React.js
Today I Learned ... react.js
🙋♂️ React.js Lecture
🙋 My Dev Blog
React Lecture CH 8
1 - context API
2 - createContext와 Provider
3 - useContext
4 - 좌클릭, 우클릭 로직
5 - 지뢰 개수 표시
6 - 빈칸 한번에 열기
7 - 승리 조건 체크, 타이머
8 - context API 최적화
빈칸 한번에 열기
- 재귀 함수(recursion function)를 이용함.
- 셀을 클릭하면 주변에 지뢰가 몇개인지 카운트한다.
- 만약, 주변에 지뢰가 하나도 없으면 0.
- 0인 칸을 클릭했다면, 그 주변 칸도 0인지 확인한다.
- 주변에 있는 모든 0인 칸이 한번에 열린다.
❕ 참고 - 왜 위,아래만 검색하는건지?
지난번에 OPEN_CELL 로직에서 맨 윗줄인지, 맨 마지막줄인지 체크했었다. 왜 좌,우는 신경쓰지 않는지?
-> 자바스크립트 특성상 tableData[row][cell]에서 row가 없으면 undefined가 나와서 에러가 발생한다.
-> 즉, 에러를 막기 위해서 row를 검사하는 것.
checkAround 함수
MineSearch.jsx
const checkAround = (row, cell) => {
if (
[
CODE.OPENED,
CODE.FLAG_MINE,
CODE.FLAG,
CODE.MINE,
CODE.QUESTION,
].includes(tableData[row][cell])
) {
return;
}
if (
row < 0 ||
row > tableData.length ||
cell < 0 ||
cell > tableData[0].length
) {
return;
}
// 주변 셀 검사 - 1) row가 맨 위가 아니라면
let around = [];
if (tableData[row - 1]) {
around = around.concat(
tableData[row - 1][cell - 1],
tableData[row - 1][cell],
tableData[row - 1][cell + 1]
);
}
// 기본 - 양옆 셀 추가
around = around.concat(
tableData[row][cell - 1],
tableData[row][cell + 1]
);
// 2) row가 맨 아래가 아니라면
if (tableData[row + 1]) {
around = around.concat(
tableData[row + 1][cell - 1],
tableData[row + 1][cell],
tableData[row + 1][cell - 1]
);
}
// 카운트 세기.
// 필터링 해줌. - 지뢰인 것의 개수 셈
const count = around.filter((v) =>
[CODE.MINE, CODE.FLAG_MINE, CODE.QUESTION_MINE].includes(v)
).length;
// 셀 내용에(text) count가 렌더링되게.
tableData[row][cell] = count;
// 🔻 새로 추가된 코드
// 현재 클릭한 게 count가 0이면?
if (count === 0) {
const near = [];
if (row - 1 > -1) {
// 제일 윗칸이 아닌지 체크
near.push([row - 1, cell - 1]);
near.push([row - 1, cell]);
near.push([row - 1, cell + 1]);
}
near.push([row, cell - 1]);
near.push([row, cell + 1]);
if (row + 1 < tableData.length) {
// 제일 아랫칸이 아닌지 체크
near.push([row + 1, cell - 1]);
near.push([row + 1, cell]);
near.push([row + 1, cell + 1]);
}
// near은 [3,2]와 같이 row, cell이 저장되어있는 배열이므로 이차원배열이다.
near.forEach((n) => {
if (tableData[n[0]][n[1]] !== CODE.OPENED) {
// near에 해당하는 셀들이 OPENED가 아니라면
checkAround(n[0], n[1]);
// 재귀함수. (자신을 다시한번 호출)
}
});
} else {
}
};콜스택 exceed를 막기 위한 캐싱
- 이미 체크한 셀은 다시 검사하지 않도록 캐싱이 필요.
- 만약, 이미 체크한 셀을 또 검사하면 계속 무한반복이 되어 콜스택 초과 오류가 발생함.

const checked = [];
const checkAround = (row, cell) => {
...
// 이미 검사한 셀인지 확인
if (checked.includes(row + ',' + cell)) {
return;
} else {
checked.push(row + ',' + cell);
}
...
}
조건에 따라 필터링
const checkAround = (row, cell) => {
console.log(row, cell);
if (
row < 0 ||
row >= tableData.length ||
cell < 0 ||
cell >= tableData[0].length
) {
return;
} // 🔺 상하좌우 없는칸은 안 열기
if (
[
CODE.OPENED,
CODE.FLAG,
CODE.FLAG_MINE,
CODE.QUESTION_MINE,
CODE.QUESTION,
].includes(tableData[row][cell])
) {
return;
} // 🔺 닫힌 칸이 아니면 열지 말기
if (checked.includes(row + '/' + cell)) {
return;
} else {
checked.push(row + '/' + cell);
} // 한 번 연칸은 무시하기
// 만약 없다면 새로 추가하기 (checked에 push)< 결과 >

승리조건 체크
열린 칸 수 체크
- 지뢰를 제외한 나머지 칸들을 다 열면 승리.
