TypeScript
🙋♂️ Ref Lecture
TypeScript BlockChain
- Target
- Lib Configuration
- Declaration File
- JS Doc
TypeScript 프로젝트 설정
- NextJS, CRA(create-react-app)을 사용하면 따로 설정을 몰라도 됨.
- 단, 설정 파일 등 수동으로 써야 할 일이 생기므로 알아둬야 함.
$ mkdir typechain
$ npm init -y
$ npm i -D typescript프로젝트 폴더에 src 폴더를 만들고, index.ts 를 생성.
const hello = () => 'hi';tsconfig.json 파일 생성
{
"include": ["src"],
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "build"
}
}- include = 컴파일 할 디렉터리 경로.
- compileOptions - outDir
-> 컴파일 후 저장할 JS 파일의 하위 디렉터리명.
package.json 수정
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc"
}참고 - typescript는 컴파일러(tsc)이다!
실행은 시켜주지 않으므로 트랜스파일러가 더 맞는 표현인듯.
$ npm run build/build/index.js가 자동 생성됨.
var hello = function () { return 'hi'; };-> ts에서는 es6 문법인 화살표 함수로 작성해주었지만,
js로 컴파일 된 것은 es5 문법으로 작성되어 있다.
또한, ts에서는 const를 사용하지만, js에서는 var로 바뀌어 있다.
-> 브라우저 호환이 더좋은 낮은 버전의 js로 바뀌어 있는 것임.
만약 이것을 따로 설정해주려면, tsconfig.json에서 target 옵션을 사용.
target
{
"include": ["src"],
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "build",
"target": "ES6",
}
}참고로 target 옵션의 기본값은 ES3 이다.
-> ES3에서는 const, let이 존재하지 않고 var만 존재함.
위와 같이 ES6으로 target 설정 후 다시 npm run build를 실행하면
🔻 /build/index.js
const hello = () => 'hi';- 화살표함수 + const 가 적용된다.
index.ts 수정
class Block {
constructor (private data: string) {}
static hello() {
return "hello!"
}
}다시 tsconfig.json의 target을 ES3로 변경 후 build를 해보면
아래와 같은 코드가 나온다.
/build/index.js
var Block = /** @class */ (function () {
function Block(data) {
this.data = data;
}
Block.hello = function () {
return 'hello!';
};
return Block;
}());마찬가지로 ES3에는 클래스가 없으므로 생성자 함수의 형태로 컴파일함.
동일하게 동작한다.
보통은 target 값은 es6로 써주는 것이 이상적임.
대부분의 node와 최신 브라우저가 es6를 지원하기 때문.
lib
- js 코드가 어디에서 동작할지. (어떤 환경에서)
- 합쳐진 라이브러리의 정의 파일을 설정.
1. 동작 환경
tsconfig.json
{
"include": ["src"],
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "build",
"target": "ES6",
"lib": ["ES6", "DOM"] // DOM은 브라우저 환경
}
}'DOM'을 lib에 추가한 후, ts 코드에서 document를 작성하면 자동완성이 되고,
브라우저 환경에서처럼 사용할 수 있다.
만약 각 메서드 등을 cmd+클릭 하면 -> .d.ts 파일로 이동한다.
document.querySelector('.hi')-> node_modules/typescript/lib 내부에 있는 lib.dom.d.ts 로 이동함
만약 lib 옵션에 'DOM'을 없앤 후 document 객체를 사용하려고 하면, 나오지 않음.
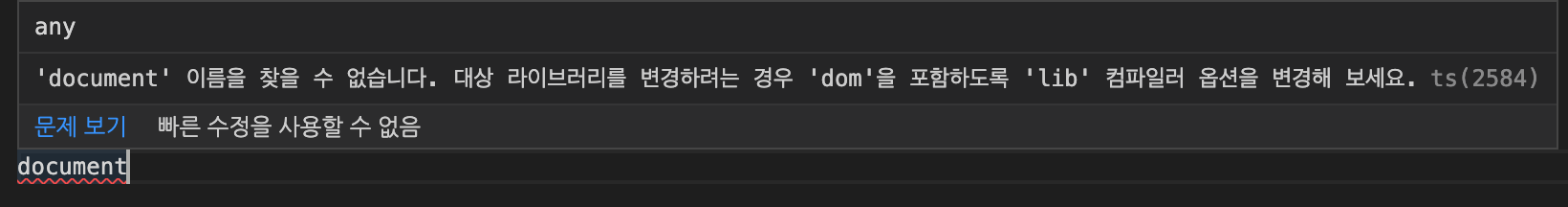
-> 자동 완성 기능을 제공하지 않고, 에러를 발생시킴.
2. D eclaration files
- 타입스크립트는 내장된 자바스크립트 API(Math 등)을 위한 기본 타입 정의는 가지고 있다.
- 자바스크립트로 만들어진 라이브러리를 타입스크립트에서 사용하려면 그것을 알게 해줘야 한다.
tsconfig.json 수정
"strict": truejs에서 strict 모드가 설정되도록 설정을 해줘야 한다.
모듈 생성
myPackage.js 생성
export function init(config) {
return true;
}
export function exit(code) {
return code + 1;
}index.ts
import { init } from "myPackage";-> 임의의 모듈 파일인 myPackage.js 파일에서 특정 함수를 임포트하면
에러가 발생한다.

d.ts 파일 생성
myPackage.js 파일에서의 타입을 설정하기 위해서 myPackage.d.ts 파일을 생성함.
declare module 'myPackage' {
// 내용
}여기까지만 해도 package가 존재하지 않는다는 에러는 사라짐.
d.ts 파일에서는 타입을 정의하는 것만 하고, 구현(implement)을 하지는 않는다.
