TypeScript
객체지향 프로그래밍
Class
🔻 typeScript 에서 constructor의 인자로 private 키워드로 프로퍼티 선언시
class Player {
constructor(
private firstName:string,
private lastName:string,
public nickName:string
) {}
}🔻 js에서는 constructor의 인자로 들어가고, this 렌더링을 진행함. (상속을 위해)
class Player {
constructor(firstName, lastName, nickName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.nickName = nickName;
}
}private, pulblic 등의 키워드는 자바스크립트에서는 쓰이지 않는다.
-> 자바스크립트에서는 프로퍼티가 키워드를 가질 수 없다. (보호 ❌)
const yjin = new Player("yjin", "lee", 'thisis');
yjin.nickName; // 'thisis'
yjin.firstName; // ❗️ error - private property위 코드는 typescript 에서는 에러가 발생하지만, (private 프로퍼티에 접근했기 때문)
javaScript에서는 아무런 문제가 발생하지 않는다.
Abstract Class (추상 클래스)
✅ 추상 클래스란?
- 다른 클래스가 상속받을 수 있는 클래스. (부모 클래스 역할)
- 단, 직접 인스턴스를 new 키워드로 생성할 수는 없음.
abstract class User {
constructor(
private firstName:string,
private lastName:string,
public nickName:string
) {}
// 추상클래스 내의 메서드
getFullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
}
class Player extends User {
}
const yjin = new User('yjin', 'lee', 'thisis'); // ❗️ error
const yjin = new Player('yjin', 'lee', 'thisis'); // OK
yjin.getFullName(); // yeonjin lee 만약 추상클래스의 메서드인 getFullName에 private 키워드가 붙는다면
yjin 인스턴스에서 사용할 수 없게 된다.
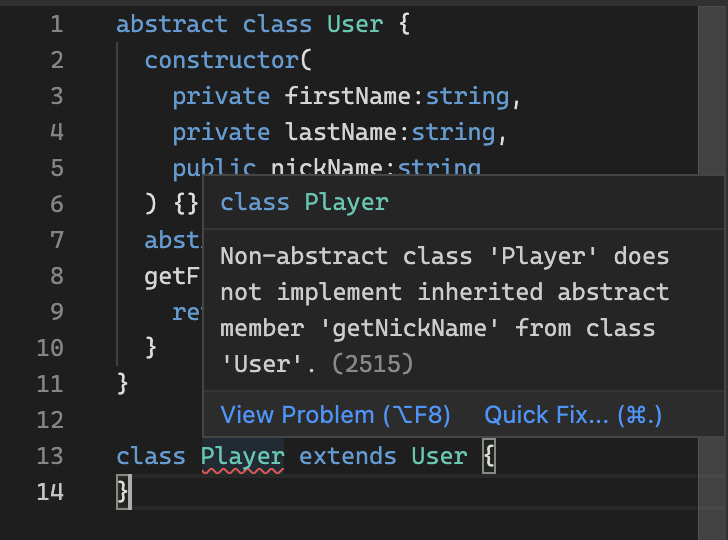
추상 메서드
abstract class User {
constructor(
private firstName:string,
private lastName:string,
public nickName:string
) {}
// 🔻추상메서드 - call signature만 적어줌.
abstract getNickName():void
// 일반 메서드
getFullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
}추상클래스 안에서는 추상 메서드를 만들 수 있다.
하지만 메서드를 구현하지 말고 대신에 call signature만 적어줘야 함.
🙋♂️ 추상 메서드 = 추상 클래스를 상속받는 모든 것이 구현해야하는 메서드.
extends로 상속받은 자식 클래스에서 getNickName을 구현해줘야 함.
✅ 구현(implementation) 이란?
- 함수 블록 내부 코드 작성하는 것.
- 추상 메서드에서는 구현을 하지말고 call signature을 작성하고,
자식 클래스에서 구현을 하면 된다.
class Player extends User {
getNickName() {
console.log(this.nickName);
}
}- 만약 nickName이 private 필드면 접근할 수 없다.
protected
- private : 인스턴스 밖에서 접근할 수 없고, 자식 클래스에서도 접근 불가
- protected : 자식 클래스에서는 접근할 수 있음. (인스턴스에서는 X)
abstract class User {
constructor(
public firstName:string,
public lastName:string,
protected nickName:string
) {}
}
// 생략
const yjin = new Player('yjin', 'lee', 'thisis');
yjin.nickName; // ❗️ errorProperty 'nickName' is protected and only accessible within class 'User' and its subclasses.
-> protected 필드는 User과 자식클래스에서만 사용 가능.