10 * 10에서 지뢰가 20개라 치면,
10*10- 20 = 80개의 셀을 무사히 클릭하면 성공임.
-> 지뢰를 건들이면 halted가 true가 되어 일시중지되므로,
결국엔 셀을 80개 클릭하면 승리.
- 칸을 하나 열때마다 증가하는
opendedCount를 생성.
let openedCount = 0;
if (tableData[row][cell] === CODE.NORMAL) {
// 내 칸이 닫힌 칸이면 -> 오픈 카운트 증가
openedCount += 1;
}- state에도 추가해줌.
const initialState = {
tableData: [],
timer: 0,
result: '',
halted: true,
openedCount: 0, // 👈 추가
};- OPEN_CELL의 return문에도 openedCount를 추가해줌.
case OPEN_CELL: {
...
return {
...state,
tableData,
openedCount: state.openedCount + openedCount,
halted,
result,
};
}-> 맨 처음에 state.openedCount 는 초기값 0이고,
openedCount는 한번 클릭할때마다 (여러 칸이 열리면 - openCount가 2이상임) +1씩 되어 이전 openedCount값에 누적된다.
row, cell, mine - state 추가
- 모든 칸수가 열린지 확인하기 위해서는
- row, cell 수와 mine의 개수를 알아야함.
-> 초기 사용자가 설정한대로.
- state에 추가해준다.
(row, cell, mine은 서로 관련된 그룹이므로 객체 형식으로 묶어줌)
const initialState = {
tableData: [],
data: { // 👈
row: 0,
cell: 0,
mine: 0,
},
timer: 0,
result: '',
halted: true,
openedCount: 0,
};- state.data는 게임 시작 버튼을 눌렀을 때,
(즉 START_GAME액션이 dispatch 되었을 때) 저장되어야 한다.
case START_GAME:
return {
...state,
data: {
row: action.row,
cell: action.cell,
mine: action.mine,
},
openedCount: 0,
tableData: plantMine(action.row, action.cell, action.mine),
halted: false,
timer: 0,
};승리 조건
if (
state.data.row * state.data.cell - state.data.mine ===
state.openedCount + openedCount
) {
// 승리시 일시정지 + result
halted = true;
result = `승리하셨습니다`;
}< 결과 >
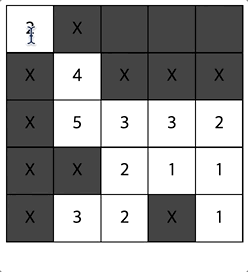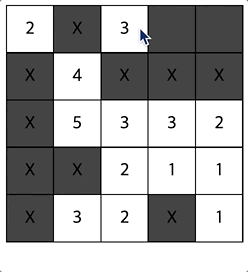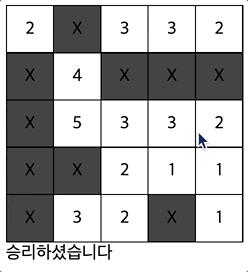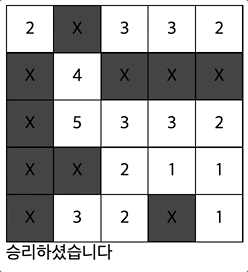
- 지뢰를 제외한 모든 칸을 열었을때, 승리 문구가 뜬다.
타이머 설정
- action에 추가해줌.
case INCREMENT_TIMER: {
return {
...state,
timer: state.timer + 1,
};
}- useEffect로 setInterval을 사용해줌.
useEffect(() => {
let timer;
if (halted === false) {
timer = setInterval(() => {
dispatch({ type: INCREMENT_TIMER });
}, 1000);
}
return () => {
clearInterval(timer);
};
}, [halted]);-> 1초마다 INCREMENT_TIMER을 dispatch 해줘서 타이머가 1씩 증가하게 함.
❗️ 주의
- if(halted === false) 를 하지 않으면, 시작 버튼을 누르지 않아도 타이머가 증가하게 된다.
- useEffect의 두번째 인자로 halted를 넘겨줘서, halted가 업데이트 될때마다 실행함. (componentDidUpdate)
- claerInterval은 return()안에 작성해주면 됨.
->clearInterval은 다시 halted가 true가 되었을 때
(승리했을 때 or 지뢰 클릭시) 멈추게 한다.