-> call signature만 작성해줌!
interface Config {
url: string;
}
declare module 'myPackage' {
function init(config: Config): boolean;
}🔻 index.ts
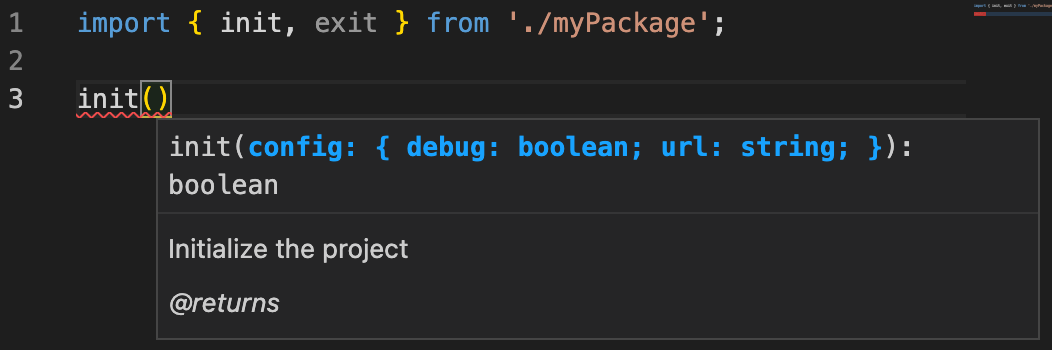
import { init } from 'myPackage';
init({ url: 'http://www.hello.com' });-> 더이상 에러 ❌
이제 두번째 함수인 exit의 타입을 정의한 후, 사용해보자.
myPackage.d.ts
interface Config {
url: string;
}
declare module 'myPackage' {
function init(config: Config): boolean;
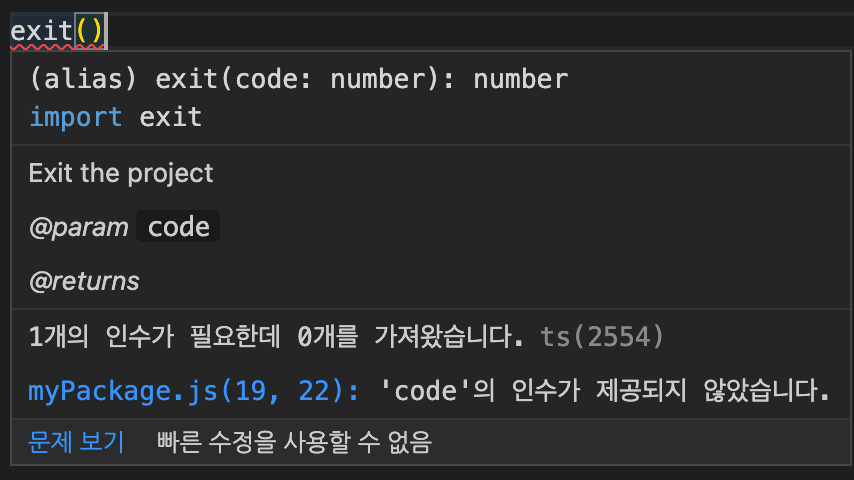
function exit(code: number): number;
}🔻 index.ts
import { init, exit } from 'myPackage';
init({
url: 'http://www.hello.com',
});
exit(123);d.ts 는
declarationfile을 의미함.
- js로 만들어진 패키지 설치시 ts에 패키지의 타입을 선언 (d.ts)
JS Doc
- js 파일을 직접 임포트 할때는 어떻게 해야하는지.
- js -> ts로 이전하는 경우.
// @ts-check로 JS 타입 체크
import { init, exit } from "./myPackage";js 파일을 임포트하는 것 이므로, ./을 붙여줘야 한다.
tsconfig.json 수정
"allowJs": true-> ts 안에 js를 허용하게 해줌.
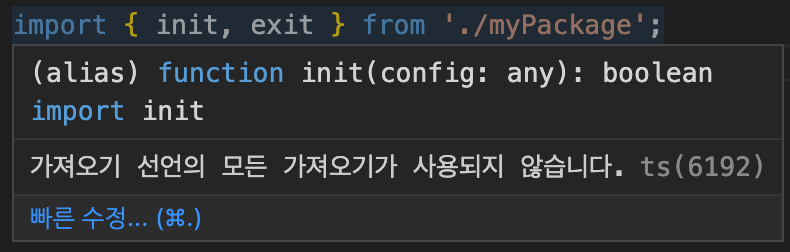
-> typescript가 알아서 타입 추론을 진행함. (any)
만약 Js를 그대로 두고 typescript의 타입 보호만 적용시키려면?
-> js 파일 최상단에 // @ts-check를 추가하면 됨.
🔻 myPackage.js
// @ts-check
/**
*
* @param {*} config
* @returns
*//** 입력 후 엔터 치면 vsCode 자동완성에 의해 위와 같이 작성됨.
아래와 같이 작성해주면 됨.
// @ts-check
/**
* Initialize the project
* @param {object} config
* @param {boolean} config.debug
* @param {string} config.url
* @returns {boolean}
*/
export function init(config) {
return true;
}
/**
* Exits the project
* @param {number} code
* @returns {number}
*/
export function exit(code) {
return code + 1;
}
-> 위와 같은 주석을 JSDoc 이라고 한다.
이는 코드가 작동하지 않게 하지는 않지만, 해당 타입이 맞는지 체크해준다.
typescript가 js 파일을 체크해주고 있는 것!
🙋♂️ js를 ts 안에서 쓰려면?
- d.ts 파일을 따로 생성. (js 전체 가져옴)
- @ts-check 사용 - js에서 타입 체크 해줌
