 상대적으로 배치된다. 지정 부모 요소가 없다면 초기 컨테이너 블록을 기준으로 한다.
- fixed : 초기 컨테이너 블록을 기준 삼아 배치한다.
<body>
<div class="static">static</div>
<div class="relative">relative</div>
<div class="absolute">absolute</div>
<div class="fixed">fixed</div>
</body>
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.static {
position: static;
background-color: red;
}
.relative {
position: relative;
background-color: yellow;
}
.absolute {
position: absolute;
background-color: green;
}
.fixed {
position: fixed;
background-color: blue;
}
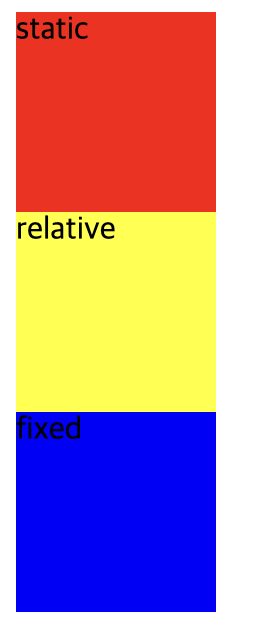
</style>먼저 <div>는 block요소기 때문에 세로로 배치된 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
<div>요소를 4번 썼는데, 화면상에서 absolute를 확인 할 수 없다.
absolute는 가장 가까운 지정 부모 요소에 상대적으로 배치(지금은 부모요소가 없으므로 초기 컨테이너 요소에 상대적으로배치)하고 fixed는 초기 컨테이너 요소에 상대적으로 배치 되었기 때문에 둘이 겹쳐져 나타났다.
.png)
<style>
.absolute {
position: absolute;
background-color: green;
z-index: 1;
}
.fixed {
position: fixed;
background-color: blue;
z-index: 0;
}
</style>이때 위처럼 z-index 속성을 주면 (더 큰 값을 가진 요소가 작은 값의 요소 위를 덮는다) absolute도 존재하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
positon : static
.png)
<style>
.static {
background-color: red;
top: 30px;
}
</style>position은 static을 기본값으로 갖기때문에 해당 속성을 지워도 영향받지 않는다.
static은 top, right, bottom, left, z-index속성에 영향을 받지 않는다.
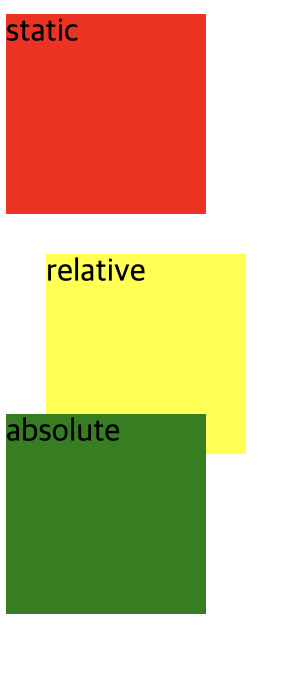
position : relative
<style>
.relative {
position: relative;
background-color: yellow;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
</style>relative는 자기자신을 기준으로 top, right, bottom, left 값에 영향을 받는다.
원래 위치했던 곳으로부터 위에서부터 20px, 왼쪽에서부터 20px이동한 모습을 볼 수 있다. 이는 다른 요소에는 영향을 주지 않는다. 따라서 레이아웃에서 요소가 차지하는 공간 자체는 static과 동일하다.
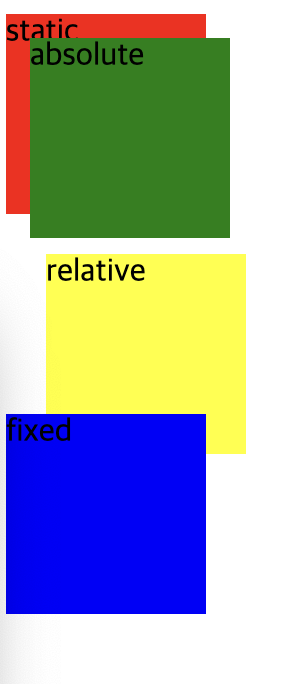
position : absolute
<style>
.absolute {
position: absolute;
background-color: green;
z-index: 1;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
</style>absolute는 가장 가까운 지정 부모 요소에대해 상대적으로 배치되며, 지정 부모 요소가 없다면 초기 컨테이너 블록을 기준으로 삼는다.
때문에 초기 컨테이너를 기준으로 위로부터 20px, 왼쪽으로부터 20px 이동한 모습을 볼 수 있다.