승리조건에 result에 timer 렌더링
if (
state.data.row * state.data.cell - state.data.mine ===
state.openedCount + openedCount
) {
halted = true;
result = `${state.timer}초만에 승리하셨습니다`; // 👈 추가
}Context API 최적화
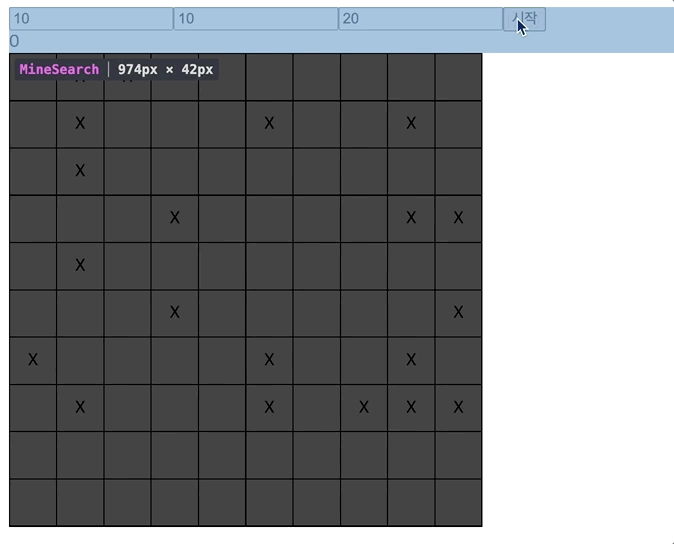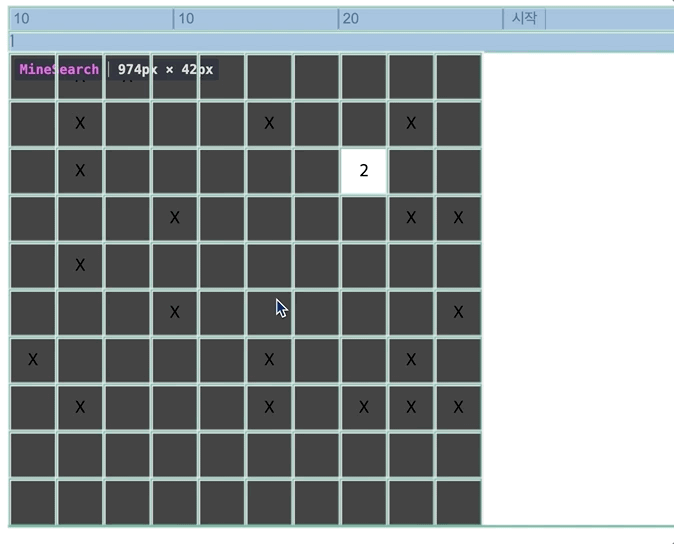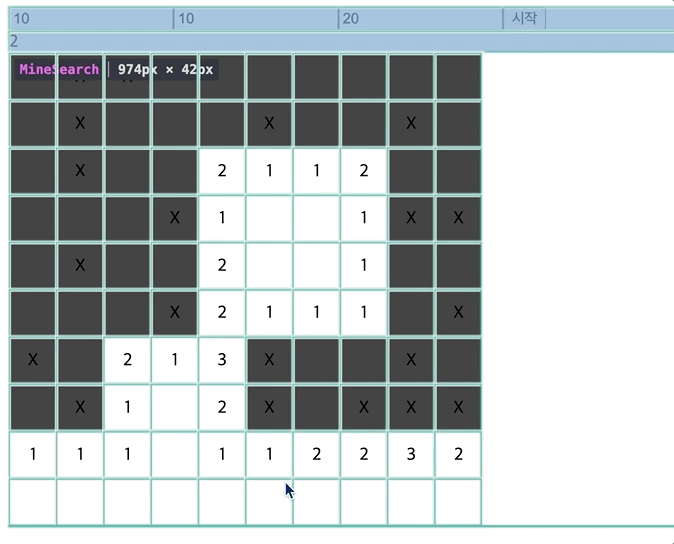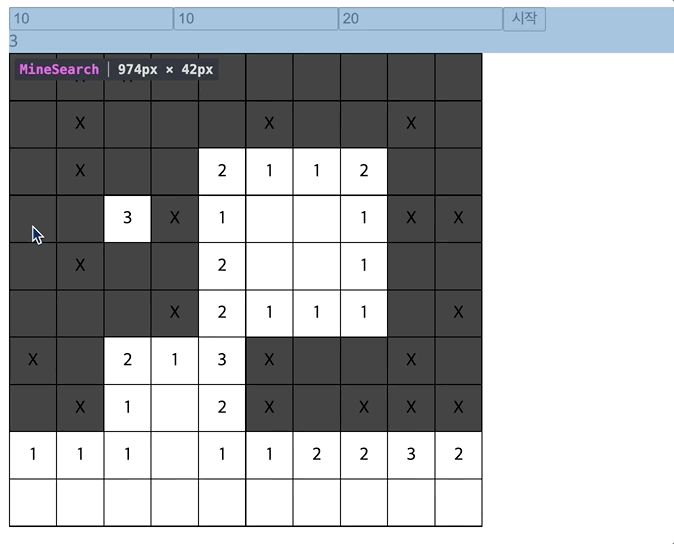
- 렌더링 되는 것을 살펴보면,
하나의 Td를 눌렀는데 모든 셀이 다 렌더링되고,
타이머, 즉 setInterval이 일어날 때 마다 전체가 계속 렌더링된다.