Hash Map 예제
type Words = {
[key: string]:string
}
class Dict {
private words: Words
// 초기값을 설정해주지 않으면 에러
constructor() {
this.words = {}
}
add(word: Word) {
if(this.words[word.term] === undefined) {
// 사전에 없는 단어면 등록
this.words[word.term] = word.def;
}
}
def(term:string) {
return this.words[term]
}
}
class Word {
constructor(
public term: string,
public def: string
) {}
}
const kimchi = new Word('kimchi', 'food');
const dict = new Dict();
dict.add(kimchi); // 클래스의 일반 메서드인 add
dict.def('kimchi');- 설명
add(word: Word) {
if(this.words[word.term] === undefined) {
// 사전에 없는 단어면 등록
this.words[word.term] = word.def;
}
}add 함수에서 Word 객체를 type처럼 사용함.
-> 함수 호출시 dict.add(kimchi)로 add함수의 인자로 kimchi(인스턴스)를 넣어줌.
Code Challenge
클래스에 메서드 추가하기.
- 단어 삭제 메서드
- 단어 수정 메서드
- 단어 출력 메서드
type Words = {
[key: string]:string
}
class Dict {
private words: Words
// 초기값을 설정해주지 않으면 에러
constructor() {
this.words = {}
}
add(word: Word) {
if(this.words[word.term] === undefined) {
// 사전에 없는 단어면 등록
this.words[word.term] = word.def;
}
}
update(word: Word) {
if(this.words[word.term]) {
this.words[word.term] = word.def;
}
}
def(term:string) {
return this.words[term]
}
del(term:string) {
if(this.words[term]) {
delete this.words[term]
// 프로퍼티 삭제
}
}
}
class Word {
constructor(
public term: string,
public def: string
) {}
}
const kimchi = new Word('kimchi', 'food');
const yjin = new Word('yjin', 'student');
const dict = new Dict();
dict.add(kimchi); // 클래스의 일반 메서드인 add
dict.add(yjin);
const updateYjin = new Word('yjin', 'developer');
dict.update(updateYjin); // term은 동일하게
dict.def('kimchi');
dict.del('yjin'); // 삭제Interface
readonly
- public 필드를 수정할 수 없게 하려면?
->readonly를 이용함
class Word {
constructor(
public readonly term: string,
public readonly def: string
) {}
}- 값을 덮어쓰지 못하게 하기 보호하기 위해 private나 Protected로 했지만,
public 필드인 경우에도readonly로 만들어주면 값을 덮어쓸 수 없음.
static 메서드
클래스의 static 메서드는 인스턴스 메서드가 아닌 클래스 자체의 메서드임.
class Dict {
private words: Words
// 초기값을 설정해주지 않으면 에러
constructor() {
this.words = {}
}
// 🔻 static 메서드
static hello () {
console.log('hello!');
}
// 🔻 인스턴스 메서드 (prototype)
add(word: Word) {
if(this.words[word.term] === undefined) {
// 사전에 없는 단어면 등록
this.words[word.term] = word.def;
}
}
}
Dict.hello(); // 'hello!'
dict.add(kimchi); interface
- type과 매우 유사하지만, 다른 점이 존재함.
- 🔻 type 사용시
type Player = {
nickname: string,
healthBBar: number
}
const yjin: Player =. {
nickname: 'yjin',
healthBar: 300
}- Type의 또다른 용법 - 특정 값 사용 가능
type Team = "red" | "blue" | "yellow"
type Player = {
nickname: string,
team: Team
}
const yjin :Player = {
nickname: 'thisis',
team: 'Pink' // ❗️ error
}- interface 사용시
type Team = "red" | "blue" | "yellow"
interface Player {
nickname: string,
team: Team
}- interface에서는 객체 모양을 지정할 때 = 없이 바로 작성해준다.
type Player = {};
interface Player {};- type의 경우에는 위와 같이 'red', 'yellow' 등의 concrete type이 아닌 다른 모든 값이 가능했지만,
interface의 경우에는 불가능하다.
interface Team = "red" | "blue" | "yellow" // ❗️ errortype은 객체가 아닌 일반 string 등도 가능한 반면,
interface는 객체만 사용 가능함.
-> interface는 클래스를 다루는 느낌처럼 하면 된다. (상속도 가능)
- 클래스처럼 상속 (extends) 가능
interface User {
name: string
}
interface Player extends User {
// name: string 상속받음
}+) type의 경우에는 & 연산자 사용함.
type Player = User & {
// 상속 받음
}- 인터페이스 확장
- 추가 선언 가능함.
- type의 경우에는 한번만 선언할 수 있음.
interface User{
name: string
}
interface User{
lastName: string
}
interface User{
health: number
}
// 🔺 same as
interface User {
name: string
lastName: string
health: number
}