<body>
<div class="absolute-parent">
absolute-parent
<div class="absolute">absolute</div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.absolute-parent {
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.absolute {
position: absolute;
background-color: green;
z-index: 1;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
</style>absolute는 부모 요소 내부에 속박되지 않는다. 따라서 요소를 기본적으로 화면상 어디든지 원하는 위치에 자유롭게 배치시킬 수 있다.

<style>
.absolute-parent {
position: relative;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.absolute {
position: absolute;
background-color: green;
z-index: 1;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
</style>단, 상위 요소중 position속성이 relative인 요소가 있다면 그 중 가장 가까운 요소의 내부에서만 요소를 자유롭게 배치할 수 있다.
사진처럼 초기 컨테이너를 기준으로 삼지 않고, 상위 엘리먼트를 기준으로 위로부터 20px, 왼쪽으로부터 20px 이동해 위치한 모습을 볼 수 있다.
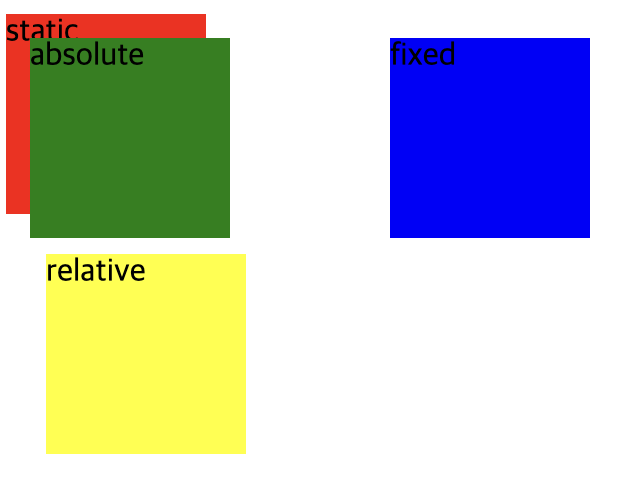
position : fixed
<style>
.fixed {
position: fixed;
background-color: blue;
top: 20px;
left: 200px;
z-index: 0;
}
</style>fixed는 원래 위치와 상관없이 위치를 지정할 수 있으며 상위 요소에 영향을 받지 않아 화면이 바뀌더라도 고정된 위치를 설정할 수 있다. 초기 컨테이너 블록을 기준으로 배치된다. 원래는 <div>의 block영향을 받아 relative하단에 위치했으나 offset값이 적용된 후 컨테이너를 기준으로 위로부터 20px, 왼쪽으로부터 200px 이동한 모습을 확인할 수 있다.
Display
css display속성은 요소를 어떻게 보여줄지를 결정한다.
주로 다음 4가지 속성값이 쓰인다.
- none : 보이지 않음
- block : 블록박스
- inline : 인라인 박스
- inline-block : block과 inline의 중간 형태

<body>
<div class="none">none</div>
<div class="block">block</div>
<div class="inline">inline</div>
<div class="inline-block">inline-block</div>
<div>inline-block next</div>
</body>
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.none {
display: none;
background-color: red;
}
.block {
display: block;
background-color: yellow;
}
.inline {
display: inline;
background-color: green;
}
.inline-block {
display: inline-block;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>none은 요소를 렌더링하지 않도록 설정하며 영역도 차지하지 않기때문에 화면에서 보이지 않는다.
block은 가로영역을 모두 채우며 다음에 위치하는 요소는 줄바꿈이 된 것 처럼 보인다. 때문에 inline요소가 block의 옆이 아닌 하단에 위치했다.
inline은 width와 height를 지정할 수 없다. 때문에 모든 <div>요소에 적용된 width와 height값이 적용되지 않았다. 또 block과 달리 줄 바꿈이 되지않는다. 때문에 다음에 위치한 inline-block요소가 하단이 아닌 옆에 위치했다.
inline-block은 block과 inline의 중간 형태라고 볼 수 있다. 줄바꿈이 되지만 width과 height값을 지정할 수있다.