-> contextAPI는 최적화에 어려움이 있다.
React.memo 로 감싸주기.
- Table.jsx와 Form.jsx를 React.memo로 감싸준다.
- 하위 컴포넌트 Tr, Td에도 memo 적용.
하위 컴포넌트도 memo가 되어있어야 상위 컴포넌트에도 memo가 적용될 수 있다.
✅ 주의 - Form에서 useContext를 사용하기 때문에
어쩔 수 없이 리렌더링이 발생.
- Td 컴포넌트에 useMemo를 사용해준다.
- Td 자체는 실행되지만, 실제로 return(=렌더링)은 클릭한 개수만큼만 되도록 한다.
import React, { useContext, useCallback, useMemo, memo } from 'react';
import {
CLICK_MINE,
CODE,
FLAG_CELL,
NORMALIZE_CELL,
OPEN_CELL,
QUESTION_CELL,
TableContext,
} from './MineSearch';
const getTdStyle = (code) => {
switch (code) {
case CODE.NORMAL:
case CODE.MINE:
return {
background: '#444',
};
case CODE.CLICKED_MINE:
case CODE.OPENED:
return {
background: 'white',
};
case CODE.QUESTION_MINE:
case CODE.QUESTION:
return {
background: 'yellow',
};
case CODE.FLAG_MINE:
case CODE.FLAG:
return {
background: 'red',
};
default:
return {
background: 'white',
};
}
};
const getTdText = (code) => {
console.log('getTdtext');
switch (code) {
case CODE.NORMAL:
return '';
case CODE.MINE:
return 'X';
case CODE.CLICKED_MINE:
return '펑';
case CODE.FLAG_MINE:
case CODE.FLAG:
return '!';
case CODE.QUESTION_MINE:
case CODE.QUESTION:
return '?';
default:
return code || '';
}
};
const Td = memo(({ rowIndex, cellIndex }) => {
const { tableData, dispatch, halted } = useContext(TableContext);
const onClickTd = useCallback(() => {
if (halted) {
return;
}
switch (tableData[rowIndex][cellIndex]) {
case CODE.OPENED:
case CODE.FLAG_MINE:
case CODE.FLAG:
case CODE.QUESTION_MINE:
case CODE.QUESTION:
return;
case CODE.NORMAL:
dispatch({ type: OPEN_CELL, row: rowIndex, cell: cellIndex });
return;
case CODE.MINE:
dispatch({ type: CLICK_MINE, row: rowIndex, cell: cellIndex });
return;
default:
return;
}
}, [tableData[rowIndex][cellIndex], halted]);
const onRightClickTd = useCallback(
(e) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (halted) {
return;
}
switch (tableData[rowIndex][cellIndex]) {
case CODE.NORMAL:
case CODE.MINE:
dispatch({ type: FLAG_CELL, row: rowIndex, cell: cellIndex });
return;
case CODE.FLAG_MINE:
case CODE.FLAG:
dispatch({ type: QUESTION_CELL, row: rowIndex, cell: cellIndex });
return;
case CODE.QUESTION_MINE:
case CODE.QUESTION:
dispatch({ type: NORMALIZE_CELL, row: rowIndex, cell: cellIndex });
return;
default:
return;
}
},
[tableData[rowIndex][cellIndex], halted]
);
console.log('td rendered');
return (
<RealTd
onClickTd={onClickTd}
onRightClickTd={onRightClickTd}
data={tableData[rowIndex][cellIndex]}
/>
);
});
const RealTd = memo(({ onClickTd, onRightClickTd, data }) => {
console.log('real td rendered'); // 실제로 렌더링
return (
<td
style={getTdStyle(data)}
onClick={onClickTd}
onContextMenu={onRightClickTd}
>
{getTdText(data)}
</td>
);
});
export default Td;-> 컴포넌트를 쪼갤 수 있음.
< 최종 완성 >

